Abstract
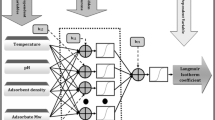
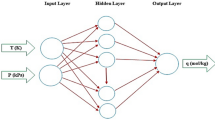
An artificial neural network (ANN) hybrid structure was proposed that, unlike the standard ANN structure optimization, allows the fit of several adsorption curves simultaneously by indirectly minimizing the real output error. To model a case study of 3-aminophenol adsorption phenomena onto avocado seed activated carbon, a hybrid ANN was applied to fit the parameters of the Langmuir and Sips isotherm models. Network weights and biases were optimized with two different methods: particle swarm optimization (PSO) and genetic algorithm (GA), due to their good convergence in large-scale problems. In addition, the data were also fitted with the Levenberg-Marquardt feedforward optimization method to compare the performance between a standard ANN model and the hybrid model proposed. Results showed that the ANN-isotherm hybrid models with both PSO and GA were able to accurately fit the experimental equilibrium adsorption capacity data using the Sips isotherm model, obtaining Pearson’s correlation coefficient (R) of the order of 0.9999 and mean squared error (MSE) around 0.5, very similar to the performance of standard ANN using Levenberg-Marquardt optimization. On the other hand, the results with Langmuir isotherm models were quite inferior in the ANN-isotherm hybrid models with both PSO and GA, with R and MSE of around 0.944 and 4.04 × 102, respectively. The proposed ANN-isotherm hybrid structure was successfully applied to estimate the parameters of adsorption isotherms, reducing the computational demand and the exhausting task of estimating the parameters of each adsorption curve individually.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Activated carbon
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- C 0 :
-
Solution initial concentration mg/L
- C e :
-
Equilibrium concentration mg/L
- F obj :
-
Objective function value Variable
- GA:
-
Genetic algorithm
- K S :
-
Sips affinity constant L/mg
- MSE:
-
Mean squared error
- N S :
-
Sips heterogeneity factor
- PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization
- q e :
-
Equilibrium adsorption capacity mg/g
- q e,t :
-
Measured equilibrium adsorption capacity mg/g
- q e,o :
-
Predicted equilibrium adsorption capacity mg/g
- q S :
-
Sips theoretical saturation capacity mg/g
- R :
-
Pearson’s coefficient of correlation
- R 2 :
-
Coefficient of determination
- RMSE :
-
Root mean squared error
- T :
-
Adsorption temperature K
References
Ali I, Aboul-Enein HY (2002) Speciation of metal ions by capillary electrophoresis. Crit Rev Anal Chem 32:337–350. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408340290765597
Ali I, Gupta VK, Aboul-Enein HY (2005) Metal ion speciation and capillary electrophoresis: application in the new millennium. Electrophoresis 26:3988–4002. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200500216
Ali I, Alharbi OML, Alothman ZA, Alwarthan A (2018a) Facile and eco-friendly synthesis of functionalized iron nanoparticles for cyanazine removal in water. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 171:606–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.07.071
Ali I, Alharbi OML, Alothman ZA, Badjah AY (2018b) Kinetics, thermodynamics, and modeling of Amido black dye photodegradation in water using Co/TiO 2 nanoparticles. Photochem Photobiol 94:935–941. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.12937
Ali I, Alharbi OML, Tkachev A et al (2018c) Water treatment by new-generation graphene materials: hope for bright future. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:7315–7329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1315-9
Ali I, Burakov AE, Melezhik AV et al (2019) Removal of copper(II) and zinc(II) ions in water on a newly synthesized polyhydroquinone/graphene nanocomposite material: kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanism. ChemistrySelect 4:12708–12718. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201902657
Basheer AA (2018a) New generation nano-adsorbents for the removal of emerging contaminants in water. J Mol Liq 261:583–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.021
Basheer AA (2018b) Chemical chiral pollution: impact on the society and science and need of the regulations in the 21 st century. Chirality 30:402–406. https://doi.org/10.1002/chir.22808
Basheer AA, Ali I (2018) Stereoselective uptake and degradation of (±)- o , p -DDD pesticide stereomers in water-sediment system. Chirality 30:1088–1095. https://doi.org/10.1002/chir.22989
Clerc M (2004) Discrete particle swarm optimization, illustrated by the Traveling Salesman Problem. In: Onwubolu G, Babu B (eds) New optimization techniques in engineering, studies in fuzziness and soft computing, vol 141. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 219–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-39930-8_8
Dotto GL, McKay G (2020) Current scenario and challenges in adsorption for water treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103988
Dotto GL, Cadaval TRS, Pinto LAA (2012) Use of Spirulina platensis micro and nanoparticles for the removal synthetic dyes from aqueous solutions by biosorption. Process Biochem 47:1335–1343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.04.029
Fagundez JLS, Netto MS, Dotto GL, Salau NPG (2021) A new method of developing ANN-isotherm hybrid models for the direct and simultaneous determination of thermodynamic parameters in the adsorption of ions Ag+, Co2+ and Cu2+ onto zeolites ZSM-5, HY, and 4A. J Environ Chem Eng 9:106126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106126
Franco DSP, Duarte FA, Salau NPG, Dotto GL (2019) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANIFS) and artificial neural network (ANN) applied for indium (III) adsorption on carbonaceous materials. Chem Eng Commun 206:1452–1462. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2019.1566129
Franco DSP, Duarte FA, Salau NPG, Dotto GL (2020) Analysis of indium (III) adsorption from leachates of LCD screens using artificial neural networks (ANN) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems (ANIFS). J Hazard Mater 384:121137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121137
Ghaedi AM, Vafaei A (2017) Applications of artificial neural networks for adsorption removal of dyes from aqueous solution: a review. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 245:20–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2017.04.015
Graupe D (1997) Principles of artificial neural networks, 2nd edn. World Scientific, Massachusetts. https://doi.org/10.1142/6429
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on neural networks. Perth, pp 1942–1948. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt CD, Vecchi MP (1983) Optimization by simulated annealing. Science (80-) 220:671–680. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.220.4598.671
Kramer O (2017) Genetic algorithm essentials (Studies in computational intelligence book 679), 1st edn. Springer, Oldenburg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52156-5
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Leite AJB, Carmalin SA, Thue PS et al (2017) Activated carbon from avocado seeds for the removal of phenolic compounds from aqueous solutions. Desalin Water Treat 71:168–181. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20540
Lima EC, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Moreno-Piraján JC, Anastopoulos I (2019) A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the Van’t Hoof equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J Mol Liq 273:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.048
Marquardt DW (1963) An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. J Soc Ind Appl Math 11:431–441
Meili L, Lins PVS, Costa MT et al (2019) Adsorption of methylene blue on agroindustrial wastes: experimental investigation and phenomenological modelling. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 141:60–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2018.07.011
Nawi NM, Khan A, Rehman MZ (2013) A new Levenberg Marquardt based back propagation algorithm trained with Cuckoo search. Proc Technol 11:18–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2013.12.157
Nethaji S, Sivasamy A, Mandal AB (2013) Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and mechanism for the adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes onto carbonaceous particles prepared from Juglans regia shell biomass. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10:231–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0112-0
Pauletto PS, Dotto GL, Salau NPG (2020a) Optimal artificial neural network design for simultaneous modeling of multicomponent adsorption. J Mol Liq 320:114418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114418
Pauletto PS, Gonçalves JO, Pinto LAA et al (2020b) Single and competitive dye adsorption onto chitosan–based hybrid hydrogels using artificial neural network modeling. J Colloid Interface Sci 560:722–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.10.106
Pauletto PS, Lütke SF, Dotto GL, Salau NPG (2020c) Forecasting the multicomponent adsorption of nimesulide and paracetamol through artificial neural network. Chem Eng J 412:127527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127527
Pérez-Marín AB, Zapata VM, Ortuño JF et al (2007) Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto orange waste. J Hazard Mater 139:122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.06.008
Rodríguez-Romero JA, Mendoza-Castillo DI, Reynel-Ávila HE et al (2020) Preparation of a new adsorbent for the removal of arsenic and its simulation with artificial neural network-based adsorption models. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103928
Saucedo-Delgado BG, De Haro-Del Rio DA, González-Rodríguez LM et al (2017) Fluoride adsorption from aqueous solution using a protonated clinoptilolite and its modeling with artificial neural network-based equations. J Fluor Chem 204:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluchem.2017.11.002
Sips R (1948) On the structure of a catalyst surface. J Chem Phys 16:490–495. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1746922
Souza PR, Dotto GL, Salau NPG (2018) Artificial neural network (ANN) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy interference system (ANFIS) modelling for nickel adsorption onto agro-wastes and commercial activated carbon. J Environ Chem Eng 6:7152–7160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.11.013
Tovar-Gómez R, Moreno-Virgen MR, Dena-Aguilar JA et al (2013) Modeling of fixed-bed adsorption of fluoride on bone char using a hybrid neural network approach. Chem Eng J 228:1098–1109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.080
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education (CAPES) and the Research Support Foundation of Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS) for the financial support of this work.
Funding
This work was supported by the Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education (CAPES) and the Research Support Foundation of Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jean Lucca Souza Fagundez: Conceptualization; Investigation; Resources; Writing, original draft; Methodology; Formal analysis.
Nina Paula Gonçalves Salau: Supervision; Project administration; Funding acquisition; Conceptualization; Writing, review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fagundez, J.L.S., Salau, N.P.G. Optimization-based artificial neural networks to fit the isotherm models parameters of aqueous-phase adsorption systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 79798–79807 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17244-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17244-5