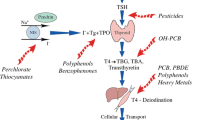
Abstract
Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) is a ubiquitous environmental endocrine disruptor. DEHP can be absorbed into the human body through the air, food, water, and skin. After entering the human body, DEHP is rapidly converted to mono(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (MEHP) with greater toxicity than DEHP. An increasing number of studies indicates that DEHP or MEHP can damage the thyroid tissue and disrupt the function, but the mechanisms remain unclear. This article reviews the toxicity of DEHP on thyroid structures and functions and summarizes the potential mechanisms to provide evidence for preventing the thyroid-related diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahmed OM, El-Gareib AW, El-Bakry AM, Abd El-Tawab SM, Ahmed RG (2008) Thyroid hormones states and brain development interactions. Int J Dev Neurosci 26:147–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2007.09.011
Aldossari K, Al-Ghamdi S, Al-Zahrani J, Al Jammah A, Alanazi B, Al-Briek A, Alanazi M (2019) Association between subclinical hypothyroidism and metabolic disorders: a retrospective chart review study in an emerging university hospital. J Clin Lab Anal 33:e22983–e22983. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.22983
Amouzegar A, Kazemian E, Gharibzadeh S, Mehran L, Tohidi M, Azizi F (2015) Association between thyroid hormones, thyroid antibodies and insulin resistance in euthyroid individuals: a population-based cohort. Diabetes Metab 41:480–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2015.04.004
Anyetei-Anum CS, Roggero VR, Allison LA (2018) Thyroid hormone receptor localization in target tissues. J Endocrinol 237:R19-r34. https://doi.org/10.1530/joe-17-0708
Arafah BM (2001) Increased need for thyroxine in women with hypothyroidism during estrogen therapy. N Engl J Med 344:1743–1749. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200106073442302
Bauerle KT, Schweppe RE, Haugen BR (2010) Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B differentially affects thyroid cancer cell growth, apoptosis, and invasion. Mol Cancer 9:117. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-9-117
Bian X-H, Sun H, Xue H, Zhang G, Zhang C-H, Liu X-L, Su J, Li S-J (2014) Expression and clinical significance of Shh/Gli-1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Tumour Biol 35:10523–10528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2365-3
Bronowicka-Kłys DE, Lianeri M, Jagodziński PP (2016) The role and impact of estrogens and xenoestrogen on the development of cervical cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 84:1945–1953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.007
Brufani C, Manco M, Nobili V, Fintini D, Barbetti F, Cappa M (2012) Thyroid function tests in obese prepubertal children: correlations with insulin sensitivity and body fat distribution. Horm Res Paediatr 78:100–105. https://doi.org/10.1159/000341363
Carvalho JC, Lisboa PC, de Oliveira E, Peixoto-Silva N, Nobre JL, Fraga MC, Manhães AC, Moura EG (2016) Effects of postnatal bromocriptine injection on thyroid function and prolactinemia of rats at adulthood. Neuropeptides 59:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2016.05.003
Cavalieri E, Rogan E (2014) The molecular etiology and prevention of estrogen-initiated cancers: Ockham’s Razor: pluralitas non est ponenda sine necessitate. Plurality should not be posited without necessity. Mol Aspects Med 36:1–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2013.08.002
Chang J-W, Lee C-C, Pan W-H, Chou W-C, Huang H-B, Chiang H-C, Huang P-C (2017) Estimated daily intake and cumulative risk assessment of phthalates in the general Taiwanese after the 2011 DEHP food scandal. Sci Rep 7:45009–45009. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45009
Chappell WH et al. (2011): Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR inhibitors: rationale and importance to inhibiting these pathways in human health. Oncotarget 2, 135–64. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.240
Chen X, Qin Q, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Zheng H, Liu C, Yang Y, Xiong W, Yuan J (2013) Activation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway promotes DEHP-induced Hep3B cell proliferation. Food Chem Toxicol 59:325–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.06.016
Chen Y, Li Z, He Y, Shang D, Pan J, Wang H, Chen H, Zhu Z, Wan L, Wang X (2014) Estrogen and pure antiestrogen fulvestrant (ICI 182 780) augment cell-matrigel adhesion of MCF-7 breast cancer cells through a novel G protein coupled estrogen receptor (GPR30)-to-calpain signaling axis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 275:176–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2014.01.005
Chiu C-Y, Sun S-C, Chiang C-K, Wang C-C, Chan D-C, Chen H-J, Liu S-H, Yang R-S (2018) Plasticizer di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate interferes with osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis in a mouse model. J Orthop Res 36:1124–1134. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.23740
Cho YJ, Park SB, Han M (2015) Di-(2-ethylhexyl)-phthalate induces oxidative stress in human endometrial stromal cells in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol 407:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2015.03.003
Couto JP, Daly L, Almeida A, Knauf JA, Fagin JA, Sobrinho-Simões M, Lima J, Máximo V, Soares P, Lyden D, Bromberg JF (2012) STAT3 negatively regulates thyroid tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:E2361–E2370. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1201232109
D’Ascola A, Scuruchi M, Ruggeri RM, Avenoso A, Mandraffino G, Vicchio TM, Campo S, Campo GM (2020) Hyaluronan oligosaccharides modulate inflammatory response, NIS and thyreoglobulin expression in human thyrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 694:108598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2020.108598
de Souza JS, Ferreira DR, Herai R, Carromeu C, Torres LB, Araujo BHS, Cugola F, Maciel RMB, Muotri AR, Giannocco G (2019) Altered gene expression of thyroid hormone transporters and deiodinases in iPS MeCP2-knockout cells-derived neurons. Mol Neurobiol 56:8277–8295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01645-2
Derwahl M, Nicula D (2014) Estrogen and its role in thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 21:T273–T283. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-14-0053
Dong J, Cong Z, You M, Fu Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Fu H, Wei L, Chen J (2019) Effects of perinatal di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure on thyroid function in rat offspring. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 67:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.01.012
Dong X, Dong J, Zhao Y, Guo J, Wang Z, Liu M, Zhang Y, Na X (2017) Effects of long-term in vivo exposure to di-2-ethylhexylphthalate on thyroid hormones and the TSH/TSHR signaling pathways in Wistar rats. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:44. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010044
Erkekoğlu P, Rachidi W, De Rosa V, Giray B, Favier A, Hincal F (2010) Protective effect of selenium supplementation on the genotoxicity of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate and mono(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate treatment in LNCaP cells. Free Radic Biol Med 49:559–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.04.038
Erythropel HC, Maric M, Nicell JA, Leask RL, Yargeau V (2014) Leaching of the plasticizer di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) from plastic containers and the question of human exposure. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:9967–9981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6183-8
Ferretti E, Tosi E, Po A, Scipioni A, Morisi R, Espinola MS, Russo D, Durante C, Schlumberger M, Screpanti I, Filetti S, Gulino A (2008) Notch signaling is involved in expression of thyrocyte differentiation markers and is down-regulated in thyroid tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:4080–4087. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-0528
Flippin JL, Hedge JM, DeVito MJ, Leblanc GA, Crofton KM (2009) Predictive modeling of a mixture of thyroid hormone disrupting chemicals that affect production and clearance of thyroxine. Int J Toxicol 28:368–381. https://doi.org/10.1177/1091581809341883
Fu G, Dai J, Li Z, Chen F, Liu L, Yi L, Teng Z, Quan C, Zhang L, Zhou T, Donkersley P, Song S, Shi Y (2020) The role of STAT3/p53 and PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway on DEHP-induced reproductive toxicity in pubertal male rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 404:115151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2020.115151
Fu Y, Dong J, Wang J, You M, Wei L, Fu H, Wang Y, Chen J (2018) Developmental exposure to di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate induces cerebellar granule cell apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Exp Neurobiol 27:472–488. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2018.27.6.472
García-Jiménez C, Santisteban P (2007) TSH signalling and cancer. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 51:654–671. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0004-27302007000500003
Gerdes N, Seijkens T, Lievens D, Kuijpers MJ, Winkels H, Projahn D, Hartwig H, Beckers L, Megens RT, Boon L, Noelle RJ, Soehnlein O, Heemskerk JW, Weber C, Lutgens E (2016) Platelet CD40 exacerbates atherosclerosis by transcellular activation of endothelial cells and leukocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 36:482–490. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.115.307074
Ghosh J, Das J, Manna P, Sil PC (2010) Hepatotoxicity of di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate is attributed to calcium aggravation, ROS-mediated mitochondrial depolarization, and ERK/NF-κB pathway activation. Free Radic Biol Med 49:1779–1791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.09.011
Grimaldi M, Boulahtouf A, Delfosse V, Thouennon E, Bourguet W, Balaguer P (2015) Reporter cell lines for the characterization of the interactions between human nuclear receptors and endocrine disruptors. Front Endocrinol (lausanne) 6:62–62. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2015.00062
Huang H-B, Chuang C-J, Su P-H, Sun C-W, Wang C-J, Wu M-T, Wang S-L (2017a) Prenatal and childhood exposure to phthalate diesters and thyroid function in a 9-year follow-up birth cohort study: Taiwan maternal and infant cohort study. Epidemiology 28(Suppl 1):S10–S18. https://doi.org/10.1097/EDE.0000000000000722
Huang H-B, Pan W-H, Chang J-W, Chiang H-C, Guo YL, Jaakkola JJK, Huang P-C (2017b) Does exposure to phthalates influence thyroid function and growth hormone homeostasis? The Taiwan Environmental Survey for Toxicants (TEST) 2013. Environ Res 153:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.11.014
Huang P-C, Li W-F, Liao P-C, Sun C-W, Tsai E-M, Wang S-L (2014) Risk for estrogen-dependent diseases in relation to phthalate exposure and polymorphisms of CYP17A1 and estrogen receptor genes. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:13964–13973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3260-6
James BC, Mitchell JM, Jeon HD, Vasilottos N, Grogan RH, Aschebrook-Kilfoy B (2018) An update in international trends in incidence rates of thyroid cancer, 1973–2007. Cancer Causes Control 29:465–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-018-1023-2
Janssen ST, Janssen OE (2017) Directional thyroid hormone distribution via the blood stream to target sites. Mol Cell Endocrinol 458:16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2017.02.037
Ji H, Liang H, Wang Z, Miao M, Wang X, Zhang X, Wen S, Chen A, Sun X, Yuan W (2019) Associations of prenatal exposures to low levels of polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) with thyroid hormones in cord plasma and neurobehavioral development in children at 2 and 4 years. Environ Int 131:105010–105010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105010
Jia P-P, Ma Y-B, Lu C-J, Mirza Z, Zhang W, Jia Y-F, Li W-G, Pei D-S (2016) The effects of disturbance on hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis in zebrafish larvae after exposure to DEHP. PLoS ONE 11:e0155762–e0155762. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155762
Jin S, Borkhuu O, Bao W, Yang Y-T (2016): Signaling pathways in thyroid cancer and their therapeutic implications. J Clin Med Res 8, 284–296. https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr2480w
Kim H, Suh JM, Hwang ES, Kim DW, Chung HK, Song JH, Hwang JH, Park KC, Ro HK, Jo EK, Chang JS, Lee TH, Lee MS, Kohn LD, Shong M (2003) Thyrotropin-mediated repression of class II trans-activator expression in thyroid cells: involvement of STAT3 and suppressor of cytokine signaling. J Immunol 171:616–627. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.171.2.616
Kim M, Jeong JS, Kim H, Hwang S, Park IH, Lee BC, Yoon SI, Jee SH, Nam KT, Lim KM (2018) Low dose exposure to di-2-ethylhexylphthalate in juvenile rats alters the expression of genes related with thyroid hormone regulation. Biomol Ther (seoul) 26:512–519. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2018.076
Kim MJ, Moon S, Oh B-C, Jung D, Choi K, Park YJ (2019a) Association between diethylhexyl phthalate exposure and thyroid function: a meta-analysis. Thyroid 29:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2018.0051
Kim MJ, Kim HH, Song YS, Kim OH, Choi K, Kim S, Oh BC, Park YJ (2021) DEHP down-regulates Tshr gene expression in rat thyroid tissues and FRTL-5 rat thyrocytes: a potential mechanism of thyroid disruption. Endocrinol Metab (seoul). https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.920
Kim S, Park G-Y, Yoo YJ, Jeong JS, Nam KT, Jee S-H, Lim K-M, Lee Y-S (2019b) Di-2-ethylhexylphthalate promotes thyroid cell proliferation and DNA damage through activating thyrotropin-receptor-mediated pathways in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem Toxicol 124:265–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.12.010
Kloas W, Lutz I (2006) Amphibians as model to study endocrine disrupters. J Chromatogr A 1130:16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.04.001
Le F, Zhang JY, Liu W, Huang XM, Luo WZ (2018) The levels of NF-κB p50 and NF-κB p65 play a role in thyroid carcinoma malignancy in vivo. J Int Med Res 46:4092–4099. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060518785846
Lee E, Ahn MY, Kim HJ, Kim IY, Han SY, Kang TS, Hong JH, Park KL, Lee BM, Kim HS (2007) Effect of di(n-butyl) phthalate on testicular oxidative damage and antioxidant enzymes in hyperthyroid rats. Environ Toxicol 22:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20259
Lee JJ, Pedley A, Marqusee E, Sutherland P, Hoffmann U, Massaro JM, Fox CS (2016) Thyroid function and cardiovascular disease risk factors in euthyroid adults: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Clin Endocrinol (oxf) 85:932–941. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.13124
Li MD, Kane JK, Matta SG, Blaner WS, Sharp BM (2000) Nicotine enhances the biosynthesis and secretion of transthyretin from the choroid plexus in rats: implications for beta-amyloid formation. J Neurosci 20:1318–1323. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.20-04-01318.2000
Liu C, Zhao L, Wei L, Li L (2015) DEHP reduces thyroid hormones via interacting with hormone synthesis-related proteins, deiodinases, transthyretin, receptors, and hepatic enzymes in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:12711–12719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4567-7
Liu C, Deng YL, Zheng TZ, Yang P, Jiang XQ, Liu EN, Miao XP, Wang LQ, Jiang M, Zeng Q (2020) Urinary biomarkers of phthalates exposure and risks of thyroid cancer and benign nodule. J Hazard Mater 383:121189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121189
Macchia PE, Takeuchi Y, Kawai T, Cua K, Gauthier K, Chassande O, Seo H, Hayashi Y, Samarut J, Murata Y, Weiss RE, Refetoff S (2001) Increased sensitivity to thyroid hormone in mice with complete deficiency of thyroid hormone receptor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:349–354. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.011306998
Marelli F, Persani L (2018) Role of Jagged1-Notch pathway in thyroid development. J Endocrinol Invest 41:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-017-0715-x
Marotta V, Russo G, Gambardella C, Grasso M, La Sala D, Chiofalo MG, D’Anna R, Puzziello A, Docimo G, Masone S, Barbato F, Colao A, Faggiano A, Grumetto L (2019) Human exposure to bisphenol AF and diethylhexylphthalate increases susceptibility to develop differentiated thyroid cancer in patients with thyroid nodules. Chemosphere 218:885–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.084
Marotta V, Malandrino P, Russo M, Panariello I, Ionna F, Chiofalo MG, Pezzullo L (2020) Fathoming the link between anthropogenic chemical contamination and thyroid cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 150:102950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.102950
Martino-Andrade AJ, Chahoud I (2010) Reproductive toxicity of phthalate esters. Mol Nutr Food Res 54:148–157. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200800312
Meeker JD, Calafat AM, Hauser R (2007) Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate metabolites may alter thyroid hormone levels in men. Environ Health Perspect 115:1029–1034. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9852
Meeker JD, Ferguson KK (2011) Relationship between urinary phthalate and bisphenol A concentrations and serum thyroid measures in U.S. adults and adolescents from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007–2008. Environ Health Perspect 119:1396–1402. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1103582
Miao H, Liu X, Li J, Zhang L, Zhao Y, Liu S, Ni S, Wu Y (2020) Associations of urinary phthalate metabolites with risk of papillary thyroid cancer. Chemosphere 241:125093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125093
Mu X, Liao X, Chen X, Li Y, Wang M, Shen C, Zhang X, Wang Y, Liu X, He J (2015) DEHP exposure impairs mouse oocyte cyst breakdown and primordial follicle assembly through estrogen receptor-dependent and independent mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 298:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.05.052
Nelson KK, Gattuso P, Xu X, Prinz RA (2010) Expression of the sonic hedgehog pathway molecules in synchronous follicular adenoma and papillary carcinoma of the thyroid gland in predicting malignancy. Surgery 148:654–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2010.07.030
Nozhat Z, Hedayati M (2016) PI3K/AKT pathway and its mediators in thyroid carcinomas. Mol Diagn Ther 20:13–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-015-0175-y
Park C, Lee J, Kong B, Park J, Song H, Choi K, Guon T, Lee Y (2019) The effects of bisphenol A, benzyl butyl phthalate, and di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate on estrogen receptor alpha in estrogen receptor-positive cells under hypoxia. Environ Pollut 248:774–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.069
Park ES, Kim H, Suh JM, Park SJ, You SH, Chung HK, Lee KW, Kwon OY, Cho BY, Kim YK, Ro HK, Chung J, Shong M (2000) Involvement of JAK/STAT (Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription) in the thyrotropin signaling pathway. Mol Endocrinol 14:662–670. https://doi.org/10.1210/mend.14.5.0458
Peter MC (2011) The role of thyroid hormones in stress response of fish. Gen Comp Endocrinol 172:198–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2011.02.023
Piana S, Zanetti E, Bisagni A, Ciarrocchi A, Giordano D, Torricelli F, Rossi T, Ragazzi M (2019) Expression of NOTCH1 in thyroid cancer is mostly restricted to papillary carcinoma. Endocr Connect 8:1089–1096. https://doi.org/10.1530/ec-19-0303
Pompura SL, Dominguez-Villar M (2018) The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in regulatory T-cell development, stability, and function. J Leukoc Biol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlb.2mir0817-349r
Qatanani M, Zhang J, Moore DD (2005) Role of the constitutive androstane receptor in xenobiotic-induced thyroid hormone metabolism. Endocrinology 146:995–1002. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2004-1350
Rajoria S, Suriano R, George A, Shanmugam A, Schantz SP, Geliebter J, Tiwari RK (2011) Estrogen induced metastatic modulators MMP-2 and MMP-9 are targets of 3,3′-diindolylmethane in thyroid cancer. PLoS ONE 6:e15879–e15879. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015879
Ramírez-Moya J, Wert-Lamas L, Santisteban P (2018) MicroRNA-146b promotes PI3K/AKT pathway hyperactivation and thyroid cancer progression by targeting PTEN. Oncogene 37:3369–3383. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0088-9
Rasoulpour RJ, Boekelheide K (2005) NF-kappaB is activated in the rat testis following exposure to mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. Biol Reprod 72:479–486. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.104.034363
Rawlings JS, Rosler KM, Harrison DA (2004) The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J Cell Sci 117:1281–1283. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.00963
Reale C, Iervolino A, Scudiero I, Ferravante A, D’Andrea LE, Mazzone P, Zotti T, Leonardi A, Roberto L, Zannini M, de Cristofaro T, Shanmugakonar M, Capasso G, Pasparakis M, Vito P, Stilo R (2016) NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO) is critical for thyroid function. J Biol Chem 291:5765–5773. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.711697
Reale C, Zotti T, Scudiero I, Vito P, Stilo R (2018) The NF-κB family of transcription factors and its role in thyroid physiology. Vitam Horm 106:195–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2017.05.003
Reyes JM, Price PS (2018) An analysis of cumulative risks based on biomonitoring data for six phthalates using the Maximum Cumulative Ratio. Environ Int 112:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.12.008
Rogers R, Ouellet G, Brown C, Moyer B, Rasoulpour T, Hixon M (2008) Cross-talk between the Akt and NF-kappaB signaling pathways inhibits MEHP-induced germ cell apoptosis. Toxicol Sci 106:497–508. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfn186
Rowdhwal SSS, Chen J (2018) Toxic effects of di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate: an overview. Biomed Res Int 2018:1750368–1750368. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1750368
Ruggeri BA, Huang L, Wood M, Cheng JQ, Testa JR (1998) Amplification and overexpression of the AKT2 oncogene in a subset of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Mol Carcinog 21:81–86
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, Yan H, Gazdar A, Powell SM, Riggins GJ, Willson JK, Markowitz S, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE (2004) High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 304:554. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1096502
Sathyanarayana S, Grady R, Barrett ES, Redmon B, Nguyen RHN, Barthold JS, Bush NR, Swan SH (2016) First trimester phthalate exposure and male newborn genital anomalies. Environ Res 151:777–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.07.043
Shayesteh L, Lu Y, Kuo WL, Baldocchi R, Godfrey T, Collins C, Pinkel D, Powell B, Mills GB, Gray JW (1999) PIK3CA is implicated as an oncogene in ovarian cancer. Nat Genet 21:99–102. https://doi.org/10.1038/5042
Shea KM, American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Environmental H (2003) Pediatric exposure and potential toxicity of phthalate plasticizers. Pediatrics 111, 1467-1474. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.111.6.1467
Shin D-J, Plateroti M, Samarut J, Osborne TF (2006) Two uniquely arranged thyroid hormone response elements in the far upstream 5′ flanking region confer direct thyroid hormone regulation to the murine cholesterol 7alpha hydroxylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res 34:3853–3861. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl506
Souter I, Bellavia A, Williams PL, Korevaar TIM, Meeker JD, Braun JM, de Poortere RA, Broeren MA, Ford JB, Calafat AM, Chavarro JE, Hauser R, Mínguez-Alarcón L (2020) Urinary concentrations of phthalate metabolite mixtures in relation to serum biomarkers of thyroid function and autoimmunity among women from a fertility center. Environ Health Perspect 128:67007. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp6740
Spanou I, Bougea A, Liakakis G, Rizonaki K, Anagnostou E, Duntas L, Kararizou E (2019) Relationship of migraine and tension-type headache with hypothyroidism: a literature review. Headache 59:1174–1186. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.13600
Staal SP (1987) Molecular cloning of the akt oncogene and its human homologues AKT1 and AKT2: amplification of AKT1 in a primary human gastric adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:5034–5037. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.84.14.5034
Sun D, Zhou L, Wang S, Liu T, Zhu J, Jia Y, Xu J, Chen H, Wang Q, Xu F, Zhang Y, Ye L (2018) Effect of Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate on the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis in adolescent rat. Endocr J 65:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.EJ17-0272
Takeuchi S, Iida M, Kobayashi S, Jin K, Matsuda T, Kojima H (2005) Differential effects of phthalate esters on transcriptional activities via human estrogen receptors alpha and beta, and androgen receptor. Toxicology 210:223–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2005.02.002
Tang X, Wu S, Shen L, Wei Y, Cao X, Wang Y, Long C, Zhou Y, Li D, Huang F, Liu B, Wei G (2018) Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP)-induced testicular toxicity through Nrf2-mediated Notch1 signaling pathway in Sprague-Dawley rats. Environ Toxicol 33:720–728. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22559
Vaiman M, Olevson Y, Habler L, Eviatar E, Zehari S, Sandbank J, Kessler A (2010a) The estrogen receptors in the papillary carcinoma of the thyroid gland. Oncol Res 18:537–540. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504010x12767359113802
Vaiman M, Olevson Y, Sandbank J, Habler L, Zehavi S, Kessler A (2010b) Are estrogen receptors alpha detectable in normal and abnormal thyroid tissue? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 267:1753–1757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-010-1269-0
van der Spek AH, Fliers E, Boelen A (2017) The classic pathways of thyroid hormone metabolism. Mol Cell Endocrinol 458:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2017.01.025
Ventrice P, Ventrice D, Russo E, De Sarro G (2013) Phthalates: European regulation, chemistry, pharmacokinetic and related toxicity. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2013.03.014
Vigneri R, Malandrino P, Gianì F, Russo M, Vigneri P (2017) Heavy metals in the volcanic environment and thyroid cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol 457:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2016.10.027
Wang Q, Liang K, Liu J, Yang L, Guo Y, Liu C, Zhou B (2013) Exposure of zebrafish embryos/larvae to TDCPP alters concentrations of thyroid hormones and transcriptions of genes involved in the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. Aquat Toxicol 126:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2012.11.009
Wang Z, Shao M, Liu Y (2017) Promotion of Wilms’ tumor cells migration and invasion by mono-2-ethyhexyl phthalate (MEHP) via activation of NF-κB signals. Chem Biol Interact 270:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.04.004
Wang Y, Li X, Yang G, Weng H, Wang X, Wang Q (2020) Changes of enzyme activity and gene expression in embryonic zebrafish co-exposed to beta-cypermethrin and thiacloprid. Environ Pollut 256:113437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113437
Wei N, Feng X, Xie Z, Zhang Y, Feng Y (2017) Long-term di (2-ethylhexyl)-phthalate exposure promotes proliferation and survival of HepG2 cells via activation of NFκB. Toxicol in Vitro 42:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2017.04.015
Wu H, Ma K, Na X (2020) Rosmarinic acid alleviates di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) -induced thyroid dysfunction via multiple inflammasomes activation. J Toxicol Sci 45:373–390. https://doi.org/10.2131/jts.45.373
Xing M (2010) Genetic alterations in the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway in thyroid cancer. Thyroid 20:697–706. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2010.1646
Xu S, Chen G, Peng W, Renko K, Derwahl M (2013) Oestrogen action on thyroid progenitor cells: relevant for the pathogenesis of thyroid nodules? J Endocrinol 218:125–133. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-13-0029
Yang S, Lee SP, Park JB, Lee H, Kang SH, Lee SE, Kim JB, Choi SY, Kim YJ, Chang HJ (2019) PM2.5 concentration in the ambient air is a risk factor for the development of high-risk coronary plaques. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 20:1355–1364. https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/jez209
Ye H, Ha M, Yang M, Yue P, Xie Z, Liu C (2017) Di2-ethylhexyl phthalate disrupts thyroid hormone homeostasis through activating the Ras/Akt/TRHr pathway and inducing hepatic enzymes. Sci Rep 7:40153. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40153
Ye T, Kang M, Huang Q, Fang C, Chen Y, Shen H, Dong S (2014) Exposure to DEHP and MEHP from hatching to adulthood causes reproductive dysfunction and endocrine disruption in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Aquat Toxicol 146:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.10.025
Yu Z, Han Y, Shen R, Huang K, Xu Y-Y, Wang Q-N, Zhou S-S, Xu D-X, Tao F-B (2018) Gestational di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure causes fetal intrauterine growth restriction through disturbing placental thyroid hormone receptor signaling. Toxicol Lett 294:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.05.013
Zhai W, Huang Z, Chen L, Feng C, Li B, Li T (2014a) Thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish larvae after exposure to mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (MEHP). PLoS ONE 9:e92465–e92465. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092465
Zhai W, Huang Z, Chen L, Feng C, Li B, Li T (2014b) Thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish larvae after exposure to mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (MEHP). PLoS ONE 9:e92465. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092465
Zhang P, Guan X, Yang M, Zeng L, Liu C (2018) Roles and potential mechanisms of selenium in countering thyrotoxicity of DEHP. Sci Total Environ 619–620:732–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.169
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81972996, 81573184).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ and WQ conducted the articles’ collection and drafted the manuscript. QX, XL, and LZ contributed to discussion and revision. LY is the corresponding author for this article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Qi, W., Xu, Q. et al. Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) and thyroid: biological mechanisms of interference and possible clinical implications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 1634–1644 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17027-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17027-y