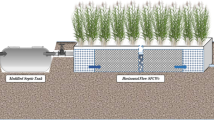
Abstract
Lumbrifiltration (LF) has been promoted as a low-cost, low maintenance and efficient solution for domestic and municipal wastewater treatment especially. However, there have been limited studies investigating the optimal operating conditions and long-term performances of LF systems (especially in temperate climates). The key objectives of this study were to (i) to present an outcome of the operating conditions and associated performance of LF the systems studied in the literature regarding removal efficiencies for nutrients and organic matter (OM) in municipal and domestic wastewater (WW) treatment contexts, (ii) to generate long term and reliable results on the potential performances of LF systems for the treatment of real municipal WW (for both OM and nutrients), (iii) to optimize operational conditions such as active layer height, earthworms density, HLR and earthworms type, conditions for which it is still unclear from the current literature which are optimal, and (iv) to assess the performances of the LF in a “temperate climate” context. Overall, LF systems showed high removal efficiencies for organic matter and nutrients for all the operating conditions tested. The study also confirmed the positive impact of earthworms in achieving high level of nitrification of ammonium after a short start-up period. The system operation and performances were maintained without maintenance for the whole duration of the study (over 250 days), showing the potential for keeping high level of performances for long-term periods. Recommendations are given in relation to LF system design such as optimal active layer height and hydraulic loading rate. The study also demonstrated the applicability and potential of Dendrobaena veneta as an alternative to Eisenia fetida (the latter generally being used in previous studies but are less available in some areas of Europe) for application in municipal wastewater treatment by LF.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
Earthworms were purchased from https://www.livinggreen.ie/.
References
APHA 2012. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. In: Federation, A.W.W.A.A.P.W.A.W.E. (ed.). Eugene W. Rice, Rodger B. Baird, Andrew D. Eaton, Lenore S. Clesceri.
Arora S, Kazmi AA (2016) Reactor performance and pathogen removal during wastewater treatment by vermifiltration. Journal of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene for Development 6(1):65–73
Arora S, Rajpal A, Bhargava R, Pruthi V, Bhatia A, Kazmi AA (2014) Antibacterial and enzymatic activity of microbial community during wastewater treatment by pilot scale vermifiltration system. Biores Technol 166:132–141
Fox S, Clifford E (2018) Detecting the end of nitrification in small and decentralized wastewater treatment systems using low-resource real-time control methods. J Environ Eng 144(8):04018069
Furlong C, Gibson WT, Oak A, Thakar G, Kodgire M, Patankar R (2016) Technical and user evaluation of a novel worm-based, on-site sanitation system in rural India. Waterlines 35(2):148–162
Ghasemi S, Mirzaie M, Hasan-Zadeh A, Ashrafnejad M, Hashemian SJ, Shahnemati SR (2020) Design, operation, performance evaluation and mathematical optimization of a vermifiltration pilot plan for domestic wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 8(1):103587
Herandez, C. and Furlong, C. (2017) Optimisation of faecal sludge processing via vermifiltration.
Huang W, Zhao Y, Wu J, Zhang J, Zheng Z (2014) Effects of different influent C/N ratios on the performance of various earthworm eco-filter systems: nutrient removal and greenhouse gas emission. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30(1):109–118
Jiang L, Liu Y, Hu X, Zeng G, Wang H, Zhou L, Tan X, Huang B, Liu S, Liu S (2016) The use of microbial-earthworm ecofilters for wastewater treatment with special attention to influencing factors in performance: a review. Biores Technol 200:999–1007
Krishnasamy K, Jaya N, Hughes R (2013) Vermifiltration systems for liquid waste management: a review. Int J Environ Waste Manage 12:382–396
Kumar C, Ghosh AK (2019) Fabrication of a vermifiltration unit for wastewater recycling and performance of vermifiltered water (vermiaqua) on onion (Allium cepa). International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture 8(4):405–415
Kumar T, Bhargava R, Prasad KSH, Pruthi V (2015) Evaluation of vermifiltration process using natural ingredients for effective wastewater treatment. Ecol Eng 75:370–377
Kumar T, Rajpal A, Arora S, Bhargava R, Hari Prasad KS, Kazmi AA (2016) A comparative study on vermifiltration using epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida and Eudrilus eugeniae. Desalin Water Treat 57(14):6347–6354
Kumar T, Rajpal A, Bhargava R, Prasad KSH (2014) Performance evaluation of vermifilter at different hydraulic loading rate using river bed material. Ecol Eng 62:77–82
Lai E, Hess M, Mitloehner FM (2018) Profiling of the microbiome associated with nitrogen removal during vermifiltration of wastewater from a commercial dairy. Front Microbiol 9:1964
Lavrnić S, Cristino S, Zapater-Pereyra M, Vymazal J, Cupido D, Lucchese G, Mancini B, Mancini ML (2019) Effect of earthworms and plants on the efficiency of vertical flow systems treating university wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(10):10354–10362
Lourenço N, Nunes LM (2017a) Is filter packing important in a small-scale vermifiltration process of urban wastewater? Int J Environ Sci Technol 14(11):2411–2422
Lourenço N, Nunes LM (2017b) Optimization of a vermifiltration process for treating urban wastewater. Ecol Eng 100:138–146
Meiyan X, Li X, Yang J (2010) Treatment performance of small-scale vermifilter for domestic wastewater and its relationship to earthworm growth, reproduction and enzymatic activity. African Journal of Biotechnology TN 9:7513–7520
Metcalf, amp and Eddy, I. (2003) Wastewater engineering : treatment and reuse. Fourth edition / revised by George Tchobanoglous, Franklin L. Burton, H. David Stensel. Boston : McGraw-Hill, [2003] ©2003.
Ndiaye, A., Andrianisa, H. A., Saapi, S. S. Y., Changotade, O. A., Adugna, A. T., Konate, Y. and Maiga, A. H. (2018) ‘Assessment on overall efficiency of urban greywater treatment by vermifiltration in hot climate: enhanced pollutants removal’, Environmental Technology, pp. 1–10.
Pasha MFK, Yeasmin D, Zoldoske D, Kc B, Hernandez J (2018) Performance of an earthworm-based biological wastewater-treatment plant for a dairy farm: case study. J Environ Eng 144(1):04017086
Singh R, Bhunia P, Dash Rajesh R (2019a) Impact of organic loading rate and earthworms on dissolved oxygen and vermifiltration. Journal of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste 23(2):04019001
Singh R, Bhunia P, Dash RR (2017) A mechanistic review on vermifiltration of wastewater: Design, operation and performance. J Environ Manage 197:656–672
Singh R, Bhunia P, Dash RR (2019b) Optimization of organics removal and understanding the impact of HRT on vermifiltration of brewery wastewater. Sci Total Environ 651:1283–1293
Singh R, Samal K, Dash RR, Bhunia P (2019c) Vermifiltration as a sustainable natural treatment technology for the treatment and reuse of wastewater: a review. J Environ Manage 247:140–151
Sinha, R., Bharambe, G. and Bapat, P. (2007) ‘Removal of high BOD and COD loadings of primary liquid waste products from dairy industry by vermifiltration technology using earthworms’, Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 27.
Sinha RK, Bharambe G, Chaudhari U (2008) Sewage treatment by vermifiltration with synchronous treatment of sludge by earthworms: a low-cost sustainable technology over conventional systems with potential for decentralization. Environmentalist 28(4):409–420
Taylor M, Clarke WP, Greenfield PF (2003) The treatment of domestic wastewater using small-scale vermicompost filter beds. Ecol Eng 21(2):197–203
Wang L, Guo F, Zheng Z, Luo X, Zhang J (2011a) Enhancement of rural domestic sewage treatment performance, and assessment of microbial community diversity and structure using tower vermifiltration. Biores Technol 102(20):9462–9470
Wang L, Guo Z, Che Y, Yang F, Chao J, Gao Y, Zhang Y (2014) The effect of vermifiltration height and wet: dry time ratio on nutrient removal performance and biological features, and their influence on nutrient removal efficiencies. Ecol Eng 71:165–172
Wang L, Zheng Z, Luo X, Zhang J (2011b) Performance and mechanisms of a microbial-earthworm ecofilter for removing organic matter and nitrogen from synthetic domestic wastewater. J Hazard Mater 195:245–253
Wang LM, Luo XZ, Zhang YM, Lian JJ, Gao YX, Zheng Z (2013) Effect of earthworm loads on organic matter and nutrient removal efficiencies in synthetic domestic wastewater, and on bacterial community structure and diversity in vermifiltration. Water Sci Technol 68(1):43–49
Wang Y, Xing M, Yang J (2017) Earthworm (Eisenia fetida) Eco-physiological Characteristics in Vermifiltration System for Wastewater Treatment Through Analyzing Differential Proteins. Water Air Soil Pollut 228(2):60
Xu D, Li Y, Howard A (2013) Influence of earthworm Eisenia fetida on removal efficiency of N and P in vertical flow constructed wetland. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(9):5922–5929
Yang F, Wang L, Wang G, Du P, Zhang Y (2015) Organic matter and nitrogen distribution, and functional groups of filter at earthworm packing bed in vermifiltration. Pol J Environ Stud 24:375–380
Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Ge Z, Hu C, Zhang H (2014) Effects of influent C/N ratios on wastewater nutrient removal and simultaneous greenhouse gas emission from the combinations of vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands and earthworm eco-filters for treating synthetic wastewater. Environ Sci Process Impacts 16(3):567–575
Funding
The INNOQUA (2016–2020) programme was funded under H2020-EU.3.5.4. (Enabling the transition towards a green economy and society through eco-innovation) (Grant agreement ID: 689817).
The funding body did not have a role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by AT and JF. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AT, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Chris Lowe
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tahar, A., Feighan, J., Hannon, L. et al. Optimization of operational conditions and performances of pilot scale lumbrifiltration for real raw municipal wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 32717–32731 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18259-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18259-8