Abstract
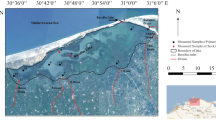
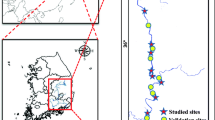
The Red River is the largest river in northern Vietnam, and it serves as the main water source for production and human activities in the Red River Delta region. Cities and provinces located in the Red River Delta, for example, Hanoi, Nam Dinh, and Ha Nam, have experienced rapid economic growth with various large urban, industrial zones, and agricultural areas. As a result of urbanization and industrialization, surface water in this region has been contaminated by multiple anthropogenic sources. In this study, in addition to water quality assessment using WQI, we used the reflectance values of visible and near-infrared bands and in situ data to build a regression model for several water quality parameters. Among ten parameters examined, two parameters, including total suspended solids (TSS) and turbidity, were used to construct regression correlation models using the Sentinel-2 multispectral images. Our results can contribute useful information for comprehensive monitoring, evaluation, and management scheme of water quality in the Red River Delta. The application of this method can overcome the limitation of actual observation results that only reflect local contamination status and require a lot of sampling and laboratory efforts.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Alastal KM, Alagha JS, Abuhabis AA, Ababou R (2015) Groundwater quality assessment using water quality index (WQI) approach: Gâz Coastal aquifer case study. Journal of Engineering Research and Technology 2(1):80–86
Baird RB, Eaton AD, Rice EW (2017) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation
Bresciani M, Giardino C, Stroppiana D, Dessena MA, Buscarinu P, Cabras L, Schenk K, Heege T, Bemet H, Bazdanis G, Tzimas A (2019) Monitoring water quality in two damment reservoirs from multispectral satellite data. European Journal of Remote Sensing 52(54):113–122
Brown R.M., McClelland N.I., Deininger R.R., O’Connor M.F. (1971) A water quality index - crashing the psychological barrier. Indicators of Environmental Quality, pp.173-182.
Cao TS, Nguyen THG, Trieu PT, Nguyen HN, Nguyen TL, Vo HC (2020) Assessment of Cau river water quality assessment using a combination of water quality and pollution indices. Journal of Water Sullly: Research and Technology-Aqua 69(2):160–172
CCME (2001) Canadian environmental quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life. CCME water quality index: technical report, 1.0.
Chavez PS (1996) Image-based atmospheric corrections – revisited and improved. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 62(9):1025–1036
Chelotti GB, Martinez JM, Roig HL, Olivietti D (2019) Space-temporal analysis of suspended sediment in low concentration reservoir by remote sensing. Brazil Journal of Water Resources 24:1–15
Chen Z, Hanson JD, Curran PJ (1991) The form of the relationship between suspended sediment concentration and spectral reflectance: its implications for the use of Daedalus 1268 data. International Journal of Remote Sensing 12(1):215–222
Chen Z, Curran PJ, Hanson JD (1992) Derivative reflectance spectroscopy to estimate suspended sediment concentration. Remote Sensing of Environment 40(1):67–77
Dabgerwal DK, Tripathi SK (2016) Assessment of surface water quality using hierarchical cluster analysis. International Journal of Environment 5(1):31–43
Dekker A, Zamurovic-Nenad Z, Hoogenboom H, Peters S (1996) Remote sensing, ecological water quality modelling and in situ measurements: a case study in shallow lakes. Hydrologycal Science Journal 41:531–547
Doxaran D, Froidefond JM, Lavender S, Castaing P (2007) Spectral signature of highly turbid waters application with SPOT data to quantify suspended particulate matter concentrations. Remote Sensing of Environment 81:149–161
Ennaji W, Barakat A, Karaoui I, El Baghdadi M, Arioua A (2018) Remote sensing approach to assess salt-affected soils in the north-east part of Tadla plain, Morocco. Geology, Ecology and Landscapes 2(1):22–28
Espinoza Villar R, Martinez J-M, Le Texier M, Guyot J-L, Fraizy P, Meneses PR, de Oliveira E (2013) A study of sediment transport in the Madeira River, Brazil, using MODIS remote-sensing images. Journal of South American Earth Sciences 44:45–54
Gholizadeh MH, Melesse AM, Reddi L (2016) A comprehensive review on water quality parameters estimation using remote sensing techniques. Sensors 16(8):2–43
Giardino C, Bresciani M, Villa P, Martinelli A (2010) Application of remote sensing in water resource management: the case study of Lake Trasimeno, Italy. Water resources management 24(14):3885–3899
Guzman VR, Santaella FG (2009) Using MODIS 250m imagery to estimate total suspended sediment in a tropical open bay. International Journal of Systems Applications, Engineering & Development 3(1):36–44
He W (2008) Water quality monitoring in slightly – polluted body through remote sensing – a case study in Guanting Reservoir Beijing, China. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering in China 2(2):163–171
Hoang TTH, Nguyen TK, Le TPQ, Dang DK, Duong TT (2016) Assessment of the water quality downstream of Red River in 2015 (Vietnam). Journal of Vietnamese Environment 8(3):167–172
Horton RK (1965) An index number system for rating water quality. Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation 37(3):300–306
Hung TL, Tarasov MK (2016) Evaluation of suspended matter concentrations in surface water of the Tri An water reservoir (Vietnam) using the remote sensing data. Moscow State University Bulletin Serial 5 – Geography(2):38–43
Karaoui I, Arioua A, Boudhar A, Hssaisoune M, Mouatassime SE, Ouhamchich KA, Elhamdouni D, Idrissi AEA, Nouaim W (2019) Evaluating the potential of Sentinel-2 satellite images for water quality characterization of artificial reservoirs: the Bin El Ouidane Reservoir case study (Morocco). Meteorology Hydrology and Water Management 7(1):31–39
Ke LC, Tran HTV, Liem VH, Tuong TN, Duyen PT (2015) Assessment of surface water pollutant models of estuaries and coastal zone of Quang Ninh – Hai Phong using Spot-5 images. Geodesy and Cartography 64(1):29-42
Kiselev V, Bulgarelli B, Heege T (2015) Sensor independent adjacency correction algorithm for coastal and inland water systems. Remote Sensing of Environment 157:85–95
Knaeps E, Dogliotti A, Raymaekers D, Ruddick K, Sterchx S (2012) In situ evidence of non-zero reflectance in the OLCI 1020 nm band for a turbid estuary. Remote Sensing of Environmen 120:133–144
Liou SM, Lo SL, Wang SH (2004) A generalized water quality index for Taiwan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 96:35–32
Luu TNM, Garnier J, Billen G, Orange D, Nemery J, Le TPQ, Tran HT, Le LA (2010) Hydrological regime and water budget of the Red River Delta (Northern Vietnam). Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 37:219–228
Marinho RR, Harmel T, Martinez JM, Filizola Junior NP (2021) Spatiatemporal dynamics of suspended sediments in the Negro River, Amazon Basin, from in situ and Sentinel-2 remote sensing data. International Journal of Geo-Information 10(2):86
Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (2018) Vietnam: National State of Environment Report 2018 on water resources.
Mobley C (1999) Estimation of the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements. Applied Optics 38:7442–7455
Moran MS (1992) Evaluation of simplified procedures for retrieval of land surface reflectance factors from satellite sensor output. Remote Sensing of Environment 41:169–184
National Centre for Water Resources Planning and Investigation (NAWAPI), Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (MONRE) (2016) The water resources planning in Hong-Thai Binh River basin.
Nguyen TTH, Zhang W, Li Z, Li J, Ge C, Liu J, Bai X, Feng H, Yu L (2016) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in Red River surface sediments, Viet Nam. Marine Pollution Bulletin 113(1-2):513–519
Nguyen TTH, Koike K, Mai TN, Canh BD, Thao NTP, Parsons M (2017a) Landsat 8/OLI two bands ratio algorithm for chlorophyll-a concentration mapping in hypertrophic waters: an application to West Lake in Hanoi (Vietnam). IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 10(11):4919–4929
Nguyen TTH, Nguyen TPT, Koike K, Mai TN (2017b) Selecting the best band ratio to estimate chlorophyll-a concentration in a tropical freshwater lake using sentinel 2A images from a case study of Lake Ba Be (Northern Vietnam). ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 6(9):290
Pham QV, Nguyen TTH, Pahlevan N, Oanh LT, Nguyen TB, Nguyen NT (2018) Using Landsat-8 images for quantifying suspended sediment concentration in Red River (Northern Vietnam). Remote Sensing 10(11):1841
Pizani FMC, Maillard P, Ferreira AFF, de Amorim CC (2020) Estimation of water quality in a reservoir from Sentinel-2 MSI and Landsat-8 OLI sensors. ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 3:401–408
Potes M, Rodrigues G, Penha AM, Novais MH, Costa MJ, Salgado R, Morais MM (2018) Use of Sentinel 2-MSI for water quality monitoring at Alqueva reservoir, Portugal. Earth Observation for Integrated Water and Basin Management, IAHS 380:73–79
Richter, R. (2009) Atmospheric/topographic correction for satellite imagery. DLR report DLR-IB 565-01/09, Wessling, Germany.
Ritchie JC, Schiebe FR, McHenry JR (1976) Remote sensing of suspended sediments in surface waters. Journal of American Society of Photogrammetry 42(12):1539–1545
Ritchie JC, Cooper CM, Yongqing J (1987) Using Landsat multispectral scanner data to estimate suspended sediments in Moon Lake, Mississippi. Remote Sensing of Environment 23:65–81
Ritchie JC, Cooper CM, Schiebe FR (1990) The relationship of MSS and TM digital data with suspended sediments, chlorophyll, and temperature in Moon Lake, Mississippi. Remote Sensing of Environment 33:137–148
Sargaonkar A, Deshpande V (2003) Development of an overall index of pollution for surface water based on a general classification scheme in Indian context. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 89:43–67
Sent G, Biguino B, Favareto L, Cruz J, Sá C, Dogliotti AI, Palma C, Brotas V, Brito AC (2021) Deriving water quality parameters using Sentinel-2 imagery: a case study in the Sado Estuary, Portugal. Remote Sensing 13:1043
Shweta T, Bhavtosh S, Prashant S, Rajendra D (2013) Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. American Journal of Water Resources 1(3):34–38
Sliwka-Kaszyńska M, Kot-Wasik A, Namieśnik J (2003) Preservation and storage of water samples. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 33(1):31–44
Tran QB, Pham AD (2020) Developing a water quality index (WQI) for river resources management in Kien Giang province, Vietnam. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 444(012054)
Tsegaye T, Sheppard D, Islam KR, Johnson A, Tadesse W, Atalay A, Marzen L (2006) Development of chemical index as a measure of in-stream water quality in response to land-use and land cover changes. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 174:161–179
Yadav S, Yamashiki Y, Susaki J, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa K (2019) Chlorophyll estimation of lake water and coastal water using Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2A satellite. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 42(3/W7):77–82
Yang W, Zhao Y, Wang D, Wu H, Lin A, He L (2020) Using principal components analysis and IDW interpolation to determine spatial and temporal changes of surface water quality of Xin’anjiang River in Huangshan, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17:2942
Yepez S, Laraque A, Martinez J, De Sa J, Carrera J, Castellanos B, Gallay M, Lopez J (2018) Retrieval of suspended sediment concentrations using Landsat-8 OLI satellite images in the Orinoco River (Venezuela). Comptes Rendus Geoscience 350(1-2):20–30
Funding
This research was funded by the Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resource and Environment (MONRE) (grant number TNMT 2018.02.15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Trinh Thi Tham, Trinh Le Hung, Trinh Thi Thuy, Vu Thi Mai, Le Thi Trinh, and Chu Vu Hai. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Trinh Thi Tham and Trinh Le Hung, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Supervision, conceptualization, and writing—review and editing were performed by Tu Binh Minh. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 68 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tham, T.T., Hung, T.L., Thuy, T.T. et al. Assessment of some water quality parameters in the Red River downstream, Vietnam by combining field monitoring and remote sensing method. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 41992–42004 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16730-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16730-0