Abstract
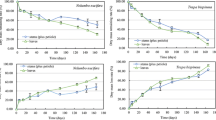
A sediment-water mesocosm experiment was set up to identify the effects of different debris biomass P. crispus decomposition on water body physicochemical properties and greenhouse gas emissions in Dongping Lake, a typical shallow macrophytic lake in the north of China. The results indicated that the decomposition of high biomass (BL-2) of P. crispus could significantly affect the physicochemical properties of water bodies, especially within the first 47 days. During the experiment, DO and water pH in BL-2 were significantly lower, while NH3-N, NO2--N, DOC, and DRP in surface water and OM in sediment were significantly higher than those in the low biomass treatment (BL-1) and zero control (CK). Moreover, the DOC in BL-1 were significantly higher than CK. The decomposition of P. crispus significantly affected the emission fluxes of CH4 and CO2, but had no significant impact on N2O emission. CH4 and CO2 fluxes were generally more significantly correlated with the properties of surface water in BL-2 than in BL-1. High debris biomass decomposition significantly promoted the emission of CH4 enhancing the source effect of water body, while the decomposition of both low and high biomass notably promoted the emission of CO2 converting the water bodies from sink to source of CO2. There were significant differences in global warming potential among the three groups in which CH4 contributed most. Considering the negative impact on water environment and elevated carbon emission during the decomposition of P. crispus, it was suggested to strengthen the management of P. crispus in Dongping Lake.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data supporting the results reported in the article can be found in figures and tables in this paper.
References
Abril M, Muñoz I, Menéndez M (2016) Heterogeneity in leaf litter decomposition in a temporary Mediterranean stream during flow fragmentation. Sci Total Environ 553:330–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.082
Badiou P, Page B, Ross L (2019) A comparison of water quality and greenhouse gas emissions in constructed wetlands and conventional retention basins with and without submerged macrophyte management for storm water regulation. Ecol Eng 127:292–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2018.11.028
Bouchard F, Laurion I, Preskienis V, Fortier D, Xu XM, Whiticar MJ (2015) Modern to millennium-old greenhouse gases emitted from ponds and lakes of the Eastern Canadian Arctic (Bylot Island, Nunavut). Biogeosciences 12(23):7279–7298. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-12-7279-2015
Cao X, Wan L, Xiao J, Chen X, Zhou Y, Wang Z, Song C (2018) Environmental effects by introducing Potamogeton crispus to recover a eutrophic Lake. Sci Total Environ 621:360–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.267
Carvalho P, Thomaz SM, Bini LM (2005) Effects of temperature on decomposition of a potential nuisance species: the submerged aquatic macrophyte Egria najas planchon (hydrocharitaceae). Braz J Biol 65:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1519-69842005000100008
Chatelain M, Guizien K (2010) Modelling coupled turbulence-dissolved oxygen dynamics near the sediment–water interface under wind waves and sea swell. Water Res 44(5):1361–1372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.11.010
Chen QF, Ma JJ, Liu JH, Zhao CS, Liu W (2013) Characteristics of greenhouse gas emission in the Yellow River Delta wetland. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 85:646–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.04.009
Corstanje R, Reddy KR, Portier KM (2006) Typha latifolia and Cladium jamaicense litter decay in response to exogenous nutrient enrichment. Aquat Bot 84(1):70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2005.07.013
Deng HG, Zhang J, Chen S, Yang LW, Wang DQ, Yu SY (2016) Metal release/accumulation during the decomposition of Potamogeton crispus in a shallow macrophytic lake. J Environ Sci 42(4):71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.07.004
Deng HG, Zhang J, Wu JJ, Yao X, Yang IW (2020a) Biological denitrification in a macrophytic lake: implications for macrophytes-dominated lake management in the north of China. Environ. Sci Pollut Res 27:42460–42471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10230-3
Deng HG, Liu T, Lu CJ, Zhang J, Cao QM (2020b) The effect of Potamogeton crispus decomposition on the dissolved concentrations and fluxes of greenhouse gas in Dongping Lake. J Lake Sci 32(5):1484–1495. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.18307/2020.0520
Deng HG, Zhang J, Liu T, Zhang J (2020c) Short-term effects of exogenous nitrate on N2O and CH4 emission from Greenbelt in Urban Riparian Zone. J Liaocheng Uni (Nat Sci Edi) 33(2):97–104. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.19728/j.issn1672-6634.2020.02.014
Gudasz C, Sobek S, Bastviken D, Koehler B, Tranvik LJ (2015) Temperature sensitivity of organic carbon mineralization in contrasting lake sediments. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 120:1215–1225. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JG002928
IPCC. Climate change (2013) The physical science basis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 2013
Kwak JH, Chang SX, Naeth MA, Naeth MA, Schaaf W (2016) Coarse woody debris effects on greenhouse gas emission rates depend on cover soil type in oil sands reclamation. Appl Soil Ecol 100:124–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2015.12.006
Liu S, Zhu Y, Meng W, He ZQ, Feng WY, Zhang C, Giesy JP (2016) Characteristics and degradation of carbon and phosphorus from aquatic macrophytes in lakes: insights from solid-state 13C NMR and solution 31P NMR spectroscopy. Sci Total Environ 543:746–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.080
Luo P, Tong X, Liu F, Huang M, Wu J (2020) Nutrients release and greenhouse gas emission during decomposition of Myriophyllum aquaticum in a sediment-water system. Environ Pollut 260:114015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114015
Lyu Z, Shao N, Akinyemi T, Whitman WB (2018) Methanogenesis. Curr Biol 28:R727–R732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.05.021
Maltais-Landry G, Maranger R, Brisson J (2009) Effect of artificial aeration and macrophyte species on nitrogen cycling and gas flux in constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 35:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2008.03.003
Meyer RL, Allen DE, Schmidt S (2008) Nitrification and denitrification as sources of sediment nitrous oxide production: a microsensor approach. Mar Chem 110(1/2):68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2008.02.004
Nikonova LG, Golovatskaya EA, Terechshenko NN (2018) Decomposition rate of peat-forming plants in the oligotrophic peatland at the first stages of destruction. Iop Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 138(1):012013. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/138/1/012013
Podgrajsek E, Sahlée E, Bastviken D, Holst J, Lindroth A, Tranvik L, Rutgersson A (2014) Comparison of floating chamber and eddy covariance measurements of Lake Greenhouse gas fluxes. Biogeosciences 11(15):4225–4233. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-11-4225-2014
Praetzel LSE, Plenter N, Schilling S, Schmiedeskamp M, Broll G, Knorr KH (2020) Organic matter and sediment properties determine in-lake variability of sediment CO2 and CH4 production and emissions of a small and shallow lake. Biogeosciences 17:5057–5078. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-17-5057-2020
Qu J, Fan M (2010) The current state of water quality and technology development for water pollution control in China. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 40(6):519–560. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380802451953
Ribaudo C, Bartoli M, Racchetti E, Longhi D, Viaroli P (2011) Seasonal fluxes of O2, DIC and CH4 in sediments with Vallisneria spiralis: indications for radial oxygen loss. Aquat Bot 94(3):134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2011.01.003
Sangsub C, Hee-Myung C, Sang-Hoon L, Jae-Kuk S, Kelly JJ (2017) Effect of elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration on growth and leaf litter decomposition of Quercus acutissima and Fraxinus rhynchophylla. PLoS One 12:e0171197. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171197
Tian CC, Wu XQ, Feng SS, Cai QJ, Yang TT, Xiao BD (2018) Relationship between the distribution of submerged plants and environment factors in Dongping Lake. Environ Sci Technol 11:15–20 (In Chinese). CNKI:SUN:FJKS.0.2018-11-003
Wang B, Ye C, Li C, Kong XL (2013) The process of nutrition release during decomposition of Hydrilla verticillata in different dissolved oxygen conditions. Chin J Appl Environ Bio 19(3):484–488. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1145.2013.00484
Wang DQ, Tan YJ, Yu ZJ, Li YJ, Chang SQ, Deng HG, Hu BB, Chen ZL (2015) Nitrous oxide production in river sediment of highly urbanized area and the effects of water quality. Wetlands 35(6):1213–1223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-015-0708-5
Wang L, Liu Q, Hu CW, Liang RJ, Qiu JC (2018) Phosphorus release during decomposition of the submerged macrophyte Potamogeton crispus. Limnology 19:355–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-018-0538-2
Welfens PJ, Perret JK, Erdem D (2010) Global economic sustainability indicator: analysis and policy options for the Copenhagen process. Int Econ & Econ Policy 7(2-3):153–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10368-010-0165-9
Wu SQ, He SB, Huang JC, Hu J, Zhou W, Gao L (2017a) Decomposition of emergent aquatic plant (Cattail) litter under different conditions and the influence on water quality. Water Air Soil Pollut 228(70):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3257-0
Wu SQ, He SB, Zhou WL, Huang J, Gao L, Zhang X (2017b) Decomposition characteristics of three different kinds of aquatic macrophytes and their potential application as carbon resource in constructed wetland. Environ Pollut 231:1122–1133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.049
Wu X, Wang W, Xie X, Wang G (2018) Net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity as affected by different water management strategies in Chinese double rice-cropping systems. Sci Rep 8(1):779. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-19110-2
Yang SS, Chen IC, Liu CP, Liu LY, Chang CH (2015) Carbon dioxide and methane emissions from Tanswei River in northern Taiwan. Atmos Pollut Res 6(1):52–61. https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2015.007
Yang L, Chen S, Zhang J, Yu S, Deng HG (2017) Environmental factors controlling the spatial distribution of subfossil Chironomidae in surface sediments of Lake Dongping, a warm temperate lake in North China. Environ Earth Sci 76(15):524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6858-4
Yu SP, Sun GY, Dou SZ, Ma YM, Ge HM (2005) The declining of hydrophyte of Dongping Lake and the influence of the south-to-north water transfer project on it. China Environ Sci 25(2):200–204. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.1360/aps040074
Yu ZJ, Li YJ, Deng HG, Wang DQ, Xu SY (2012) Effect of Scirpus mariqueter on nitrous oxide emissions from a subtropical monsoon estuarine wetland. J Geophys Res 117:G02017. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JG001850
Yu QZ, Mickler RA, Liu Y, Sun LG, Zhou L, Zhang BH, Deng HG, Liang LL (2020) Remote sensing of Potamogeton crispus L. in Dongping Lake in the North China Plain based on vegetation phenology. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 48:563–573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01103-w
Zhang J, Deng HG, Wu AQ, Chen SY, Wang DQ (2013) Decomposition of Potamogeton crispus and its effect on the aquatic environment of Dongping Lake. Acta Scien Circum 33(9):2590–2596 (in Chinese). CNKI:SUN:HJXX.0.2013-09-034
Zhang L, Zhang S, Lv X, Zheng Q, Zhang Z, Yan L (2018a) Dissolved organic matter release in overlying water and bacterial community shifts in biofilm during the decomposition of Myriophyllum verticillatum. Sci Total Environ 633:929–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.275
Zhang W, Jin X, Meng X, Tang W, Shan B (2018b) Phosphorus transformations at the sediment-water interface in shallow freshwater ecosystems caused by decomposition of plant debris. Chemosphere 201:328–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.006
Zhang K, Liu YH, Chen Q, Luo HB, Zhu ZY, Chen W, Chen J, Mo Y (2018c) Effect of submerged plant species on CH4 flux and methanogenic community dynamics in a full-scale constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 115:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2018.02.025
Zhang W, Gu P, Zhu W, Jin C, Zheng Z (2020) Effects of cyanobacterial accumulation and decomposition on the microenvironment in water and sediment. J Soils Sediments 20:2510–2525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02539-5
Zhou Y, Zhou X, Han R, Xu X, Wang G, Liu X, Bi F, Feng D (2017) Reproduction capacity of, Potamogeton crispus, fragments and its role in water purification and algae inhibition in eutrophic lakes. Sci Total Environ 580:1421–1428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.108
Zhou XH, Wang MY, Wen CZ, Liu D (2019a) Nitrogen release and its influence on anammox bacteria during the decay of Potamogeton crispus with different values of initial debris biomass. Sci Total Environ 650:604–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.358
Zhou Y, Zhou L, Zhang Y, Souza JG, Davidson TA (2019b) Autochthonous dissolved organic matter potentially fuels methane ebullition from experimental lakes. Water Res 166:115048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115048
Zhu L, Shi W, Van DB, Kong L, Qin B (2020) Algal accumulation decreases sediment nitrogen removal by uncoupling nitrification-denitrification in shallow eutrophic lakes. Environ Sci Technol 54:6194–6201. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b05549
Funding
This work was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41401563, 41807430, 41977322) and the Liaocheng University Research Foundation (Grant No. 318011909, 318012019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huanguang Deng: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing-Original Draft, Supervision, Funding acquisition
Ju Zhang: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing-Review & Editing, Funding acquisition
Jinjia Wu: Investigation, Writing-Review & Editing
Liwei Yang: Investigation, Funding acquisition
Yinghao Zhang: Formal analysis, Writing-Review & Editing
Xin Yao: Funding acquisition, Writing-Review & Editing
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 26 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, ., Zhang, J., Wu, J. et al. Physicochemical properties and greenhouse gas emissions of water body during the decomposition of Potamogeton crispus with different values of initial debris biomass. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 5505–5516 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15823-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15823-0