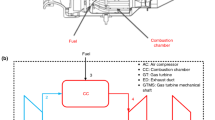
Abstract
Recently, as a result of the increasing use of fossil fuels in the world, environmentally friendly alternative fuel researches have become an important topic. The present study aims to examine the possible consequences of hydrogen fuel usage as an alternative fuel on the general performance, sustainability performance and environmental performance in the medium scale aircraft turboprop engine. Within this aim, a comprehensive exergetic analysis of the turboprop engine is conducted for both the hydrogen fuel utilization case and jet fuel utilization case. Then, depending on the fourteen performance metrics determined for the concept of the study, the effects of hydrogen fuel usage were observed. As per the results, the fuel mass stream rate reduces from 0.0145 kg/s to 0.052 kg/s compared to the jet fuel usage, while the stationary stream of air mass rate is 8.66 kg/s. Pollutant emissions mass stream rate decreases from 8.805 kg/s to 8.712 kg/s. The fuel exergy rate of the overall system rises from 6588.29 kW to 7002.36 kW. The product exergy rate of the overall system drops from 1135.928 kW to 1134.495 kW. The waste exergy rate of the overall system increases from 5452.36 kW to 5867.87 kW. While the exergetic sustainability index and sustainable efficiency factor of the system decrease from 0.21 to 0.19 and decrease from 1.21 to 1.19, the environmental effect factor and ecological effect factor of the system increment from 4.80 to 5.17, an increment from 5.80 to 6.17, respectively. The environmental effect factor of the overall system increment from 2.36 to 2.57, while the sustainable efficiency factor of the overall system reduces from 1.42 to 1.38.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and other material related to this paper will be available upon request.
References
Akdeniz HY, Balli O (2021a) Impact of different fuel usages on thermodynamic performances of a high bypass turbofan engine used in commercial aircraft. Energy 238:121745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121745
Akdeniz HY, Balli O (2021b) Energetic and exergetic assessment of operating biofuel, hydrogen and conventional JP-8 in a J69 type of aircraft turbojet engine. J Therm Anal Calorim https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-10879-z
Akdeniz HY, Balli O (2021c) Effects of bypass ratio change trend on performance in a military aircraft turbofan engine with comparative assessment. J Energy Resour Technol 143:120905. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4051297
Aydin H, Turan O, Karakoc TH, Midilli A (2012) Component-based exergetic measures of an experimental turboprop/turboshaft engine for propeller aircrafts and helicopters. IJEX 11:322. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEX.2012.050228
Aydın H, Turan Ö, Karakoç TH, Midilli A (2013) Exergo-sustainability indicators of a turboprop aircraft for the phases of a flight. Energy 58:550–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.04.076
Balli O (2017a) Advanced exergy analyses of an aircraft turboprop engine (TPE). Energy 124:599–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.02.121
Balli O (2017b) Exergy modeling for evaluating sustainability level of a high by-pass turbofan engine used on commercial aircrafts. Appl Therm Eng 123:138–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.05.068
Balli O (2019) A parametric study of hydrogen fuel effects on exergetic, exergoeconomic and exergoenvironmental cost performances of an aircraft turbojet engine. Int J Turbo Jet Engines. https://doi.org/10.1515/tjj-2019-0043
Ballı Ö (2020a) General aviation and thermodynamic performance analyses of micro turbojet engine used on drones and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV). Journal of Aviation Research 2(2):115–141
Balli O (2020b) Exergetic, exergoeconomic, sustainability and environmental damage cost analyses of J85 Turbojet engine with afterburner. Int J Turbo Jet Engines 37:167–194. https://doi.org/10.1515/tjj-2017-0019
Balli Ö (2020c) Performance assessment of a medium-scale turboprop engine designed for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) based on exergetic and sustainability metrics. J Therm Eng 6(5):697–706. https://doi.org/10.18186/thermal.796753
Balli O, Caliskan H (2021a) On-design and off-design operation performance assessmentsof an aero turboprop engine used on unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in terms of aviation, thermodynamic, environmental and sustainability perspectives. Energy Convers Manag 243:114403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2021.114403
Balli O, Caliskan H (2021b) Turbofan engine performances from aviation, thermodynamic and environmental perspectives. Energy 232:121031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121031
Balli O, Hepbasli A (2013) Energetic and exergetic analyses of T56 turboprop engine. Energy Convers Manag 73:106–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2013.04.014
Balli O, Sohret Y, Karakoc HT (2018) The effects of hydrogen fuel usage on the exergetic performance of a turbojet engine. Int J Hydrog Energy 43:10848–10858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.12.178
Bejan A, Siems DL (2001) The need for exergy analysis and thermodynamic optimization in aircraft development. Int J Exergy 1:14–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1164-0235(01)00005-X
Bullerdiek N, Neuling U, Kaltschmitt M (2021) A GHG reduction obligation for sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) in the EU and in Germany. J Air Transp Manag 92:102020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jairtraman.2021.102020
Caglayan H, Caliskan H (2019) Thermodynamic based economic and environmental analyses of an industrial cogeneration system. Appl Therm Eng 158:113792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.113792
Caglayan H, Caliskan H (2021) Advanced exergy analyses and optimization of a cogeneration system for ceramic industry by considering endogenous, exogenous, avoidable and unavoidable exergies under different environmental conditions. Renew Sust Energ Rev 140:110730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.110730
Caliskan H (2017) Energy, exergy, environmental, enviroeconomic, exergoenvironmental (EXEN) and exergoenviroeconomic (EXENEC) analyses of solar collectors. Renew Sust Energ Rev 69:488–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.203
Caliskan H, Mori K (2017) Environmental, enviroeconomic and enhanced thermodynamic analyses of a diesel engine with diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC) and diesel particulate filter (DPF) after treatment systems. Energy 128:128–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.04.014
Caliskan H, Lee D-Y, Hong H (2019) Enhanced thermodynamic assessments of the novel desiccant air cooling system for sustainable energy future. J Clean Prod 211:213–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.174
Çengel YA, Boles MA (2015) Thermodynamics: an engineering approach, Eighth edn. McGraw-Hill Education, New York
Coban K, Colpan CO, Karakoc TH (2017) Application of thermodynamic laws on a military helicopter engine. Energy 140:1427–1436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.07.179
Dong K, Sun R, Jiang H, Zeng X (2018) CO2 emissions, economic growth, and the environmental Kuznets curve in China: what roles can nuclear energy and renewable energy play? J Clean Prod 196:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.271
Ebadi MJ, Gorji-Bandpy M (2005) Exergetic analysis of gas turbine plants. IJEX 2:31. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEX.2005.006431
Ehyaei MA, Anjiridezfuli A, Rosen MA (2013) Exergetic analysis of an aircraft turbojet engine with an afterburner. Therm Sci 17:1181–1194. https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI110911043E
Etele J, Rosen MA (2001) Sensitivity of exergy efficiencies of aerospace engines to reference environment selection. Int J Exergy 1:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1164-0235(01)00014-0
Jawad H, Jaber MY, Bonney M, Rosen MA (2016) Deriving an exergetic economic production quantity model for better sustainability. Appl Math Model 40:6026–6039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2016.01.042
John CB, Raja SA, Deepanraj B, Ong HC (2021) Palm stearin biodiesel: preparation, characterization using spectrometric techniques and the assessment of fuel properties. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-01265-0
Khan MK, Teng J-Z, Khan MI, Khan MO (2019) Impact of globalization, economic factors and energy consumption on CO2 emissions in Pakistan. Sci Total Environ 688:424–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.065
Koch C, Cziesla F, Tsatsaronis G (2007) Optimization of combined cycle power plants using evolutionary algorithms. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 46:1151–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2006.06.025
Kotas TJ (1995) The exergy method of thermal plant analysis, Reprint ed. with corrections. Krieger Pub, Malabar, Fla
Latypov AF (2009) Exergy analysis of ramjet. Thermophys Aeromech 16:303–313. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0869864309020152
Mahmood N, Wang Z, Hassan ST (2019) Renewable energy, economic growth, human capital, and CO2 emission: an empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:20619–20630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05387-5
Midilli A, Dincer I (2009) Development of some exergetic parameters for PEM fuel cells for measuring environmental impact and sustainability. Int J Hydrog Energy 34:3858–3872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.02.066
Milano J, Ong HC, Masjuki HH, Silitonga AS, Chen WH, Kusumo F, Dharma S, Sebayang AH (2018) Optimization of biodiesel production by microwave irradiation-assisted transesterification for waste cooking oil-Calophyllum inophyllum oil via response surface methodology. Energy Convers Manag 158:400–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.12.027
Neuling U, Kaltschmitt M (2018) Techno-economic and environmental analysis of aviation biofuels. Fuel Process Technol 171:54–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.09.022
Pata UK (2021) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, economic complexity, CO2 emissions, and ecological footprint in the USA: testing the EKC hypothesis with a structural break. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:846–861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10446-3
Rakopoulos C, Giakoumis E (2006) Second-law analyses applied to internal combustion engines operation. Prog Energy Combust Sci 32:2–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2005.10.001
Ranasinghe K, Guan K, Gardi A, Sabatini R (2019) Review of advanced low-emission technologies for sustainable aviation. Energy 188:115945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.115945
Saravanamuttoo HIH (ed) (2009) Gas turbine theory, 6th edn. Pearson Prentice Hall, Harlow, England; New York
Shahbaz M, Solarin SA, Hammoudeh S, Shahzad SJH (2017) Bounds testing approach to analyzing the environment Kuznets curve hypothesis with structural beaks: the role of biomass energy consumption in the United States. Energy Econ 68:548–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.10.004
Şöhret Y (2018a) Exergo-sustainability analysis and ecological function of a simple gas turbine aero-engine. Journal of. Therm Eng 4:2083–2095. https://doi.org/10.18186/journal-of-thermal-engineering.414990
Şöhret Y (2018b) Ecologic performance and sustainability evaluation of a turbojet engine under on-design conditions. Aviation 22:166–173. https://doi.org/10.3846/aviation.2018.7085
Şöhret Y, Kıncay O, Karakoç TH (2015) Combustion efficiency analysis and key emission parameters of a turboprop engine at various loads. J Energy Inst 88:490–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2014.09.010
Şöhret Y, Sogut MZ, Karakoc TH, Turan O (2016) Customised application of exergy analysis method to PW120A turboprop engine for performance evaluation. IJEX 20:48. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEX.2016.076678
Şöhret Y, Ekici S, Karakoc TH (2018) Using exergy for performance evaluation of a conceptual ramjet engine burning hydrogen fuel. Int J Hydrog Energy 43:10842–10847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.12.060
Suryan A, Kim HD, Setoguchi T (2013) Comparative study of turbulence models performance for refueling of compressed hydrogen tanks. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:9562–9569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.07.055
Teng J-Z, Khan MK, Khan MI, Chishti MZ, Khan MO (2021) Effect of foreign direct investment on CO2 emission with the role of globalization, institutional quality with pooled mean group panel ARDL. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:5271–5282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10823-y
TurAF (2010) Turkish Air Forces.1’st Air Supply and Maintenance Center. Test Cell Reports. Turkey: Eskisehir,
TurAF (2017) 1.HBFM-1’st Air Maintenance Factories Directorate. Turbojet and Turboprop Project Document for UAV.
Turan O (2015) An exergy way to quantify sustainability metrics for a high bypass turbofan engine. Energy 86:722–736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.04.026
Tuzcu H, Sohret Y, Caliskan H (2021) Energy, environment and enviroeconomic analyses and assessments of the turbofan engine used in aviation industry. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 40:e13547. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13547
Ünal F, Temir G, Köten H (2018) Energy, exergy and exergoeconomic analysis of solar-assisted vertical ground source heat pump system for heating season. J Mech Sci Technol 32:3929–3942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0744-1
Wang Z, Danish ZB, Wang B (2018) Renewable energy consumption, economic growth and human development index in Pakistan: evidence form simultaneous equation model. J Clean Prod 184:1081–1090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.260
Xu W, Li Q, Huang M (2015) Design and analysis of liquid hydrogen storage tank for high-altitude long-endurance remotely-operated aircraft. Int J Hydrog Energy 40:16578–16586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.09.028
Yuksel B, Balli O, Gunerhan H, Hepbasli A (2020) Comparative performance metric assessment of a military turbojet engine utilizing hydrogen and kerosene fuels through advanced exergy analysis method. Energies 13:1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051205
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The author agrees on ethics on publishing the article. The author consents to participate in this research study.
Consent for publication
The author consents to publish the current research in the Environmental Science and Pollution Research journal.
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akdeniz, H.Y. Systematic benchmarking of performance, environmental and sustainability impacts of utilization of alternative cleaner fuel in an aircraft gas turbine engine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 51012–51029 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16508-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16508-4