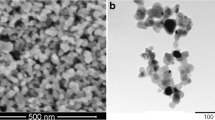
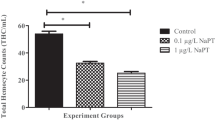
Abstract
Nanoparticle (NP) pollution is a worldwide problem. Copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) are one of the most used NPs in a variety of applications, which results in their increased release into the marine environment. In the present work, the marine mussel Lithophaga lithophaga was used as a model organism to evaluate the toxic effects of CuO NPs following 28 days of exposure to sub-lethal concentrations (5 and 20 μg/L). The time points were 1 day of exposure to assess the cell viability, phagocytosis in mussel haemocytes and genotoxicity (DNA damage in gills), 1, 14 and 28 days of exposure to evaluate copper concentrations in water and gills, as well as metallothionein concentration in gills, while gill histology and SEM examination were done after 28 days of exposure. The results indicated that the accumulation of CuO NPs in gills increased with concentration and time. Mussel exposure to CuO NPs increased neutral red uptake. However, the phagocytic abilities decreased in haemocytes with increased concentration. CuO NPs caused DNA damage in the gills even at low concentrations (5 µg/L). CuO NPs caused histopathological alterations in gills, such as brown cell accumulation, necrosis, dwarfism of filaments and ciliary erosion. In conclusion, exposure of the mussel L. lithophaga to CuO NPs led to concentration- and time-dependent responses for all the examined biomarkers. Thus, L. lithophaga may be used as a bioindicator organism in the assessment of CuO NP toxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available.
References
Abdul-Salam JM, Michelson IEH (1980) Phagocytosis by amoebocytes of Biomphalaria glabrata: absence of opsonic factor. Malacol Rev 13:81–83
Al-bairuty GA (2013) Histopathological effects of metal and metallic nanoparticles on the body systems of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Dissertation, University of Plymouth
Almeida JC, Cardoso CED, Pereira E, Freitas R (2019) Toxic effects of metal nanoparticles in marine invertebrates. In: Gonçalves G, Marques P (Eds) Nanostructured materials for treating aquatic pollution. Engineering Materials. Springer, Cham, Switzerland, pp175–224.
Alnashiri HM (2015) The ecotoxicology of different forms of copper (nano and micro and salt) in marine mussels. Dissertation, Heriot-Watt University -Edinburgh, Scotland, United Kingdom.
Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet A, Barka S, Pellerin S, Rainbow PS (2006) Metallothioneins in aquatic invertebrates: their role in metal detoxification and their use as biomarkers. Aquat Toxicol 76:160–202
Anyaogu KC, Fedorov AV, Neckers DC (2008) Synthesis, characterization, and antifouling potential of functionalized copper nanoparticles. Langmuir 24(8):4340–4346
Babich H, Borenfreund E (1992) Neutral red assay for toxicology in vitro. In: Watson RR (ed) In vitro methods of toxicology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp 237–251
Ben Khedher S, Jebali J, Houas Z, Nawei H, Jrad A, Banni M, Boussetta H (2014) Metals bioaccumulation and histopathological biomarkers in Carcinus maenas crab from Bizerta lagoon. Tunisia Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:4343–4357
Bhavan PS, Geraldine P (2000) Histopathology of the hepatopancreas and gills of the prawn Macrobrachium malcolmsonii exposed to endosulfan. Aquat Toxicol 50:331–339
Canesi L, Corsi I (2016) Effects of nanomaterials on marine invertebrates. Sci Total Environ 565:933–940
Canesi L, Ciacci C, Fabbri R, Marcomini A, Pojana G, Gallo G (2012) Bivalve molluscs as a unique target group for nanoparticle toxicity. Mar Environ Res 76:16–21
Canesi L, Ciacci C, Vallotto D, Gallo G, Marcomini A, Pojana G (2010) In vitro effects of suspensions of selected nanoparticles (C60 fullerene, TiO2, SiO2) on Mytilus hemocytes. Aquat Toxicol 96:151–158
D’Angelo, G., Gargiullo, S., 1978. Guida alle conchigle Mediterranee. Gruppo Editore Fabbri, Milano. 224.
Dasari TP, Pathakoti K, Hwang HM (2013) Determination of the mechanism of photoinduced toxicity of selected metal oxide nanoparticles (ZnO, CuO, Co3O4 and TiO2) to E. coli bacteria. J. Environ. Sci. 25(5):882–888
David JAO, Fontanetti CS (2005) Surface morphology of Mytella falcata gill filaments from three regions of the Santos estuary. Braz J Morphol Sci 22(4):203–210
Devescovi M (2009) Biometric differences between date mussels Lithophaga lithophaga colonizing artificial and natural structures. Acta Adriatica. Int J Mar Sci 50:129–138
De Vico G, Carella F (2012) Morphological features of the inflammatory response in molluscs. Res Vet Sci 93:1109–1115
Dufour SC, Beninger PG (2001) A functional interpretation of cilia and mucocyte distributions on the abfrontal surface of bivalve gills. Mar Biol 138(2):295–309
Felgenhauer B (1987) Techniques for preparing crustaceans for scanning electron microscopy. J Crust Biol 7:71–76
Federici G, Shaw BJ, Handy RD (2007) Toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): gill injury, oxidative stress, and other physiological effects. Aquat Toxicol 84:415–430
Ghadimi M, Zangenehtabar S, Homaeigohar S (2020) An overview of the water remediation potential of nanomaterials and their ecotoxicological impacts. Water 12(4):1150
Gagné F, Auclair J, Turcotte P (2008) Ecotoxicity of Cd Te quantum dots to freshwater mussels: impacts on immune system, oxidative stress and genotoxicity. Aquat Toxicol 86(3):333–340
Galinou-Mitsoudi S, Sinis AI (1995) Age and growth of Lithophaga lithophaga (Linnaeus, 1758) (Bivalvia: Mytilidae), based on annual growth lines in the shell. J Mollus Stud 61:435–453
García-Negrete CA, Blasco J, Volland M, Rojas TC, Hampel M, Lapresta-Fernández A, Jiménez de Haro MC, Soto M, Fernández A (2013) Behaviour of Au-citrate nanoparticles in seawater and accumulation in bivalves at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ Pollut 174:134–141
Gomes T, Araújo O, Pereira R, Almeida AC, Cravo A, Bebianno MJ (2013) Genotoxicity of copper oxide and silver nanoparticles in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar Environ Res 84:51–59
Gomes T, Chora S, Pereira CG, Cardoso C, Bebianno MJ (2014a) Proteomic response of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to CuO NPs and Cu2+: an exploratory biomarker discovery. Aquat Toxicol 155:327–336
Gomes T, Pereira CG, Cardoso C, Sousa VS, Teixeira MR, Pinheiro JP, Bebianno MJ (2014b) Effects of silver nanoparticles exposure in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar Environ Res 101:208–214
Gomes T, Pereira CG, Cardoso C, Pinheiro JP, Cancio I, Bebianno MJ (2012) Accumulation and toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles in the digestive gland of Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat Toxicol 118–119:72–79
Gomes T, Pinheiro JP, Cancio I, Catarina G, Pereira CG, Cardoso C, Bebianno MJ (2011) Effects of copper nanoparticles exposure in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Environ Sci Technol 45:9356–9362
Gonzalez, J.T., Halcon, R.M.A., Barrajon, A., Calvo, M., Frias, A., Morreno, D., Saavedra, L., 2000. Estudio sobre la biologia, conservacio´ny problema´tica del da ´til de mar (Lithophaga lithophaga) en Espana. Madrid, Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Direccio´n General de Conservacio´n de la Naturaleza 66.
Gunawant C, Teoh WY, Marquis CP, Amal R (2011) Cytotoxic origin of copper (II) Oxide nanoparticles: comparative studies with micron-sized particles, leachate, and metal salts. ACS Nano 5:7214–7225
Holsapple MP, Farland WH, Landry TD, Monteiro-Riviere NA, Carter JM, Walker NJ, Thomas KV (2005) Research strategies for safety evaluation of nanomaterials, part II: toxicological and safety evaluation of nanomaterials, current challenges and data needs. Toxicol Scie 88(1):12–17
Hu W, Culloty S, Darmody G, Lynch Davenport S, Ramirez-Garcia S, Dawson KA, Lynch I, BlascoSheehan JD (2014) Toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles in the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis: a redox proteomic investigation. Chemosphere 108:289–299
Katsumiti A, Thorley AJ, Arostegui I, Reip P, Valsami-Jones E, Tetley TD, Cajaraville MP (2018) Cytotoxicity and cellular mechanisms of toxicity of CuO NPs in mussel cells in vitro and comparative sensitivity with human cells. Toxicol Vitro 48:146–158
Koffyberg FP, Benko FA (1982) A photoelectrochemical determination of the position of the conduction and valence band edges of p-type CuO. J Appl Phys 53:1173–1177
Koehler A, Marx U, Broeg K, Bahns S, Bressling J (2008) Effects of nanoparticles in Mytilus edulis gill and hepatopancreas – a new threat to marine life. Mar Environ Res 66:12–14
Liu Z, Wu Y, Guo Z, Liu Y, Shen Y, Zhou P, Lu X (2014) Effects of internalized gold nanoparticles with respect to cytotoxicity and invasion activity in lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 9(6):e99175
Lowe DM, Fossato VU, Depledge MH (1995) Contaminant-induced lysosomal membrane damage in blood cells of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Venice Lagoon: an in vitro study. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 129:189–196
Luengen AC, Friedman CS, Raimondi PT, Flegal AR (2004) Evaluation of mussel immune responses as indicators of contamination in San Francisco Bay. Mar Environ Res 57:197–212
Luoma SN, Rainbow PS (2005) Why is metal bioaccumulation so variable? Biodynamics as a unifying concept. Environ Sci Technol 39:1921–1931
Mallatt J (1985) Fish gill structural changes induced by toxicants and other irritants: a statistical review. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 42:630–648
Marquis BJ, Love SA, Braun KL, Haynes CL (2009) Analytical methods to assess nanoparticle toxicity. Analyst 134:425–439
Martín-Díaz ML, Jiménez-Tenorio N, Sales D, Delvalls TA (2008) Accumulation and histopathological damage in the clam Ruditapes philippinarum and the crab Carcinus maenasto assess sediment toxicity in Spanish ports. Chemosphere 71:1916–1927
Moore MN (2006) Do nanoparticles present ecotoxicological risks for the health of the aquatic environment? Environ Int 32:967–976
Moreau JL, Baudrimont M, Carrier P, Peltier G, Bourdineaud JP (2008) Metal binding and antioxidant properties of chimeric triand tetra-domained metallothioneins. Biochimie 90:705–716
Mortimer M, Kasemets K, Kahru A (2010) Toxicity of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles to ciliated protozoa Tetrahymena thermophila. Toxicology 269(2–3):182–189
Mouneyrac C, Buffet PE, Poirier L, Zalouk-Vergnoux A, Guibbolini M, Faverney CR, Gilliland D, Berhanu D, Dybowska A, Châtel A, PerreinEttajni H, Pan JF, Thomas-Guyon H, Reip P, Valsami-Jones E (2014) Fate and effects of metal-based nanoparticles in two marine invertebrates, the bivalve mollusk Scrobicularia plana and the annelid polychaete Hediste diversicolor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:7899–7912
Nessim RB, Salem DMSA, Abdel Ghani SAH, Abou-Taleb AEA (2010) Level of some major constituents of the Egyptian Mediterranean Coastal waters. Egypt J Aquat Res 36:1–9
Okbah MA, Nasr SM, Soliman NF, Khairy MA (2014) Distribution and contamination status of trace metals in the Mediterranean coastal sediments. Egypt Soil Sed Contam 23:656–676
Olurin K, Olojo E, Mbaka G, Akindele A (2006) Histopathological responses of the gill and liver tissues of Clarias gariepinus fingerlings to the herbicide, glyphosate. Afr J Biotechnol 5:2480–2487
Rocha TL, Gomes T, Sousa VS, Mestre NC, Bebianno MJ (2015) Ecotoxicological impact of engineered nanomaterials in bivalve molluscs: an overview. Mar Environ Res 111:74–88
Romeis, B., 1989. Mikroskopische Technik, 17 Auflage, Urban & Schwarzenberg, München– Wien – Baltimore.
Riisgård HU, Funch P, Larsen PS (2015) The mussel filter–pump–present understanding, with a re-examination of gill preparations. Acta Zoo 96:273–282
Ruiz P, Katsumiti A, Nieto JA, Bori J, Jimeno-Romero A, Reip P, Arostegui I, Orbea A, Cajaraville MP (2015) Short-term effects on antioxidant enzymes and long-term genotoxic and carcinogenic potential of CuO nanoparticles compared to bulk CuO and ionic copper in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar Environ Res 111:107–120
Sheir SK, Handy RD (2010) Tissue injury and cellular immune responses to cadmium chloride exposure in the common mussel Mytilus edulis: modulation by lipopolysaccharide. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 59:602–613
Sheir SK, Handy RD, Henry TB (2013) Effect of pollution history on immunological responses and organ histology in the marine mussel Mytilus edulis exposed to cadmium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 64:1–170
Singh CR, Kathiresan K, Anandhan S (2015) A review on marine based nanoparticles and their potential applications. Afr J Biotech 14(18):1525–1532
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low-levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Sunila I (1986) Chronic histopathological effects of short term copper and cadmium exposure on the gill of the mussel, Mytilus edulis. J Invert Pathol 47:125–142
Tedesco S, Doyle H, Redmond G, Sheehan D (2008) Gold nanoparticles and oxidative stress in Mytilus edulis. Mar Environ Res 66(1):131–133
Tsunekawa S, Fukuda T, Kasuya A (2000) Blue shift in ultraviolet absorption spectra of monodisperse CeO 2–x nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 87:1318–1321
Usheva LN, Frolova LT (2006) Morphofunctional changes of the digestive gland in the bivalve mollusk Crenomytilus grayanus (Dunker, 1853) in normal conditions and after parasitic invasion by trematodes. Russ J Mar Biol 32:96–105
Van Den Brink NW, Kokalj AJ, Silva PV, Lahive E, Norrfors K, Baccaro M, Khodaparast Z, Loureiro S, Drobne D, Cornelis G, Lofts S (2019) Tools and rules for modelling uptake and bioaccumulation of nanomaterials in invertebrate organisms. Environ Sci Nano 6:1985–2001
Van OR, Porte-Visa C, Van den Brink NW (2005) Ecotoxicological testing of marine and freshwater ecosystems. In: Munawar M, Den Besten PJ (eds) Biomarkers in environmental assessment. Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, pp 87–152
Viarengo A, Arena N, Canesi L, Alia FA, Orunesu M (1994) Structural and biochemical alterations in the gills of copper exposed mussels. In: Renzoni A, Mattei N, Lari L (eds) Contaminants in the environment. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 135–144
Viarengo A, Ponzano E, Dondero F (1997) A simple spectrophotometric method for metallothionein evaluation in marine organisms: an application to Mediterranean and Antarctic Molluscs. Mar Environ Res 44:69–84
Zaroogian G, Yevich P, Anderson S (1993) Effect of selected inhibitors on cadmium, nickel and benzo [a] pyrene uptake into brown cells of Mercenaria mercenaria. Mar Environ Res 35:41–45
Zha S, Rong J, Guan X, Tang Y, Han Y, Liu G (2019) Immunotoxicity of four nanoparticles to a marine bivalve species, Tegillarca granosa. J Hazard Mater 377:237–248
Zhu H, Han D, Meng Z, Wu D, Zhang C (2011) Preparation and thermal conductivity of CuO nanofluid via a wet chemical method. Nanoscale Res Lett 6:181
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate the help provided by Professor Dr. Ahmed El-Hamalawy, Prof. of Solid State Physics, Lab. of Renewable Energy (LORE), Faculty of Science, Menoufia University, in the results of CuO nanoparticle characterization.
Funding
The current study was funded personally by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AEE was responsible for the conceptualization, review and supervision of the work.
SSE was responsible for the review, writing of the original draft and supervision of the work.
GYO was responsible for the review, editing and supervision.
RME was responsible for the methodology, analysis, investigations and writing of the original draft.
ASA was responsible for the review of the work.
SKS was responsible for the conceptualization, methodology, validation, investigations, resources, writing of the original draft, editing, visualization and supervision of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No ethical approval is needed for invertebrate animals (bivalves) according to the IACUC approval sheet.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Bruno Nunes.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Essawy, A.E., sherif, S.S.E., Osman, G.Y. et al. Immune responses, DNA damage and ultrastructural alterations of gills in the marine mussel Lithophaga lithophaga exposed to CuO nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 15800–15815 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16889-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16889-6