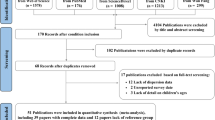
Abstract
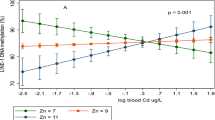
Excess heavy metals increase the risk of various diseases. Electronic waste (e-waste) is a potential route to heavy metal exposure, and Taizhou is a large e-waste dismantling area in China. In this study, we acquire blood samples from residents living near an e-waste recycling area (exposed group) and other residents in a selected reference area (reference group) for a comparative study in Taizhou in December 2017. Seven heavy metals, including cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), cadmium (Cd), tin (Sn), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), and lead (Pb), are quantitatively determined in all blood samples. It is discovered that the levels of Co, Ni, Sn, and Pb in the exposed group are higher than those in the reference group. Additionally, two crucial biomarkers of coronary heart disease (CHD), i.e., troponin (Tn) and myeloperoxidase (MPO), and two biomarkers of oxidative stress, i.e., malondialdehyde (MDA) and 8-isoprostane (8-I), are measured. We discovered that the levels of these indicators in the exposed group are significantly higher than those in the reference group. Meanwhile, both the Spearman correlation and multiple linear regression analysis show that Ni is positively correlated with Tn, MPO, 8-I, and MDA. Hence, we hypothesize that exposure to e-waste increases the risk of CHD and that Ni is an important contributor to the initiation of the disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Available on request.
References
Abraham DM, Marchuk DA (2014) Inhibition of the cardiomyocyte-specific troponin i-interacting kinase limits oxidative stress, injury, and adverse remodeling due to ischemic heart disease. Circ Res 114:938–940
Ali S, Awan Z, Mumtaz S, Shakir HA, Ahmad F, Ulhaq M, Tahir HM, Awan MS, Sharif S, Irfan M, Khan MA (2020) Cardiac toxicity of heavy metals (cadmium and mercury) and pharmacological intervention by vitamin c in rabbits. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:29266–29279
Banday AA, Muhammad AB, Fazili FR, Lokhandwala M (2007) Mechanisms of oxidative stress-induced increase in salt sensitivity and development of hypertension in Sprague-Dawley rats. Hypertension 49:664–671
Chao SH, Bu CH, Cheung WY (1990) Activation of troponin-c by cd-2+ and pb-2+. Arch Toxicol 64:490–496
Cuevas AK, Liberda EN, Gillespie PA, Allina J, Chen LC (2010) Inhaled nickel nanoparticles alter vascular reactivity in c57bl/6 mice. Inhal Toxicol 22:100–106
Ebrahimi M, Khalili N, Razi S, Keshavarz-Fathi M, Khalili N, Rezaei N (2020) Effects of lead and cadmium on the immune system and cancer progression. J Environ Health Sci Eng 18:335–343
Farkhondeh T, Afshari R, Mehrpour O, Samarghandian S (2020) Mercury and atherosclerosis: cell biology, pathophysiology, and epidemiological studies. Biol Trace Elem Res 196:27–36
Gorudko IV, Kostevich VA, Sokolov AV, Shamova EV, Buko IV, Konstantinova EE, Vasiliev VB, Cherenkevich SN, Panasenko OM (2012) Functional activity of neutrophils in diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease: role of myeloperoxidase in the development of oxidative stress. Bull Exp Biol Med 154:23–26
Grotto D, Valentini J, Fillion M, Passos CJS, Garcia SC, Mergler D, Barbosa F Jr (2010) Mercury exposure and oxidative stress in communities of the Brazilian amazon. Sci Total Environ 408:806–811
Guo C, Wei YJ, Yan LL, Li ZG, Qian Y, Liu HJ, Li Z, Li X, Wang Z, Wang J (2020) Rare earth elements exposure and the alteration of the hormones in the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (hpt) axis of the residents in an e-waste site: a cross-sectional study. Chemosphere 252:126488
Haga Y, Clyne N, Hatori N, HoffmanBang C, Pehrsson SK, Ryden L (1996) Impaired myocardial function following chronic cobalt exposure in an isolated rat heart model. Trace Elem Electrolytes 13:69–74
He Y, Liu Q, Wang J, Wang DW, Ding H, Wang W (2020) Prognostic value of elevated cardiac troponin I in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Clin Cardiol 43:338–345
Houston MC (2011) Role of mercury toxicity in hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and stroke. J Clin Hypertens 13:621–627
Ito F, Sono Y, Ito T (2019) Measurement and clinical significance of lipid peroxidation as a biomarker of oxidative stress: Oxidative stress in diabetes, atherosclerosis, and chronic inflammation. Antioxidants 8:72
Kalahasthi RB, Rao RHR, Murthy RBK (2006) Plasma lipid peroxidation and erythrocyte antioxidants status in workers exposed to nickel. Biomarkers 11:241–249
Kukongviriyapan U, Pannangpetch P, Kukongviriyapan V, Donpunha W, Sompamit K, Surawattanawan P (2014) Curcumin protects against cadmium-induced vascular dysfunction, hypertension and tissue cadmium accumulation in mice. Nutrients 6:1194–1208
Kurniati NF, Angelia T, Artarini AA, Nurfatwa M (2018) Myocardial infarction elevates inflammation and contributes to the formation of atheroma plaques in the aorta of hypercholesterolaemic rats. Makara J Health Res 22:40–45
Larsson SC, Wolk A (2016) Urinary cadmium and mortality from all causes, cancer and cardiovascular disease in the general population: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int J Epidemiol 45:782–791
Li Z, Guo C, Li X, Wang Z, Wu J, Qian Y, Wei Y (2020) Associations between metal exposure and global DNA methylation in potentially affected people in e-waste recycling sites in Taizhou City, China. Sci Total Environ 711:135100
Liao JW, Huang W, Liu G (2017) Animal models of coronary heart disease. J Biomed Res 31:3–10
Liu CG, Xie GM, Huang WF, Yang YC, Li P, Tu ZG (2012) Elevated serum myeloperoxidase activities are significantly associated with the prevalence of ACS and high LDL-C levels in CHD patients. J Atheroscler Thromb 19:435–443
Lou SY, Zhong LK, Yang XC, Xue T, Gai RH, Zhu DF, Zhao Y, Yang B, Ying M, He Q (2013) Efficacy of all-trans retinoid acid in preventing nickel induced cardiotoxicity in myocardial cells of rats. Food Chem Toxicol 51:251–258
Love D, Barrett T, Hawkins C (2017) Role of the myeloperoxidase oxidant hypothiocyanous acid (HOSCN) in the adaption of cells to oxidative stress during inflammation. Free Radic Biol Med 108:S29–S30
Mair J, Thomekromer B, Wagner I, Lechleitner P, Dienstl F, Puschendorf B et al (1994) Concentration-time courses of troponin and myosin subunits after acute myocardial-infarction. Coron Artery Dis 5:865–872
Myong JP, Kim HR, Jang TW, Lee HE, Koo JW (2014) Association between blood cadmium levels and 10-year coronary heart disease risk in the general Korean population: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008-2010. PLoS One 9:e111909
Owumi SE, Olayiwola YO, Alao GE, Gbadegesin MA, Odunola OA (2020) Cadmium and nickel co-exposure exacerbates genotoxicity and not oxido-inflammatory stress in liver and kidney of rats: protective role of omega-3 fatty acid. Environ Toxicol 35:231–241
Patrono C, Falco A, Davi G (2005) Isoprostane formation and inhibition in atherothrombosis. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:198–203
Ra K, Kim ES, Kim KT, Kim JK, Lee JM, Choi JY (2013) Assessment of heavy metal contamination and its ecological risk in the surface sediments along the coast of Korea. J Coast Res 65:105–110
Reisgen M, Thomas K, Beilmann V, Markert A, Gerhards B, Krichel T, et al (2020). Increased neutrophilgranulocyte and myeloperoxidase (mpo) levels indicate acute inflammation due to the exposure of zinc- andcopper-containing welding fumes. Journal of occupational and environmental medicine 62:618–627
Shah KS, Maisel AS, Fonarow GC (2018) Troponin in heart failure. Heart Fail Clin 14:57
Valera B, Muckle G, Poirier P, Jacobson SW, Jacobson JL, Dewailly E (2012) Cardiac autonomic activity and blood pressure among Inuit children exposed to mercury. Neurotoxicology 33:1067–1074
Vassalle C, Bianchi S, Bianchi F, Landi P, Battaglia D, Carpeggiani C (2012) Oxidative stress as a predictor of cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease patients. Clin Chem Lab Med 50:1463–1468
Vaziri ND (2008) Mechanisms of lead-induced hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Am J Phys Heart Circ Phys 295:H454–H465
Wirtz PH, von Kanel R (2017) Psychological stress, inflammation, and coronary heart disease. Curr Cardiol Rep 19:111
Wu SW, Yang D, Wei HY, Wang B, Huang J, Li HY, Shima M, Deng F, Guo X (2015) Association of chemical constituents and pollution sources of ambient fine particulate air pollution and biomarkers of oxidative stress associated with atherosclerosis: a panel study among young adults in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 135:347–353
Xiao LL, Zhou Y, Ma JX, Cao LM, Zhu CM, Li W, Wang D, Fan L, Ye Z, Chen W (2019) Roles of C-reactive protein on the association between urinary cadmium and type 2 diabetes. Environ Pollut 255:113341
Xu X, Liao W, Lin Y, Dai Y, Shi Z, Huo X (2018) Blood concentrations of lead, cadmium, mercury and their association with biomarkers of DNA oxidative damage in preschool children living in an e-waste recycling area. Environ Geochem Health 40:1481–1494
Yang X, He T, Han S, Zhang X, Sun Y, Xing Y et al (2019) The role of traditional Chinese medicine in the regulation of oxidative stress in treating coronary heart disease. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2019:3231424
Yu EA, Akormedi M, Asampong E, Meyer CG, Fobil JN (2017) Informal processing of electronic waste at Agbogbloshie, Ghana: workers’ knowledge about associated health hazards and alternative livelihoods. Glob Health Promot 24:90–98
Zhang YN, Yan FH, Jiang WH (2019) Relationship between self-management behaviors and health-related quality of life among Chinese patients with coronary heart disease: a cross-sectional study. Contemp Nurse 55:554–564
Zhang YQ, Jiang YF, Chen M, Zhang NN, Zhou YF (2020) Association between myeloperoxidase rs2333227 polymorphism and susceptibility to coronary heart disease. Arch Med Sci 16:1231–1238
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21477119).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wang and Xue is mainly responsible for the data analysis and drafts the manuscript. Li and Wei curated the study and oversaw the coordination. All authors were involved this study and read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of Peking University Health Science Center in Beijing, China.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All of the authors have reviewed and approved the manuscript for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Xue, K., Wang, Z. et al. Effects of e-waste exposure on biomarkers of coronary heart disease (CHD) and their associations with level of heavy metals in blood. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 49850–49857 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15656-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15656-x