Abstract
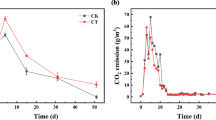
This study investigated the effectiveness of bio-augmenting aerobic cell culture to mitigate ammonia and hydrogen sulfide emission in sewage sludge composting amended with reed straw (with the weight ratio of 1:0.3–0.4). During the 20-day aerated lab-scale composting, adding 200-mL culture (56.80 NTU) reduced ammonia and hydrogen sulfide emissions by 38.00% and 54.32%, and conserved total nitrogen and sulfate by 39.42% and 70.75%, respectively. Organic matters degradation was quick started 1 day ahead. Comparing to the control, nitrate content increased 38.75% at the end of the compost. Bioaugmentation evened the distributions of bacterial communities in the thermophilic phase. The shift was mainly due to 22.97% of relative abundance of Proteobacteria depressed and 157.16% of Bacteroidetes increased, which were beneficial for nitrogen conservation and glycan breakdown, respectively. In summary, the results demonstrated that bioaugmentation addition could be an effective strategy for enhanced sludge composting.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becarelli S, Chicca I, Siracusa G, La China S, Gentini A, Lorenzi R, Munz G, Petroni G, Levin DB, Di Gregorio S (2019) Hydrocarbonoclastic Ascomycetes to enhance co-composting of total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) contaminated dredged sediments and lignocellulosic matrices. New Biotechnol 50:27–36
Belyaeva ON, Haynes RJ (2009) Chemical, microbial and physical properties of manufactured soils produced by co-composting municipal green waste with coal fly ash. Bioresour Technol 100(21):5203–5209
Bernal MP, Navarro AF, Roig A, Cegarra J, García D (1996) Carbon and nitrogen transformation during composting of sweet sorghum bagasse. Biol Fertil Soils 22:141–148
Borowski S, Matusiak K, Powalowski S, Pielech-Przybylska K, Makowski K, Nowak A, Rosowski M, Komorowski P, Gutarowska B (2017) A novel microbial-mineral preparation for the removal of offensive odors from poultry manure. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 119:299–308
Cai L, Chen T, Gao D, Yang J, Chen J, Zheng G, Du W (2010) Investigation on calorific value of sewage sludges in large and middle cities of China. China Water & Wastewater 15:106–108 (In Chinese)
Chan M, Selvam A, Wong JW (2016) Reducing nitrogen loss and salinity during “struvite” food waste composting by zeolite amendment. Bioresour Technol 200:838–844
Costa LAM, Costa MSSM, Damaceno FM, Chiarelotto M, Bofinger J, Gazzola W (2021) Bioaugmentation as a strategy to improve the compost quality in the composting process of agro-industrial wastes. Environ Technol Innov 22:101478
Dai X, Li X, Zhang D, Chen Y, Dai L (2016) Simultaneous enhancement of methane production and methane content in biogas from waste activated sludge and perennial ryegrass anaerobic co-digestion: the effects of pH and C/N ratio. Bioresour Technol 216:323–330
Doloman A, Mahajan A, Pererva Y, Flann NS, Miller CD (2020) A model for bioaugmented anaerobic granulation. Front Microbiol 11:1–12
Du J, Zhang Y, Qu M, Yin Y, Fan K, Hu B, Zhang H, Wei M, Ma C (2019) Effects of biochar on the microbial activity and community structure during sewage sludge composting. Bioresour Technol 272:171–179
Eichner CA, Erb RW, Timmis KN, Wagner-Döbler I (1999) Thermal gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of bioprotection from pollutant shocks in the activated sludge microbial community. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:102–109
Finkmann W, Altendorf K, Stackebrandt E, Lipski A (2000) Characterization of N2O-producing Xanthomonas-like isolates from biofilters as Stenotrophomonas nitritireducens sp. nov., Luteimonas mephitis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Pseudoxanthomonas broegbernensis gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:273–282
Grant CA, Mahli SS, Karamanos RE (2012) Sulfur management for rapeseed. Field Crop Res 128:119–128
He X, Bao W, Gu B, Leng L (2007) The characteristic of gross caloric values of higher plants in China. Ecol Environ 3:973–981 (In Chinese)
He P, Wei S, Shao L, Lü F (2018) Emission potential of volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) and ammonia from sludge compost with different bio-stability under various oxygen levels. Waste Manag 73:113–122
Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Kuypers M, Marchant H, Kartal B (2018) The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat Rev Microbiol 16(5):263–276
Lapébie P, Lombard V, Drula E, Terrapon N, Henrissat B (2019) Bacteroidetes use thousands of enzyme combinations to break down glycans. Nat Commun 10(2043):1–7
Li Y, Li W (2015) Nitrogen transformation and losses during composting of sewage sludge with acidified sawdust in a laboratory reactor. Waste Manag Res 33(2):139–145
Li W, Wu C, Wang K, Meng L, Lv L (2017) Nitrogen loss reduction by adding sucrose and beet pulp in sewage sludge composting. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 124:297–303
Liu D, Zhang R, Wu H, Xu D, Tang Z, Yu G, Xu Z, Shen Q (2011) Changes in biochemical and microbiological parameters during the period of rapid composting of daily manure with rice chaff. Bioresour Technol 102(19):9040–9049
McGenity TJ, Timmis KN, Fernandez BN (2017) Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology Protocols. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 105–115
Meng L, Li W, Zhang S, Wu W, Jiang W, Sha C (2016) Effect of different extra carbon sources on nitrogen loss control and the change of bacterial populations in sewage sludge composting. Ecol Eng 94:238–243
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (MEE) (2012) Soil-determination of water-soluble and acid-soluble sulfate - gravimetric method (HJ 635-2012). Chinese Environment Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China (MOHURD) (2005) Determination method for municipal sludge in wastewater treatment plant (CJ/T 221-2005). Standards Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Negi S, Mandpe A, Hussain A, Kumar S (2020) Collegial effect of maggots larvae and garbage enzyme in rapid composting of food waste with wheat straw or biomass waste. J Clean Prod 258:1–9
Paredes C, Bernal MP, Roig A, Cegarra J (2001) Effects of olive mill wastewater addition in composting of agro-industrial and urban wastes. Biodegradation 12:225–234
Poorsoleiman MS, Hosseini SA, Etminan A, Abtahi H, Koolivand A (2020) Effect of two-step bioaugmentation of an indigenous bacterial strain isolated from oily waste sludge on petroleum hydrocarbons biodegradation: scaling-up from a liquid mineral medium to a two-stage composting process. Environ Technol Innov 17:100558
Quan Y, Wu H, Yin Z, Fang Y, Yin C (2017) Effect of static magnetic field on trichloroethylene removal in a biotrickling filter. Bioresour Technol 239:7–16
Santos A, Bustamante MA, Moral R, Bernal MP (2016a) Carbon conservation strategy for the management of pig slurry by composting: initial study of the bulking agent influence. Mitig Adapt Strateg Glob Chang 21(7):1093–1105
Santos A, Bustamante MA, Tortosa G, Moral R, Bernal MP (2016b) Gaseous emissions and process development during composting of pig slurry: the influence of the proportion of cotton gin waste. J Clean Prod 112:81–90
Shannon CE (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 27:623–656
Shao X, Zheng J (2014) Soil organic carbon, black carbon, and enzyme activity under long term fertilization. J Integr Agric 13(3):517–524
Shou Z, Yuan H, Shen Y, Liang J, Zhu N, Gu L (2017) Mitigating inhibition of undissociated volatile fatty acids (VFAs) for enhanced sludge-rice bran composting with ferric nitrate amendment. Bioresour Technol 244:672–678
Shou Z, Zhu N, Yuan H, Dai X, Shen Y (2019) Buffering phosphate mitigates ammonia emission in sewage sludge composting: enhanced organics removal coupled with microbial ammonium assimilation. J Clean Prod 227:189–198
Stamper DM, Walch M, Jacobs RN (2003) Bacterial population changes in a membrane bioreactor for graywater treatment monitored by denaturing gradient gel electrophoretic analysis of 16S rRNA gene fragments. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(2):852–860
Thierry S, Macarie H, Iizuka T, Geißdörfer W, Assih EA, Spanevello M, Verhe F, Thomas P, Fudou R, Monroy O, Labat M, Ouattara AS (2004) Pseudoxanthomonas mexicana sp. nov. and Pseudoxanthomonas japonensis sp. nov., isolated from diverse environments, and emended descriptions of the genus Pseudoxanthomonas Finkmann et al. 2000 and of its type species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54(6):2245–2255
Toledo M, Gutierrez MC, Siles JA, Martin MA (2018) Full-scale composting of sewage sludge and market waste: stability monitoring and odor dispersion modeling. Environ Res 167:739–750
Wang WK, Liang CM (2021) Enhancing the compost maturation of swine manure and rice straw by applying bioaugmentation. Sci Rep 11:6103
Xin X, He J, Qiu W, Tang J, Liu T (2015) Microbial community related to lysozyme digestion process for boosting waste activated sludge biodegradability. Bioresour Technol 175:112–119
Xin X, He J, Qiu W (2017) Performance and microbial community evolutions in anaerobic fermentation process of waste activated sludge affected by solids retention time. Water Air Soil Pollut 228(6):1–13
Xu Y, Lu Y, Dai X (2018) Spatial configuration of extracellular organic substances responsible for the biogas conversion of sewage sludge. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(7):8308–8316
Yaman C (2020) Monitoring of biochemical parameters and GHG emissions in bioaugmented manure composting. Processes 8:681
Zang B, Li S, Michel F, Li G, Luo Y, Zhang D, Li Y (2016) Effects of mix ratio, moisture content and aeration rate on sulfur odor emissions during pig manure composting. Waste Manag 56:498–505
Zhang X, Ward BB, Sigman DM (2020) Global nitrogen cycle: critical enzymes, organisms, and processes for nitrogen budgets and dynamics. Chem Rev 120(12):5308–5351
Zhao Y, Xu C, Ai S, Wang H, Gao Y, Yan L, Mei Z, Wang W (2019) Biological pretreatment enhances the activity of functional microorganisms and the ability of methanogenesis during anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 290:1–8
Acknowledgements
We appreciate Liu Bingtao for the help and suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed in the current study was included in this article.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province [grant number 182300410165] and Ph.D. Science Foundation of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power [grant number 201901002].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cheng Qingli, Zhang Longlong, and Wang Dawei contributed to the conception and design of this study. All authors took part in the whole composting process. Parameters were measured by Zhang Longlong, Wang Dawei, and Niu Bochao and analyzed by Cheng Qingli and Zhang Longlong. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Cheng Qingli and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Diane Purchase
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Q., Zhang, L., Wang, D. et al. Bioaugmentation mitigates ammonia and hydrogen sulfide emissions during the mixture compost of dewatered sewage sludge and reed straw. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 68487–68497 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15446-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15446-5