Abstract
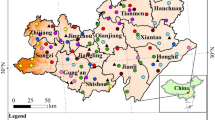
As a key input variable to many global climates, land surfaces and crop models, cropping intensity (CI) accurately assesses and predicts crops’ output, in view of the global decline in food production in recent years due to declining natural resources, urban expansion and declining quality of arable land. Hence, research on CI mapping can have a contribution to solve this problem. Unfortunately, existing remote sensing data for CI mapping research, including Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Landsat images, are not adequate for obtaining CI information at higher spatial and temporal resolution. In this regard, we develop an algorithm to extract CI based on per-pixel physiognomy. To be specific, the algorithm is based on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform and constructs a high temporal (10 days) spatial (30 m) resolution dataset with the fusion of Landsat 7/8 and Sentinel-2 A/B image data and extracts CI information using a time series of peak discovery method, threshold method and phenological period feature extraction to obtain the 2018 Chinese Huai River Basin (HRB) CI map. Our results suggest that the overall accuracy (OA) of CI extraction in the HRB is 92.72%, with a kappa coefficient of 0.864. The single-season crop, double-season crop and three-season crop account for 41.6%, 57.7% and 0.7% of the total farmland area, respectively. Compared to existing CI identification and extraction methods, this approach achieves higher accuracy in the identification and extraction of CI information over a larger area.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due personal privacy of research participants may be compromised but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bai X, Shi P, Liu Y (2014) Society: realizing China’s urban dream. Nature (London) 509:158–160. https://doi.org/10.1038/509158a
Belgiu M, Csillik O (2018) Sentinel-2 cropland mapping using pixel-based and object-based time-weighted dynamic time warping analysis. Remote Sens Environ 204:509–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.10.005
Biradar CM, Xiao X (2011) Quantifying the area and spatial distribution of double- and triple-cropping croplands in India with multi-temporal MODIS imagery in 2005. Int J Remote Sens 32:367–386. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160903464179
Bond-Lamberty B, Thomson A (2010) Temperature-associated increases in the global soil respiration record. Nature 464:579–582. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08930
Braswell BH, Hagen SC, Frolking SE, Salas WA (2003) A multivariable approach for mapping sub-pixel land cover distributions using MISR and MODIS: application in the Brazilian Amazon region. Remote Sens Environ 87:243–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2003.06.002
Carlson TN, Ripley DA (1997) On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens Environ 62:241–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(97)00104-1
Chaplin Kramer R, Sharp RP, Weil C et al (2019) Global modeling of nature’s contributions to people. Science (American Association for the Advancement of Science) 366:255–258. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw3372
Chen J, Jönsson P, Tamura M, Gu Z, Matsushita B, Eklundh L (2004) A simple method for reconstructing a high-quality NDVI time-series data set based on the Savitzky–Golay filter. Remote Sens Environ 91:332–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.03.014
Chen Y, Song X, Wang S, Huang J, Mansaray LR (2016) Impacts of spatial heterogeneity on crop area mapping in Canada using MODIS data. Isprs J Photogramm 119:451–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2016.07.007
Chen B, Xiao X, Li X, Pan L, Doughty R, Ma J, Dong J, Qin Y, Zhao B, Wu Z, Sun R, Lan G, Xie G, Clinton N, Giri C (2017) A mangrove forest map of China in 2015: analysis of time series Landsat 7/8 and Sentinel-1A imagery in Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform. Isprs J Photogramm 131:104–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.07.011
Chen B, Xiao X, Ye H, Ma J, Doughty R, Li X, Zhao B, Wu Z, Sun R, Dong J, Qin Y, Xie G (2018) Mapping forest and their spatial–temporal changes from 2007 to 2015 in tropical Hainan Island by integrating ALOS/ALOS-2 L-Band SAR and Landsat optical images. Ieee J-Stars 11:852–867. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2795595
Ellis EC, Neerchal N, Peng K, Xiao HS, Wang H, Zhuang Y, Li SC, Wu JX, Jiao JG, Ouyang H, Cheng X, Yang LZ (2009) Estimating long-term changes in China’s village landscapes. Ecosystems 12:279–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-008-9222-4
Fan C, Zheng B, Myint SW, Aggarwal R (2014) Characterizing changes in cropping patterns using sequential Landsat imagery: an adaptive threshold approach and application to Phoenix, Arizona. Int J Remote Sens 35:7263–7278. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2014.967891
Fisher JI, Mustard JF (2007) Cross-scalar satellite phenology from ground, Landsat, and MODIS data. Remote Sens Environ 109:261–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2007.01.004
Foley JA, Defries R, Asner GP, Barford C, Bonan G, Carpenter SR, Chapin FS, Coe MT, Daily GC, Gibbs HK, Helkowski JH, Holloway T, Howard EA, Kucharik CJ, Monfreda C, Patz JA, Prentice IC, Ramankutty N, Snyder PK (2005) Global consequences of land use. Science 309:570–574. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1111772
Frolking S, Qiu J, Boles S, Xiao X, Liu J, Zhuang Y, Li C, Qin X (2002) Combining remote sensing and ground census data to develop new maps of the distribution of rice agriculture in China. Global Biogeochem Cy 16:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001GB001425
Galford GL, Mustard JF, Melillo J, Gendrin A, Cerri CC, Cerri CEP (2008) Wavelet analysis of MODIS time series to detect expansion and intensification of row-crop agriculture in Brazil. Remote Sens Environ 112:576–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2007.05.017
Ganguly S, Friedl MA, Tan B, Zhang X, Verma M (2010) Land surface phenology from MODIS: characterization of the collection 5 global land cover dynamics product. Remote Sens Environ 114:1805–1816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2010.04.005
Ghimire P, Lei D, Juan N (2020) Effect of image fusion on vegetation index quality—a comparative study from Gaofen-1, Gaofen-2, Gaofen-4, Landsat-8 OLI and MODIS Imagery. Remote Sens-Basel 12:1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101550
Gray J, Friedl M, Frolking S, Ramankutty N, Nelson A, Gumma MK (2014) Mapping Asian cropping intensity with MODIS. Ieee J-Stars 7:3373–3379. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2344630
Griffiths P, Nendel C, Hostert P (2019) Intra-annual reflectance composites from Sentinel-2 and Landsat for national-scale crop and land cover mapping. Remote Sens Environ 220:135–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.10.031
Han Z, Dian Y, Xia H, Zhou J, Jian Y, Yao C, Wang X, Li Y (2020) Comparing fully deep convolutional neural networks for land cover classification with high-spatial-resolution Gaofen-2 images. Isprs Int J Geo-Inf 9:478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9080478
Hao P, Wang L, Niu Z, et al (2015) Potential of multitemporal Gaofen-1 panchromatic/multispectral images for crop classification: case study in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China, https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JRS.9.096035
Holben BN (1986) Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int J Remote Sens 7:1417–1434. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431168608948945
Irons JR, Dwyer JL, Barsi JA (2012) The next Landsat satellite: the Landsat Data Continuity Mission. Remote Sens Environ 122:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.08.026
Jain M, Mondal P, Defries RS et al (2013) Mapping cropping intensity of smallholder farms: A comparison of methods using multiple sensors. Remote Sens Environ 134:210–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2013.02.029
Jiang X, Ma J, Xiao G, Shao Z, Guo X (2021) A review of multimodal image matching: Methods and applications. Inform Fusion 73:22–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2021.02.012
Jin Z, Azzari G, You C, di Tommaso S, Aston S, Burke M, Lobell DB (2019) Smallholder maize area and yield mapping at national scales with Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens Environ 228:115–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.04.016
Kandasamy S, Baret F, Verger A, Neveux P, Weiss M (2013) A comparison of methods for smoothing and gap filling time series of remote sensing observations – application to MODIS LAI products. Biogeosciences 10:4055–4071. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-10-4055-2013
Kleynhans W, Olivier JC, Wessels KJ, Salmon BP, van den Bergh F, Steenkamp K (2011) Detecting land cover change using an extended Kalman Filter on MODIS NDVI Time-Series Data. Ieee Geosci Remote S 8:507–511. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2010.2089495
Lambin EF, Meyfroidt P (2011) Global land use change, economic globalization, and the looming land scarcity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:3465–3472. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1100480108
Lenney MP, Woodcock CE, Collins JB, Hamdi H (1996) The status of agricultural lands in Egypt: the use of multitemporal NDVI features derived from landsat TM. Remote Sens Environ 56:8–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(95)00152-2
Li L, Friedl M, Xin Q, Gray J, Pan Y, Frolking S (2014) Mapping crop cycles in China using MODIS-EVI time series. Remote Sens-Basel 6:2473–2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6032473
Li D, Yu W, Shao Z (2021) Smart city based on digital twins. Computational Urban Science 1(4):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43762-021-00005-y
Liu J, Zhu W, Cui X (2012) A Shape-matching Cropping Index (CI) Mapping method to determine agricultural cropland intensities in China using MODIS time-series Data. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 78:829–837. https://doi.org/10.14358/PERS.78.8.829
Liu L, Xu X, Zhuang D, Chen X, Li S (2013) Changes in the potential multiple cropping system in response to climate change in China from 1960-2010. PLoS One 8:e80990. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080990
Liu C, Zhang Q, Tao S, Qi J, Ding M, Guan Q, Wu B, Zhang M, Nabil M, Tian F, Zeng H, Zhang N, Bavuudorj G, Rukundo E, Liu W, Bofana J, Beyene AN, Elnashar A (2020a) A new framework to map fine resolution cropping intensity across the globe: algorithm, validation, and implication. Remote Sens Environ 251:112095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.112095
Liu L, Xiao X, Qin Y, Wang J, Xu X, Hu Y, Qiao Z (2020b) Mapping cropping intensity in China using time series Landsat and Sentinel-2 images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens Environ 239:111624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111624
Lobell DB, Asner GP (2004) Cropland distributions from temporal unmixing of MODIS data. Remote Sens Environ 93:412–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.08.002
Lobell DB, Azzari G, Burke M, Gourlay S, Jin Z, Kilic T, Murray S (2020) Eyes in the Sky, Boots on the ground: assessing satellite- and ground-based approaches to crop yield measurement and analysis. Am J Agric Econ 102:202–219. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajae/aaz051
Luo C, Qi B, Liu H, Guo D, Lu L, Fu Q, Shao Y (2021) Using time series Sentinel-1 Images for object-oriented crop classification in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens-Basel 13:561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040561
Macedo MN, Defries RS, Morton DC et al (2012) Decoupling of deforestation and soy production in the southern Amazon during the late 2000s. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:1341–1346. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1111374109
Mandanici E, Bitelli G (2016) Preliminary comparison of Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 imagery for a combined use. Remote Sens-Basel 8:1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8121014
Morton JF (2007) The impact of climate change on smallholder and subsistence agriculture. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences - PNAS 104:19680–19685. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0701855104
Nana Yaw Danquah Twumasi ZSAO (2019) Remote sensing and GIS methods in urban disaster monitoring and management – an overview https://www.ijtsrd.com/papers/ijtsrd23976.pdf
Neil Adger W (1999) Social vulnerability to climate change and extremes in coastal Vietnam. World Dev 27:249–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0305-750X(98)00136-3
Ning J, Liu J, Kuang W, Xu X, Zhang S, Yan C, Li R, Wu S, Hu Y, du G, Chi W, Pan T, Ning J (2018) Spatiotemporal patterns and characteristics of land-use change in China during 2010–2015. J Geogr Sci 28:547–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-018-1490-0
Oliphant AJ, Thenkabail PS, Teluguntla P, Xiong J, Gumma MK, Congalton RG, Yadav K (2019) Mapping cropland extent of Southeast and Northeast Asia using multi-year time-series Landsat 30-m data using a random forest classifier on the Google Earth Engine Cloud. Int J Appl Earth Obs 81:110–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2018.11.014
Peng J, Tian L, Liu Y, Zhao M, Hu Y', Wu J (2017) Ecosystem services response to urbanization in metropolitan areas: thresholds identification. Sci Total Environ 607–608:706–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.218
Piao S, Ciais P, Huang Y et al (2010) The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 467:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09364
Pretty J (2003) Social capital and the collective management of resources. Science 302:1912–1914. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1090847
Qiu B, Lu D, Tang Z, Song D, Zeng Y, Wang Z, Chen C, Chen N, Huang H, Xu W (2017) Mapping cropping intensity trends in China during 1982–2013. Appl Geogr 79:212–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2017.01.001
Roy DP, Kovalskyy V, Zhang HK, Vermote EF, Yan L, Kumar SS, Egorov A (2016) Characterization of Landsat-7 to Landsat-8 reflective wavelength and normalized difference vegetation index continuity. Remote Sens Environ 185:57–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2015.12.024
Shao Z, Cai J (2018) Remote sensing image fusion with deep convolutional neural network. Ieee J-Stars 11:1656–1669. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2805923
Shao Z, Deng J, Wang L, Fan Y, Sumari N, Cheng Q (2017) Fuzzy autoencode based cloud detection for remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens-Basel 9:311. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9040311
Shao Z, Cai J, Fu P, Hu L, Liu T (2019a) Deep learning-based fusion of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 images for a harmonized surface reflectance product. Remote Sens Environ 235:111425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111425
Shao Z, Pan Y, Diao C, Cai J (2019b) Cloud detection in remote sensing images based on multiscale features-convolutional neural network. Ieee T Geosci Remote 57:4062–4076. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2889677
Shao Z, Ding L, Li D, Altan O, Huq ME, Li C (2020a) Exploring the relationship between urbanization and ecological environment using remote sensing images and statistical data: a case study in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sustainability-Basel 12:5620. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145620
Shao Z, Huq ME, Cai B, Altan O, Li Y (2020b) Integrated remote sensing and GIS approach using Fuzzy-AHP to delineate and identify groundwater potential zones in semi-arid Shanxi Province, China. Environ Model Softw 134:104868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2020.104868
Steinier J, Termonia Y, Deltour J (1972) Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least square procedure. Anal Chem 44:1906–1909. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60319a045
Sumari NS, Tanveer H, Shao Z, Kira ES (2019) Geospatial distribution and accessibility of primary and secondary schools: a case of Abbottabad City, Pakistan. Proceedings of the ICA 2:1–11. https://doi.org/10.5194/ica-proc-2-125-2019
Tao J, Wu W, Zhou Y et al (2017) Mapping winter wheat using phenological feature of peak before winter on the North China Plain based on time-series MODIS data. J Integr Agric 16:348–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(15)61304-1
Teluguntla P, Thenkabail PS, Oliphant A, Xiong J, Gumma MK, Congalton RG, Yadav K, Huete A (2018) A 30-m Landsat-derived cropland extent product of Australia and China using random forest machine learning algorithm on Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform. Isprs J Photogramm 144:325–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.07.017
Tian H, Huang N, Niu Z, Qin Y, Pei J, Wang J (2019) Mapping winter crops in China with multi-source satellite imagery and phenology-based algorithm. Remote Sens-Basel 11:820. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070820
Verbesselt J, Hyndman R, Newnham G, Culvenor D (2010) Detecting trend and seasonal changes in satellite image time series. Remote Sens Environ 114:106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2009.08.014
Waldner F, Canto GS, Defourny P (2015) Automated annual cropland mapping using knowledge-based temporal features. Isprs J Photogramm 110:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.09.013
Wang Z, Yao F, Li W, Wu J (2017) Saturation correction for nighttime lights data based on the relative NDVI. Remote Sens-Basel 9:759. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070759
Wang J, Xiao X, Liu L, Wu X, Qin Y, Steiner JL, Dong J (2020) Mapping sugarcane plantation dynamics in Guangxi, China, by time series Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 and Landsat images. Remote Sens Environ 247:111951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.111951
Wardlow BD, Kastens JH, Egbert SL (2006) Using USDA crop progress data for the evaluation of greenup onset date calculated from MODIS 250-meter data. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 72:1225–1234. https://doi.org/10.14358/PERS.72.11.1225
Wardlow B, Egbert S, Kastens J (2007) Analysis of time-series MODIS 250 m vegetation index data for crop classification in the U.S. Central Great Plains. Remote Sens Environ 108:290–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2006.11.021
White MA, Thornton PE, Running SW (1997) A continental phenology model for monitoring vegetation responses to interannual climatic variability. Global Biogeochem Cy 11:217–234. https://doi.org/10.1029/97GB00330
Wu J, Song J, Li W, Zheng M (2016a) The accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural land and the associated potential ecological risks in Shenzhen, China. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:1428–1440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5303-z
Wu J, Yao F, Li W, Si M (2016b) VIIRS-based remote sensing estimation of ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei: a spatiotemporal statistical model. Remote Sens Environ 184:316–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.07.015
Wu J, Chen B, Mao J, Feng Z (2018) Spatiotemporal evolution of carbon sequestration vulnerability and its relationship with urbanization in China’s coastal zone. Sci Total Environ 645:692–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.086
Wu J, Sha W, Zhang P, Wang Z (2020a) The spatial non-stationary effect of urban landscape pattern on urban waterlogging: a case study of Shenzhen City. Sci Rep-Uk 10:7369. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64113-1
Wu J, Zhou J, Zhang W (2020b) A framework to classify environmental inequity in absolute and relative terms, and its application in Beijing. Sustainability-Basel 12:4757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114757
Wu J et al (2020c) Dynamic monitoring of long time series of ecological quality in urban agglomerations using google earth engine cloud computing: a case study of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao greater Bay Area, China. Acta Ecol Sin 40:8461–8473. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb202006251650
Xiao TSB, Jiyuan L, Dafang Z et al (2004) Mapping paddy rice agriculture in Southern China using multi-temporal MODIOS images https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.12.009, 95, 480, 492
Xiao X, Boles S, Liu J, Zhuang D, Frolking S, Li C, Salas W, Moore B III (2005) Mapping paddy rice agriculture in southern China using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens Environ 95:480–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.12.009
Yan H, Xiao X, Huang H, Liu J, Chen J, Bai X (2014) Multiple cropping intensity in China derived from agro-meteorological observations and MODIS data. Chin Geogr Sci 24:205–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-013-0637-2
Yao F, Si M, Li W, Wu J (2018) A multidimensional comparison between MODIS and VIIRS AOD in estimating ground-level PM2. 5 concentrations over a heavily polluted region in China. Sci Total Environ 618:819–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.209
Yao Y, Leung Y, Fung T, Shao Z, Lu J, Meng D, Ying H, Zhou Y (2021) Continuous multi-angle remote sensing and its application in urban land cover classification. Remote Sens-Basel 13:413. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030413
Yu H, He J, Zhou H, Guan F, Li L, Ren B, Wang Z (2018) Extraction and analysis of traditional Chinese medicine crops based on multitemporal high resolution data-taking Qiaocheng district of Bozhou as an example. ISPRS - International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences XLII-3:2153–2160. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-3-2153-2018
Zhang P, Anderson B, Tan B, Huang D, Myneni R (2005) Potential monitoring of crop production using a satellite-based Climate-Variability Impact Index. Agric For Meteorol 132:344–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2005.09.004
Zhang L, Shao Z, Wang Z (2016) Estimation of forest aboveground biomass using the integration of spectral and textural features from GF-1 satellite image, 2016. IEEE:353–357. https://doi.org/10.1109/EORSA.2016.7552828
Zhang X, Wu J, Peng J, Cao Q (2017) The uncertainty of nighttime light data in estimating carbon dioxide emissions in china: a comparison between DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. Remote Sens-Basel 9:797. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080797
Zhang HK, Roy DP, Yan L, Li Z, Huang H, Vermote E, Skakun S, Roger JC (2018) Characterization of Sentinel-2A and Landsat-8 top of atmosphere, surface, and nadir BRDF adjusted reflectance and NDVI differences. Remote Sens Environ 215:482–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.04.031
Zhou L, Tucker CJ, Kaufmann RK, Slayback D, Shabanov NV, Myneni RB (2001) Variations in northern vegetation activity inferred from satellite data of vegetation index during 1981 to 1999. J Geophys Res-Atmos 106:20069–20083. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JD000115
Zhu Z, Woodcock CE (2012) Object-based cloud and cloud shadow detection in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens Environ 118:83–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.10.028
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the National Ecosystem Research Network of China, Henan Dabieshan National Field Observation & Research Station of Forest Ecosystems (Xinyang China) for providing data samples for this research and Professor Shao Zhenfeng from State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering of Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing, Wuhan University, for his suggestions for improvement and revision of this article.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China project 42071220 (study on the internal and external mechanisms of the temporal and spatial evolution of specialized villages in the Yellow River Basin) and 41807066 (Scaling effects of runoff and sand transport in small watershed systems from the perspective of erosion energy flow), College Students’ Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project (S202010475127 and S202110475125).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W.; methodology, Y.W.; data analysis and processing, Y.W., R.T. and L.F.; software, Y.W., R.T. and L.F.; validation, Y.W., L.F. and R.T.; field trips, Y.W., L.F. and R.T.; writing-original draft preparation, Y.W.; writing-review and editing, W.Z.; visualization, Y.W. and R.T.; supervision, W.Z.; funding acquisition, W.Z. L.T. and Y.W.; all authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
This manuscript contains any form of data of any person, with the consent of the owner and the author of this study. All authors agree to publish the data and images in this manuscript in the Journal of Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Fan, L., Tao, R. et al. Research on cropping intensity mapping of the Huai River Basin (China) based on multi-source remote sensing data fusion. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 12661–12679 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15387-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15387-z