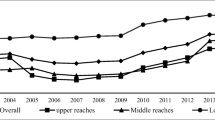
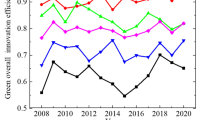
Abstract
Both innovation-driven development and green development are important ways to achieve regional sustainable development. This study considers the innovation-driven development and green development evaluation systems of 130 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. The entropy TOPSIS method is used to measure the innovation-driven development index and the green development index of 130 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Then, a coupling coordination evaluation model and a spatiotemporal heterogeneity analysis model are constructed to discuss the coupling coordination index of regional innovation-driven development and green development in the Yangtze River Economic Belt and to determine its temporal and spatial distribution characteristics. Finally, we choose a spatial panel regression model to explore the relationship between the innovation-driven development index and the green development index of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. The research results show that there is a significant difference between the innovation-driven development index and the green development index of the 130 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt in terms of the temporal and spatial distribution. The level of innovation-driven development lags behind the level of green development on the whole, and the two fail to form a good spatial matching degree. The coordination index of the two has an imbalanced distribution feature, and there is a significant direct or indirect relationship between the two structural indicators in a mathematical sense. This study improves the academic community’s understanding of the interaction between innovation-driven development and green development, provides scientifically based support for green development, and offers guidance for the implementation of innovation capabilities.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Alheet AF, Hamdan Y (2020) Evaluating innovation-driven economic growth: a case of Jordan. Entrep Sustain Issues 7:1790
An M, Butsic V, He W, Zhang Z, Qin T, Huang Z, Yuan L (2018) Drag effect of water consumption on urbanization—a case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2000 to 2015. Water 10:1115
Burnett JW, Bergstrom JC, Dorfman JH (2013) A spatial panel data approach to estimating U.S. state-level energy emissions. Energy Econ 40:396–404
Cao W, Zhang Y, Qian P(2019). The effect of innovation-driven strategy on green economic development in China—An empirical study of smart cities. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(9):1520
Chan P, Lee M-H (2019a) Prioritizing sustainable city indicators for Cambodia. Urban Science 3:104
Chan P, Lee M-H (2019b) Developing sustainable city indicators for Cambodia through Delphi processes of panel surveys. Sustainability 11:3166
Chen C, Han J, Fan P (2016a) Measuring the level of industrial green development and exploring its influencing factors: empirical evidence from China’s 30 provinces. Sustainability 8:153
Chen L, Zhang X, He F, Yuan R (2019) Regional green development level and its spatial relationship under the constraints of haze in China. J Clean Prod 210:376–387
Chen Y-S, Chang T-W, Lin C-Y, Lai P-Y, Wang K-H (2016b) The influence of proactive green innovation and reactive green innovation on green product development performance: the mediation role of green creativity. Sustainability 8:966
Craig MP (2020) ‘Treasury Control’ and the British environmental state: the political economy of green development strategy in UK central government. New Polit Econ 25:30–45
De Marchi V (2012) Environmental innovation and R&D cooperation: empirical evidence from Spanish manufacturing firms. Res Policy 41:614–623
del Rio Gonzalez P (2004) Public policy and clean technology promotion. The synergy between environmental economics and evolutionary economics of technological change. Int J Sustain Dev 7:200–216
Dutta S, Lanvin B, Wunsch-Vincent, S (2014) The Global Innovation Index 2014: The Human Factor in Innovation. Cornell University: 283
Dutta S, Lanvin B, Wunsch-Vincent S (2017). Global Innovation Index 2017. Cornell University: 387–399
Dutta S, Lanvin B, Wunsch-Vincent, S. (2018).The Global Innovation Index 2018. Cornell University: 177–183
Fei R, Cui A, Qin K (2020) Can technology R&D continuously improve green development level in the open economy? Empirical evidence from China’s industrial sector. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:34052–34066
Feng Z, Chen W (2018) Environmental regulation, green innovation, and industrial green development: an empirical analysis based on the spatial Durbin model. Sustainability, 10(1):223
Freeman J, Gary Graham D, Chen T (2015) Green supplier selection using an AHP-Entropy-TOPSIS framework. Supply Chain Manag Int J 20:327–340
Gu W, Zhao X, Yan X, Wang C, Li Q (2019) Energy technological progress, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions: empirical evidence from China. J Clean Prod 236:117666
He L, Zhang L, Zhong Z, Wang D, Wang F (2019) Green credit, renewable energy investment and green economy development: empirical analysis based on 150 listed companies of China. J Clean Prod 208:363–372
Hu A (2014) China: innovative green development. Springer Berlin Heidelberg: 160–185
Kim Y-J, Lee J-H, Lee S-G, Lee H-H (2021) Developing sustainable competitive strategies in the beauty service industry: a SWOT-AHP approach. Sustainability 13:10852
Koulinas GK, Demesouka OE, Sidas KA, Koulouriotis DE (2021) A TOPSIS—risk matrix and Monte Carlo expert system for risk assessment in engineering projects. Sustainability 13:11277
Latif Z, Jianqiu Z, Ullah R, Pathan ZH, Latif S (2017a) Application of optical frequency comb in high-capacity long distance optical communication for China-Pakistan economic corridor. J Opt Commun 38:331–340
Latif Z, Latif S, Ximei L, Pathan ZH, Salam S, Jianqiu Z (2018) The dynamics of ICT, foreign direct investment, globalization and economic growth: panel estimation robust to heterogeneity and cross-sectional dependence. Telematics Inform 35:318–328
Latif Z, Xin W, Khan D, Iqbal K, Pathan ZH, Salam S, Jan N (2017b) ICT and sustainable development in South Asian countries. Hum Syst Manag 36:353–362
Latif Z, Yang M, Pathan ZH, Jan N (2017c) Challenges and prospects of ICT and trade development in Asia human systems management (36) 211–219. 10.3233. HSM-171780
Laužikas M, Dailydaitė S (2014) Impacts of social capital on transformation from efficiency to innovation-driven business. J Bus Econ Manag 16:37–51
Li B, Wu S (2017) Effects of local and civil environmental regulation on green total factor productivity in China: a spatial Durbin econometric analysis. J Clean Prod 153:342–353
Li H, He F, Deng G (2020) How does environmental regulation promote technological innovation and green development? New evidence from China. Pol J Environ Stud 29:689
Li W, Wang J, Chen R, Xi Y, Liu SQ, Wu F, Masoud M, Wu X (2019) Innovation-driven industrial green development: the moderating role of regional factors. J Clean Prod 222:344–354
Li X, Liu Y, Song T (2014) Calculation of the green development index. Soc Sci China 6:69–95
Lin B, Benjamin NI (2017) Green development determinants in China: a non-radial quantile outlook. J Clean Prod 162:764–775
Liu D, Wu L, Yang Y (2020) A hybrid weight assignment model for urban underground space resources evaluation integrated with the weight of time dimension. Appl Sci 10:5152
Liu X, Gao T, Wang X (2018) Regional innovation index of China: 2017. How Frontier Regions Innovate, Springer, Singapore: 29
Ma L, Long H, Chen K, Tu S, Zhang Y, Liao L (2019) Green growth efficiency of Chinese cities and its spatio-temporal pattern. Resour Conserv Recycl 146:441–451
Maceika A, Bugajev A, Šostak OR, Vilutienė T (2021) Decision tree and AHP methods application for projects assessment: a case study. Sustainability 13:5502
Meirun T, Mihardjo LW, Haseeb M, Khan SAR, Jermsittiparsert K (2021) The dynamics effect of green technology innovation on economic growth and CO2 emission in Singapore: new evidence from bootstrap ARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:4184–4194
Mensah CN, Long X, Boamah KB, Bediako IA, Dauda L, Salman M (2018) The effect of innovation on CO 2 emissions of OCED countries from 1990 to 2014. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:29678–29698
Perveen S, Kamruzzaman M, Yigitcanlar T (2017) Developing policy scenarios for sustainable urban growth management: a Delphi approach. Sustainability 9:1787
Pimonenko T, Lyulyov O, Us Y (2018) Green development of small and medium enterprises of Ukraine: the EU experience 2:69–78
Ranta V, Keränen J, Aarikka-Stenroos L (2020) How B2B suppliers articulate customer value propositions in the circular economy: four innovation-driven value creation logics. Ind Mark Manage 87:291–305
Redding S (2002) Path dependence, endogenous innovation, and growth. Int Econ Rev 43:1215–1248
Rogerson CM (2018) Innovation-driven local economic development: in search of best practice implementation for South Africa. Euro Economica 37:21–34
Shao S, Luan R, Yang Z, Li C (2016) Does directed technological change get greener: empirical evidence from Shanghai’s industrial green development transformation. Ecol Ind 69:758–770
Song M, Guan Y, Wang J, Zhao J (2016) Evaluation of urban industrial ecological transformation in China. Clean Technol Environ Policy 18:2649–2662
Sotarauta M, Suvinen N (2019) Place leadership and the challenge of transformation: policy platforms and innovation ecosystems in promotion of green growth. Eur Plan Stud 27:1748–1767
Sultana I, Ahmed I, Azeem A (2015) An integrated approach for multiple criteria supplier selection combining Fuzzy Delphi, Fuzzy AHP & Fuzzy TOPSIS. J Intel Fuzzy Syst 29:1273–1287
Sun C, Tong Y, Zou W (2018) The evolution and a temporal-spatial difference analysis of green development in China. Sustain Cities Soc 41:52–61
Wang M-X, Zhao H-H, Cui J-X, Fan D, Lv B, Wang G, Li Z-H, Zhou G-J (2018) Evaluating green development level of nine cities within the Pearl River Delta, China. J Clean Prod 174:315–323
Wang Q, Mao Z, Xian L, Liang Z (2019a) A study on the coupling coordination between tourism and the low-carbon city. Asia Pac J Tour Res 24:550–562
Wang Q, Qu J, Wang B, Wang P, Yang T (2019) Green technology innovation development in China in 1990–2015. Sci Total Environ 696:134008
Wang X, Shao Q (2019) Non-linear effects of heterogeneous environmental regulations on green growth in G20 countries: evidence from panel threshold regression. Sci Total Environ 660:1346–1354
Wang Z, Cheng Y, Ye X, Wei YHD (2016) Analyzing the space-time dynamics of innovation in China: ESDA and spatial panel approaches. Growth Chang 47:111–129
Wu S, Zhang K (2021) Influence of urbanization and foreign direct investment on carbon emission efficiency: evidence from urban clusters in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 13:2722
Yang T-K, Yan M-R (2019) Exploring the enablers of strategic orientation for technology-driven business innovation ecosystems. Sustainability, 11(20):5779
Yang Y, Huang P (2019) Has the level of green development in the northwestern provinces of China truly improved? A case study of Shaanxi. Sustain Cities Soc 51:101779
Yuan B, Xiang Q (2018) Environmental regulation, industrial innovation and green development of Chinese manufacturing: based on an extended CDM model. J Clean Prod 176:895–908
Yuan Q, Yang D, Yang F, Luken R, Saieed A, Wang K (2020) Green industry development in China: an index based assessment from perspectives of both current performance and historical effort. J Clean Prod 250:119457
Zhang J, Chang Y, Zhang L, Li D (2018) Do technological innovations promote urban green development?—a spatial econometric analysis of 105 cities in China. J Clean Prod 182:395–403
Zhang M, Li B (2020) How to improve regional innovation quality from the perspective of green development? Findings from entropy weight method and fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis. IEEE Access 8:32575–32586
Zhao M, Tan L, Zhang W, Ji M, Liu Y, Yu L (2010) Decomposing the influencing factors of industrial carbon emissions in Shanghai using the LMDI method. Energy 35:2505–2510
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 42001237, 41901326, and 42071212), the Philosophy and Social Science Research of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (2020SJA0093), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20190742).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wei Wang: conceptualization, methodology, software, and writing. Lei Zhou: visualization, investigation, and writing. Wei Chen: writing, software, and validation. Chao Wu: writing, reviewing, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Zhou, L., Chen, W. et al. Research on the coordination characteristics and interaction between the innovation-driven development and green development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 22952–22969 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17470-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17470-x