Abstract
Tibial dyschondroplasia (TD) is a common skeletal disease occurred in growth plate of fast-growing broilers. Thiram is a sort of chemical used for pesticide and fungicide. The excessive use of thiram increased the threat to animal and human health. In this study, we aimed to investigate the therapeutic mechanism of chlorogenic acid (CGA) on thiram-induced tibial dyschondroplasia. Broiler chickens were divided into three different groups, e.g., control, TD, and CGA. CGA was administrated after the induction of TD from 4th day to 7th day. Biochemical analysis was performed to detect the content of calcium (Ca) and phosphorus (P). Histological changes and degradation of extracellular matrix were observed through hematoxylin-eosin (H & E) and Masson staining. To further determine the mechanism, TUNEL staining and western blot were also performed to detect the apoptosis changes in growth plate of all groups. The results showed the disproportionation of Ca and P content and upregulation of apoptosis during the development of TD. But, after the administration of CGA, the ratio of Ca:P was upregulated, and the apoptosis was also downregulated. The current study shows the toxic effect of thiram on chickens and suggests that CGA is associated with a mechanism that plays a significant role in apoptosis induced by thiram in poultry industry.
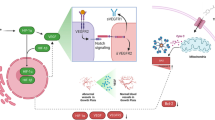
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated in this study are included within the article.
References
Ahmed M, Mohanad M, Ahmed A, Aboulhoda B, El-Awdan S (2021): Mechanistic insights into the protective effects of chlorogenic acid against indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in rats: modulation of the cross talk between autophagy and apoptosis signaling. Life Sci., 119370
Arnold A, Dennison E, Kovacs C, Mannstadt M, Rizzoli R, Brandi M, Clarke B, Thakker R (2021): Hormonal regulation of biomineralization. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 17(5):261–275
Caplan A (1987) The cellular and molecular embryology of bone formation. Bone Miner. Res. 5:117–183
Chen W-P, Tang J-L, Bao J-P, Hu P-F, Shi Z-L, Wu L-D (2011) Anti-arthritic effects of chlorogenic acid in interleukin-1β-induced rabbit chondrocytes and a rabbit osteoarthritis model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 11:23–28
da Costa C, Checler F (2010) A novel parkin-mediated transcriptional function links p53 to familial Parkinson ' s disease. Cell cycle 9:16–17
Derakhshan A, Chen Z, Van Waes C (2017) Therapeutic small molecules target inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in cancers with deregulation of extrinsic and intrinsic cell death pathways. Clinical Cancer Research 23:1379–1387
Dies H, Siampani M, Escobedo C, Docoslis A (2018): Direct detection of toxic contaminants in minimally processed food products using dendritic surface-enhanced raman scattering substrates. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 18
Domico LM, Cooper KR, Bernard LP, Zeevalk GD (2007) Reactive oxygen species generation by the ethylene-bis-dithiocarbamate (EBDC) fungicide mancozeb and its contribution to neuronal toxicity in mesencephalic cells. Neurotoxicology 28:1079–1091
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X (2000) Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102:33–42
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon H, Kimchi A (2009) Life and death partners: apoptosis, autophagy and the cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 16:966–975
Farnum C, Wilsman N (1989) Condensation of hypertrophic chondrocytes at the chondro-osseous junction of growth plate cartilage in Yucatan swine: relationship to long bone growth. The American Journal of Anatomy 186:346–358
Favaloro B, Allocati N, Graziano V, Di Ilio C, De Laurenzi V (2012) Role of apoptosis in disease. Aging 4:330–349
Filipe OM, Santos SA, Domingues MRM, Vidal MM, Silvestre AJ, Santos EB (2014) Effect of copper ions on the degradation of thiram in aqueous solution: identification of degradation products by HPLC–MS/MS. J. Hazard. Mater. 279:125–132
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, el-Deiry WS, Fulda S, Gottlieb E, Green DR, Hengartner MO, Kepp O, Knight RA, Kumar S, Lipton SA, Lu X, Madeo F, Malorni W, Mehlen P, Nuñez G, Peter ME, Piacentini M, Rubinsztein DC, Shi Y, Simon HU, Vandenabeele P, White E, Yuan J, Zhivotovsky B, Melino G, Kroemer G (2012) Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell death differentiation 19:107–120
Ge Q, Ying J, Shi Z, Mao Q, Jin H, Wang P, Chen J, Yuan W, Tong P, Li J (2021) Chlorogenic acid retards cartilaginous endplate degeneration and ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via suppressing NF-κB signaling. Life Sci. 274:119324
Halimah M, Zulkifli H, Vijaya S, Tan Y, Wei P, Let C, May C (2010) Life cycle assessment of oil palm seedling production (Part 1). Journal of Oil Palm Research 22:878–886
Héraud F, Héraud A, Harmand M (2000) Apoptosis in normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 59:959–965
Jahejo A, Jia F, Raza S, Shah M, Yin J, Ahsan A, Waqas M, Niu S, Ning G, Zhang D, Khan A, Tian W (2021) Screening of toll-like receptor signaling pathway-related genes and the response of recombinant glutathione S-transferase A3 protein to thiram induced apoptosis in chicken erythrocytes. Developmental and Comparative Immunology 114:103831
Kaufmann T, Strasser A, Jost P (2012) Fas death receptor signalling: roles of Bid and XIAP. Cell Death Differentiation 19:42–50
Kaur S, Kumar M, Kaur P, Kaur V, Kaur S (2016) Modulatory effects of Cassia fistula fruits against free radicals and genotoxicity of mutagens. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 98:220–231
Kaur S, Kumar A, Thakur S, Kumar K, Sharma R, Sharma A, Singh P, Sharma U, Kumar S, Landi M, Brestič M, Kaur S (2020a): Cassia fistula antioxidant, antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing efficacy of fractions from L. leaves. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 9(2):173
Kaur S, Pandit K, Chandel M, Kaur S (2020b) Antiproliferative and apoptogenic effects of Cassia fistula L. n-hexane fraction against human cervical cancer (HeLa) cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 27:32017–32033
Kelly P, Strasser A (2011) The role of Bcl-2 and its pro-survival relatives in tumourigenesis and cancer therapy. Cell death differentiation 18:1414–1424
Kopeina G, Zhivotovsky B (2021): Caspase-2 as a master regulator of genomic stability. Trends Cell Biol.
López-Armada M, Caramés B, Cillero-Pastor B, Lires-Deán M, Maneiro E, Fuentes I, Ruíz C, Galdo F, Blanco F (2005) Phosphatase-1 and -2A inhibition modulates apoptosis in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes independently of nitric oxide production. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64:1079–1082
Pimentel A, Ureña-Torres P, Bover J, Luis Fernandez-Martín J, Cohen-Solal M (2020): Bone fragility fractures in CKD patients. Calcif. Tissue Int.
Rath N, Huff W, Bayyari G, Balog J (1998) Cell death in avian tibial dyschondroplasia. Avian Dis. 42:72–79
Rath N, Huff W, Balog J, Huff G (2004) Comparative efficacy of different dithiocarbamates to induce tibial dyschondroplasia in poultry. Poultr. Sci. 83:266–274
Ripley BD, Lissemore LI, Leishman PD, Denommé MA, Ritter L (2000) Pesticide residues on fruits and vegetables from Ontario, Canada, 1991–1995. J. AOAC Int. 83:196–213
Roberson K, Hill C, Ferket P (1993) Additive amelioration of tibial dyschondroplasia in broilers by supplemental calcium or feed deprivation. Poultr. Sci. 72:798–805
Thind T, Hollomon D (2018) Thiocarbamate fungicides: reliable tools in resistance management and future outlook. Pest Manage. Sci. 74:1547–1551
Tian W, Li J, Qin P, Wang R, Ning G, Qiao J, Li H, Bi D, Pan S, Guo D (2013) Screening of differentially expressed genes in the growth plate of broiler chickens with tibial dyschondroplasia by microarray analysis. BMC Genomics 14:276
Van Delft MF, Huang DC (2006) How the Bcl-2 family of proteins interact to regulate apoptosis. Cell Res. 16:203–213
Wang Z, Yang L, Ye X, Huang C, Yang W, Zhang L, Wu Z, Fu F (2020) Multicolor visual screening of total dithiocarbamate pesticides in foods based on sulfydryl-mediated growth of gold nanobipyramids. Anal. Chim. Acta 1139:59–67
Whelan R, Kaplinskiy V, Kitsis R (2010) Cell death in the pathogenesis of heart disease: mechanisms and significance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 72:19–44
Wong W, Puthalakath H (2008) Bcl-2 family proteins: the sentinels of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. IUBMB life 60:390–397
Xu M, Yang L, Zhu Y, Liao M, Chu L, Li X, Lin L, Zheng G (2019) Collaborative effects of chlorogenic acid and caffeine on lipid metabolism via the AMPKα-LXRα/SREBP-1c pathway in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Food function 10:7489–7497
Yao X, Xu J, Hao J, Wan Y, Chen T, Zhang D, Li L (2018) Microwave assisted extraction for the determination of chlorogenic acid in Flos Lonicerae by direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry (DART-MS). Journal of Chromatography B, Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences 1092:82–87
You L, Zhao Y, Kuca K, Wang X, Oleksak P, Chrienova Z, Nepovimova E, Jaćević V, Wu Q, Wu W (2021) Hypoxia, oxidative stress, and immune evasion: a trinity of the trichothecenes T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol (DON). Arch. Toxicol. 95:1899–1915
Yun N, Kang J-W, Lee S-M (2012) Protective effects of chlorogenic acid against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat liver: molecular evidence of its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 23:1249–1255
Zenmyo M, Komiya S, Kawabata R, Sasaguri Y, Inoue A, Morimatsu M (1996) Morphological and biochemical evidence for apoptosis in the terminal hypertrophic chondrocytes of the growth plate. The Journal of Pathology 180:430–433
Zhang J, Huang S, Tong X, Zhang L, Jiang X, Zhang H, Mehmood K, Li J (2019): Chlorogenic acid alleviates thiram-induced tibial dyschondroplasia by modulating caspases, BECN1 expression and ECM degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20(13):3160
Zhang H, Wang Y, Mehmood K, Chang Y, Tang Z, Li Y (2020) Treatment of tibial dyschondroplasia with traditional Chinese medicines: "lesson and future directions". Poultr. Sci. 99:6422–6433
Acknowledgements
We thank Lihong Zhang, Shucheng Huang, and Xiaole Tong for helpful discussion about experiment design and analysis.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number No. 31873031], the National Key Research and Development Program of China [grant number No. 2017YFD0502200], and Tibet Agricultural and Animal Husbandry University flexible introduction of talent project funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jialu Zhang: conceptualization, formal analysis. Jialu Zhang, Kangkang Guo, and Jiakui Li: writing, review and editing. Jialu Zhang and Jiakui Li: conceptualization. Jialu Zhang: investigation. Jialu Zhang, Bihao Luo, Juanjuan Liu: formal analysis. Jialu Zhang: software. Jialu Zhang: methodology. Muhammad Waqas, Muhammad Fakhar-e-Alam Kulyar: investigation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Huazhong Agricultural University (Permit No. 4200695757).
Consent to participate
All authors have given consent to their contribution.
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed with the content and all have given explicit consent to publish.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Evaluate thiram toxic effect on bone metabolism parameters.
• The application of chlorogenic acid recovered the disorders of Ca and P levels and matrix degradation in chickens which suffered tibial dyschondroplasia.
• Chlorogenic acid can alleviate the tibial dyschondroplasia through inhibiting the intrinsic apoptosis pathway.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, ., Luo, B., Liu, J. et al. Chlorogenic acid inhibits apoptosis in thiram-induced tibial dyschondroplasia via intrinsic pathway. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 68288–68299 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15286-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15286-3