Abstract
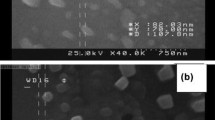
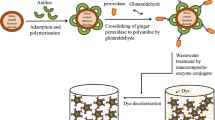
To enhance the dye removal efficiency by natural enzyme, horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was immobilized onto amine-functionalized superparamagnetic iron oxide and used as a biocatalyst for the oxidative degradation of acid black-HC dye. The anchored enzyme was characterized by vibrating sample magnetometry, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetry, scanning electron microscopy, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller and Barrett–Joyner–Halenda methods, nitrogen adsorption–desorption measurements, Zeta potential, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The Michaelis constant values of free and immobilized HRP were determined to be 4.5 and 5 mM for hydrogen peroxide and 12.5 and 10 mM for guaiacol, respectively. Moreover, the maximum values of free and immobilized HRP were 2.4 and 2 U for H2O2, respectively, and 1.25 U for guaiacol. The immobilized enzyme was thermally stable up to 60°C, whereas the free peroxidase was stable only up to 40°C. In the catalytic experiment, the immobilized HRP exhibited superior catalytic activity compared with that of free HRP for the oxidative decolorization and removal of acid black-HC dye. The influence of experimental parameters such as the catalyst dosage, pH, H2O2 concentration, and temperature on the removal efficiency was investigated. The reaction followed second-order kinetics, and the thermodynamic activation parameters were determined.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Please contact the authors for data requests.
References
Ahmad R, Khare SK (2018) Immobilization of Aspergillus niger cellulase on multiwall carbon nanotubes for cellulose hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 252:72–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.12.082
Ali M, Husain Q, Sultana S, Ahmad M (2018) Immobilization of peroxidase on polypyrrole-cellulose-graphene oxide nanocomposite via non-covalent interactions for the degradation of Reactive Blue 4 dye. Chemosphere 202:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.073
Araghi SH, Entezari MH (2015) Amino-functionalized silica magnetite nanoparticles for the simultaneous removal of pollutants from aqueous solution. Appl Surf Sci 333:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.01.211
Bilal M, Iqbal HMN (2021) Armoring bio-catalysis via structural and functional coordination between nanostructured materials and lipases for tailored applications. Int J Biol Macromol 166:818–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.239
Bilal M, Iqbal HM, Shah SZH, Hu H, Wang W, Zhang X (2016) Horseradish peroxidase-assisted approach to decolorize and detoxify dye pollutants in a packed bed bioreactor. J Environ Manag 183:836–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.09.040
Bilal M, Asgher M, Parra-Saldivar R, Hu H, Wang W, Zhang X, Iqbal HM (2017a) Immobilized ligninolytic enzymes: an innovative and environmental responsive technology to tackle dye-based industrial pollutants–a review. Sci Total Environ 576:646–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.137
Bilal M, Iqbal HM, Hu H, Wang W, Zhang X (2017b) Enhanced bio-catalytic performance and dye degradation potential of chitosan-encapsulated horseradish peroxidase in a packed bed reactor system. Sci Total Environ 575:1352–1360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.215
Boudrant J, Woodley JM, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2020) Parameters necessary to define an immobilized enzyme preparation. Process Biochem 90:66–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2019.11.026
Cipolatti EP, Valerio A, Henriques RO, Moritz DE, Ninow JL, Freire DM, Manoel EA, Fernandez-Lafuente R, de Oliveira D (2016) Nanomaterials for biocatalyst immobilization–state of the art and future trends. RSC Adv 6(106):104675–104692. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra22047a
Diao M, Ayékoué BN, Dibala D, Dabonné S, Dicko MH (2014) Purification and characterization of sweet potato (Ipomoea Batatas) peroxidase. J Anim Plant Sci 22:3419–3432
Ding S, Cargill AA, Medintz IL, Claussen JC (2015) Increasing the activity of immobilized enzymes with nanoparticle conjugation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 34:242–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2015.04.005
Donadelli JA, Einschlag FSG, Laurenti E, Magnacca G, Carlos L (2018) Soybean peroxidase immobilized onto silica-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: effect of silica layer on the enzymatic activity. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 161:654–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.11.043
Donohue MD, Aranovich G (1999) A new classification of isotherms for Gibbs adsorption of gases on solids. Fluid Phase Equilib 158:557–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3812(99)00074-6
Dulman V, Cucu-Man SM, Olariu RI, Buhaceanu R, Dumitraş M, Bunia I (2012) A new heterogeneous catalytic system for decolorization and mineralization of Orange G acid dye based on hydrogen peroxide and a macroporous chelating polymer. Dyes Pigments 95:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2012.03.024
El-Alaily T, El-Nimr M, Saafan S, Kamel M, Meaz T, Assar S (2015) Construction and calibration of a low cost and fully automated vibrating sample magnetometer. J Magn Magn Mater 386:25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.03.051
Enache DF, Vasile E, Simonescu CM, Răzvan A, Nicolescu A, Nechifor AC, Oprea O, Pătescu RE, Onose C, Dumitru F (2017) Cysteine-functionalized silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles as potential nanoadsorbents. J Solid State Chem 253:318–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2017.06.013
Garcia-Galan C, Berenguer-Murcia Á, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Rodrigues RC (2011) Potential of different enzyme immobilization strategies to improve enzyme performance. Adv Synth Catal 353(16):2885–2904. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201100534
Gemeay AH, Keshta BE, El-Sharkawy RG, Zaki AB (2019) Chemical insight into the adsorption of reactive wool dyes onto amine-functionalized magnetite/silica core-shell from industrial wastewaters. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:32341–32358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06530-y
Guzik U, Hupert-Kocurek K, Wojcieszyńska D (2014) Immobilization as a strategy for improving enzyme properties-application to oxidoreductases. Molecules 19:8995–9018. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19078995
He F (2011) Bradford protein assay. Bio 101:e45. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.45
Hoffmann C, Grundtvig IP, Thrane J, Garg N, Gernaey KV, Pinelo M, Woodley JM, Krühne U, Daugaard AE (2018) Experimental and computational evaluation of area selectively immobilized horseradish peroxidase in a microfluidic device. Chem Eng J 332:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.050
Hosseinifar A, Shariaty-Niassar M, Seyyed Ebrahimi S, Moshref-Javadi M (2017) Synthesis, characterization, and application of partially blocked amine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Langmuir 33:14728–14737. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b02093
Iyer PV, Ananthanarayan L (2008) Enzyme stability and stabilization—aqueous and non-aqueous environment. Process Biochem 43(10):1019–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2008.06.004
Jesionowski T, Zdarta J, Krajewska B (2014) Enzyme immobilization by adsorption: a review. Adsorption. 20(5-6):801–821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-014-9623-y
Jun LY, Mubarak NM, Yon LS, Bing CH, Khalid M, Jagadish P, Abdullah EC (2019) Immobilization of peroxidase on functionalized MWCNTs-buckypaper/polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposite membrane. Sci Rep 9(1):2215. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39621-4
Katchalski-Katzir E (1993) Immobilized enzymes--learning from past successes and failures. Trends Biotechnol 11:471–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7799(93)90080-S
Kulshrestha Y, Husain Q (2006) Bioaffinity-based an inexpensive and high yield procedure for the immobilization of turnip (Brassica rapa) peroxidase. Biomol Eng 23:291–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioeng.2006.07.004
Kumar V, Misra N, Goel NK, Thakar R, Gupta J, Varshney L (2016) A horseradish peroxidase immobilized radiation grafted polymer matrix: a biocatalytic system for dye waste water treatment. RSC Adv 6:2974–2981. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA20513A
Ladole MR, Muley AB, Patil ID, Talib M, Parate VR (2014) Immobilization of tropizyme-P on amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for fruit juice clarification. J Biochem Tech 5:838–845
Li ZL, Cheng L, Zhang LW, Liu W, Ma WQ, Liu L (2017) Preparation of a novel multi-walled-carbon-nanotube/cordierite composite support and its immobilization effect on horseradish peroxidase. Process Saf Environ Prot 107:463–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.02.021
Lineweaver H, Burk D (1934) The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J Am Chem Soc 56:658–666. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01318a036
Liu Y, Li Y, Li X-M, He T (2013) Kinetics of (3-aminopropyl) triethoxylsilane (APTES) silanization of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 29:15275–15282. https://doi.org/10.1021/la403269u
López-Serrano P, Cao L, Van Rantwijk F, Sheldon RA (2002) Cross-linked enzyme aggregates with enhanced activity: application to lipases. Biotechnol Lett 24(16):1379–1383
Lyddiatt A (2002) Process chromatography: current constraints and future options for the adsorptive recovery of bioproducts. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13(2):95–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0958-1669(02)00293-8
Ma M, Zhang Y, Yu W, Shen H-y, Zhang H-q GN (2003) Preparation and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles coated by amino silane. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 212:219–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(02)00305-9
Mahdavi M, Ahmad MB, Haron MJ, Namvar F, Nadi B, Rahman MZA, Amin J (2013) Synthesis, surface modification and characterisation of biocompatible magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Molecules 18:7533–7548. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077533
Mateo C, Palomo JM, Fernandez-Lorente G, Guisan JM, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2007) Improvement of enzyme activity, stability and selectivity via immobilization techniques. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 40(6):1451–1463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2007.01.018
Mielgo I, Palma C, Guisan J, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Moreira M, Feijoo G, Lema J (2003) Covalent immobilisation of manganese peroxidases (MnP) from Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Bjerkandera sp. BOS55. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 32:769–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(03)00066-8
Min K, Yoo YJ (2014) Recent progress in nanobiocatalysis for enzyme immobilization and its application. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 19:553–567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-014-0173-7
Mohamed SA, Aly A, Mohamed TM, Salah HA (2008) Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on nonwoven polyester fabric coated with chitosan. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 144:169–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-8026-x
Mohamed TM, El-Souod SMA, Ali EM, El-Badry MO, El-Keiy MM, Aly AS (2014) Immobilization and characterization of inulinase from Ulocladium atrum on nonwoven fabrics. J Biosci 39:785–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-014-9477-1
Mutneja R, Singh R, Kaur V, Wagler J, Fels S, Kroke E (2016) Schiff base tailed silatranes for the fabrication of functionalized silica based magnetic nano-cores possessing active sites for the adsorption of copper ions. New J Chem 40:1640–1648. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ02287H
Namdeo M (2017) Magnetite nanoparticles as effective adsorbent for water purification: a review. Adv Recycling Waste Manag 2:126–129. https://doi.org/10.4172/2475-7675.1000135
Nanayakkara S, Zhao Z, Patti AF, He L, Saito K (2014) Immobilized horseradish peroxidase (I-HRP) as biocatalyst for oxidative polymerization of 2, 6-dimethylphenol. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:1947–1950. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc500392k
Pandey VP, Awasthi M, Singh S, Tiwari S, Dwivedi UN (2017) A comprehensive review on function and application of plant peroxidases. Biochem Anal Biochem 6:308. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-1009.1000308
Pasternack RM, Rivillon Amy S, Chabal YJ (2008) Attachment of 3-(aminopropyl) triethoxysilane on silicon oxide surfaces: dependence on solution temperature. Langmuir 24:12963–12971. https://doi.org/10.1021/la8024827
Pereira M, Oliveira L, Murad E (2012) Iron oxide catalysts: Fenton and Fentonlike reactions–a review. Clay Miner 47:285–302. https://doi.org/10.1180/claymin.2012.047.3.01
Petcharoen K, Sirivat A (2012) Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mater Sci Eng B 177:421–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2012.01.003
Phan NT, Jones CW (2006) Highly accessible catalytic sites on recyclable organosilane-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles: an alternative to functionalized porous silica catalysts. J Mol Catal 253:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2006.03.019
Prasad C, Yuvaraja G, Venkateswarlu P (2017) Biogenic synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using Pisum sativum peels extract and its effect on magnetic and Methyl orange dye degradation studies. J Magn Magn Mater 424:376–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.10.084
Ramalingam B, Parandhaman T, Choudhary P, Das SK (2018) Biomaterial functionalized graphene-magnetite nanocomposite: a novel approach for simultaneous removal of anionic dyes and heavy-metal ions. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:6328–6341. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00139
Rudra S, Shivhare U, Basu S, Sarkar B (2008) Thermal inactivation kinetics of peroxidase in coriander leaves. Food Bioprocess Technol 1:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-007-0013-2
Sahoo JK, Paikra SK, Mishra M, Sahoo H (2019) Amine functionalized magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, antibacterial activity and rapid removal of Congo red dye. J Mol Liq 282:428–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.03.033
Sun H, Jin X, Long N, Zhang R (2017) Improved biodegradation of synthetic azo dye by horseradish peroxidase cross-linked on nano-composite support. Int J Biol Macromol 95:1049–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.093
Tang T, Fan H, Ai S, Han R, Qiu Y (2011) Hemoglobin (Hb) immobilized on amino-modified magnetic nanoparticles for the catalytic removal of bisphenol A. Chemosphere 83:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.075
Tomotani EJ, Vitolo M (2006) Method for immobilizing invertase by adsorption on Dowex® anionic exchange resin. Braz J Pharm Sci 42:245–249. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-93322006000200009
Tonami H, Uyama H, Nagahata R, Kobayashi S (2004) Guaiacol oxidation products in the enzyme-activity assay reaction by horseradish peroxidase catalysis. Chem Lett 33:796–797. https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.2004.796
Tong XD, Dong XY, Sun Y (2002) Lysozyme adsorption and purification by expanded bed chromatography with a small-sized dense adsorbent. Biochem Eng J 12(2):117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-703X(02)00063-3
Tupper J, Stratford M, Hill S, Tozer G, Dachs G (2010) In vivo characterization of horseradish peroxidase with indole-3-acetic acid and 5-bromoindole-3-acetic acid for gene therapy of cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 17:420–428. https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2009.86
Venkateswarlu S, Rao YS, Balaji T, Prathima B, Jyothi N (2013) Biogenic synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using plantain peel extract. Mater Lett 100:241–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.03.018
Vineh MB, Saboury AA, Poostchi AA, Mamani L (2018a) Physical adsorption of horseradish peroxidase on reduced graphene oxide nanosheets functionalized by amine: a good system for biodegradation of high phenol concentration in wastewater. Int J Environ Res 12:45–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-018-0067-1
Vineh MB, Saboury AA, Poostchi AA, Rashidi AM, Parivar K (2018b) Stability and activity improvement of horseradish peroxidase by covalent immobilization on functionalized reduced graphene oxide and biodegradation of high phenol concentration. Int J Biol Macromol 106:1314–1322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.133
Williams A, Frasca V (2001) Ion-exchange chromatography. Curr Protoc Protein Sci. Chapter 8:Unit8.2 15. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471140864.ps0802s15
Xu Q, Wang M (2010) Effect of electric field on horseradish peroxidase activity and its structure. In: 2010 3rd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics. IEEE, New York, pp 1307–1309. https://doi.org/10.1109/BMEI.2010.5639251
Yang Y, Zhao M, Yao P, Huang Y, Dai Z, Yuan H, Ni C (2018) Comparative studies on enzyme activity of immobilized horseradish peroxidase in silica nanomaterials with three different shapes and methoxychlor degradation of vesicle-like mesoporous SiO2 as carrier. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18:2971–2978. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.14300
Zhang Y, Wu H, Huang X, Zhang J, Guo S (2011) Effect of substrate (ZnO) morphology on enzyme immobilization and its catalytic activity. Nanoscale Res Lett 6:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-6-450
Zhu H, Hu Y, Jiang G, Shen G (2011) Peroxidase-like activity of aminopropyltriethoxysilane-modified iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles and its application to clenbuterol detection. Eur Food Res Technol 233:881–887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-011-1582-x
Funding
This research project is funded by the Research Fund—Tanta University (TU- 03-16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BK: Methodology, Writing—Original draft preparation. AG: Conceptualization, Supervision, Investigation. AK: Formal analysis, Reviewing, and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santiago V. Luis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 22 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keshta, B.E., Gemeay, A.H. & Khamis, A.A. Impacts of horseradish peroxidase immobilization onto functionalized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a biocatalyst for dye degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 6633–6645 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16119-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16119-z