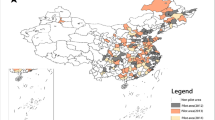
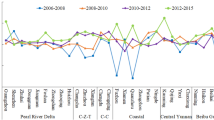
Abstract
Free-trade zones are highlands of regional development that have a radiating effect on surrounding cities. This paper uses Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration (YRDUA) data from 2003 to 2018, to examine the impact of the China (Shanghai) pilot free-trade zone (SPFTZ) on green total factor productivity (GTFP) in the YRDUA. It uses the regression discontinuity (RD) method and analyzes the influence mechanism with the help of the mediating effect model. The paper presents the following major findings. The establishment of the SPFTZ significantly promoted GTFP in the YRDUA, with technological progress being the main driving force. An analysis using the mediating effect model found that financial efficiency and industrial structure upgrading play a complete mediating role in GTFP growth in the YRDUA. Therefore, the SPFTZ should make use of its policy advantages, take full advantage of the effect of the green growth pole, and promote green mutual development with the YRDUA.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
The data is from China City Statistical Yearbook.
References
Bambang H (2012) The small medium-sized enterprise’s characteristic in Batam free trade zone that able to acquire debt. Procedia Economics and Finance 76–85.
Caj J (2016) The impact of insurance provision on household production and financial decisions. Am Econ J Econ Pol 8(2):44–88
Chen J, Wang SJ, Zhou CS et al (2019) Does the path of technological progress matter in mitigating China’s PM2.5 concentrations? Evidence from three urban agglomerations in China. Environ Pollut 254:113012
Chen WL, Huang XJ, Liu YH et al (2019b) The impact of high-tech industry agglomeration on green economy efficiency—evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 11(19):5189
Chen XD, Li HY, Qin QD et al (2021) Market-oriented reforms and China’s green economic development: An empirical study based on stochastic frontier analysis. Emerg Mark Financ Trade 57(4):949–971
Cheng YY, Shao TY, Lai HL et al (2019) Total-factor eco-efficiency and its influencing factors in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(20):3814
Demirel P, Kesidou E (2019) Sustainability-oriented capabilities for eco-innovation: meeting the regulatory, technology, and market demands. Bus Strateg Environ 28(5):847–857
Du HB, Chen ZN, Zhang ZK et al (2020) The rebound effect on energy efficiency improvements in China’s transportation sector: a CGE analysis. J Manag Sci Eng 5(4):249–263
Erdogan AM (2014) Bilateral trade and the environment: a general equilibrium model based on new trade theory. Int Rev Econ Financ 34:52–71
Feng F, Xu YY, Han J (2019) An empirical study on the spillover effect of free trade pilot zone on the economic growth of Yangtze River Delta. Forum of World Economics & Politics 5:118–138 (In Chinese)
Feng R, Chen L, Liu CM (2020) Research on the effect of the construction of free trade zone on the upgrading of industrial structure. Inquiry into Economic Issues 9:26–42 (In Chinese)
Fukuyama H, Weber WL (2009) A directional slacks-based measure of technical inefficiency. Socioecon Plann Sci 43(4):274–287
Gao J, Yu ZW, Wang LC et al (2019) Suitability of regional development based on ecosystem service benefits and losses: a case study of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. China. Ecol Indicators 107:105579
Hausmann R, Obach J, Santos, MA (2016) Special economic zones in Panama: technology spillovers from a labor market perspective. CID Working Papers 326, Center for International Development at Harvard University.
He J (2006) Pollution haven hypothesis and environmental impacts of foreign direct investment: the case of industrial emission of sulfur dioxide (SO2) in Chinese provinces. Ecol Econ 60(1):228–245
He LY, Liu RY, Zhong ZQ et al (2019) Can green financial development promote renewable energy investment efficiency? A consideration of bank credit. Renew Energy 143:974–984
Huang DX, Chan RCK (2018) On “land finance” in urban China: theory and practice. Habitat Int 75:96–104
Ji Q, Zhang DY (2019) How much does financial development contribute to renewable energy growth and upgrading of energy structure in China? Energy Policy 128:114–124
Jiang YF, Wang HY, Liu ZK (2021) The impact of the free trade zone on green total factor productivity——evidence from the Shanghai pilot free trade zone. Energy Policy 148:112000
Krugman PR (1979) Increasing returns, monopolistic competition, and international trade. J Int Econ 9(4):469–479
Li HJ, Su NF (2020) Financial factors, openness and the natural interest rate in China. Chin World Econ 28(4):76–100
Li HQ, Chen JH, Wan Z et al (2020) Spatial evaluation of knowledge spillover benefits in China’s free trade zone provinces and cities. Growth Chang 51(3):1158–1181
Li K, Lin BQ (2017) Economic growth model, structural transformation, and green productivity in China. Appl Energy 187:489–500
Liu ZK, Cao FF, Dennis B (2019) Does the China-Korea free trade area promote the green total factor productivity of China’s manufacturing industry? J Korea Trade 23(5):27–44
Liu ZK, Xin L (2019) Has China’s Belt and Road Initiative promoted its green total factor productivity?——Evidence from primary provinces along the route. Energy Policy 129:360–369
Long XL, Wang X, Mensah CN et al (2019) Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of environmental efficiency for China’s hotel sector: new evidence through metafrontier global Malmquist-Luenberger. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:27534–27541
Long XL, Wu C, Zhang JJ et al (2018) Environmental efficiency for 192 thermal power plants in the Yangtze River Delta considering heterogeneity: a metafrontier directional slacks-based measure approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 82(3):3962–3971
Long XL, Zhao XC, Cheng FX (2015) The comparison analysis of total factor productivity and eco-efficiency in China’s cement manufactures. Energy Policy 81:61–66
Mundaca L, Neij L, Markandya A et al (2016) Towards a green energy economy? Assessing policy choices, strategies and transitional pathways. Appl Energy 179:1283–1292
Qu CY, Shao J, Shi ZK (2020) Does financial agglomeration promote the increase of energy efficiency in China? Energy Policy 146:111810
Shen W, Vanhullebusch M (2015) Where is the alchemy? The experiment of the Shanghai free trade zone in freeing the foreign investment regime in China. Eur Bus Org Law Rev 16(2):321–352
Shipan CR, Volden C (2012) Policy diffusion: seven lessons for scholars and practitioners. Public Adm Rev 72(6):788–796
Song ML, Wang J, Wang SH et al (2019) Knowledge accumulation, development potential and efficiency evaluation: an example using the Hainan free trade zone. J Knowl Manag 23(9):1673–1690
Tachie AK, Long XL, Dauda L et al (2020) The influence of trade openness on environmental pollution in EU-18 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(28):35535–35555
Tian GJ, Guo ZM (2020) Free trade zone development, spatial spillover effect and industrial location differentiation in southern Jiangsu. J Soochow University (philosophy & Social Science Edition) 41(4):103–112 (In Chinese)
Wang XL, Wang L, Wang S et al (2020) Marketisation as a channel of international technology diffusion and green total factor productivity: research on the spillover effect from China’s first-tier cities. Technol Anal Strateg Manag 33(5):491–504
Waugh ME, Ravikumar B (2016) Measuring openness to trade. NBER Working Paper 22147
Xiang D, Zhao TZ, Zhang N (2021) Does public subsidy promote sustainable innovation? The case of Chinese high-tech SMEs. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:53493–53506
Xiao HJ, Shan YL, Zhang N et al (2019) Comparisons of CO2 emission performance between secondary and service industries in Yangtze River Delta cities. J Environ Manag 252:109667
Yao DQ, Whalley J (2016) The China (Shanghai) pilot free trade zone: background, developments and preliminary assessment of initial impacts. World Economy 39(1):2–15
Yu YT, Zhang N, Kim JD (2020) Impact of urbanization on energy demand: an empirical study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Energy Policy 39:111354
Yuan HX, Feng YD, Lee CC et al (2020) How does manufacturing agglomeration affect green economic efficiency? Energy Economics 92:104944
Yuan HX, Feng YD, Lee J et al (2019) The spatial threshold effect and its regional boundary of financial agglomeration on green development: a case study in China. J Clean Prod 244:118670
Yuan WH, Li JC, Meng L et al (2019) Measuring the area green efficiency and the influencing factors in urban agglomeration. J Clean Prod 241:118092
Zhang DY, Li J, Ji Q (2020) Does better access to credit help reduce energy intensity in China? Evidence from manufacturing firms. Energy Policy 145:111710
Zhang DY, Li J, Ji Q (2021a) Climate variations, culture and economic behaviour of Chinese households. Climatic Change, 167https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-021-03145-6
Zhang DY, Zhang ZW, Ji Q et al (2021) Board characteristics, external governance and the use of renewable energy: international evidence. J Int Financial Markets, Institutions & Money 72:101317
Zhao X, Shang YP, Song ML (2020) Industrial structure distortion and urban ecological efficiency from the perspective of green entrepreneurial ecosystems. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences 72:100757
Zheng YX, Cheng YX, Li L (2020) Factors affecting regional economic synergy in China – based on research on high-tech industry. IEEE Access 8:14123–14133
Zhou Q, Song YA, Wan NN et al (2020) Non-linear effects of environmental regulation and innovation – spatial interaction evidence from the Yangtze River Delta in China. Environ Sci Policy 114(2):263–274
Funding
This work was supported by the National Social Science Fund of China (grant number: 20BJL058) and the Natural Science Fund of Shandong Province (grant number: ZR2020MG074).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hongyan Wang: methodology; software; formal analysis; writing—original draft; writing—review and editing. Yihan Zhang: software, data curation, investigation. Zuankuo Liu: conceptualization; writing—review and editing; project administration; funding acquisition. Rongkun Liu: analysis with constructive discussions. Kanyong Li: analysis with constructive discussions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Liu, Z. et al. The impact and mechanisms of the Shanghai pilot free-trade zone on the green total factor productivity of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 40997–41011 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17758-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17758-y