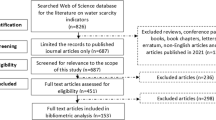
Abstract
With the scarcity of water resources and the development of recycled water production technology, the promotion of global recycled water use is attracting more and more attention. An increasing number of publications have examined the reuse of recycled water from different perspectives to promote the sustainable use of global water resources. The purpose of this research is to systematically and comprehensively evaluate the knowledge structure, development trends, research hotspots, and frontier predictions in the global research field of recycled water use. Based on 910 screened articles from the Web of Science Core Collection from 1990 to 2020, this paper visualizes and analyzes recycled water use from the perspectives of scientific output characteristics, research collaboration networks, highly cited articles and core journals, and keywords. The results indicate that research interest in recycled water use is on the rise. Authoritative experts, high-impact institutions, and core journals are also identified. The study shows that water resources management, public health, and public acceptance are all hot topics and frontiers of research. This study provides valuable guidance for researchers to support recycled water research directions and regulatory authorities for the interest in recycled water use.












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Asano T, Burton F, Leverenz H, Tsuchihashi R, Tchobanoglous G (2007) Water reuse issues, technologies and applications. McGraw-Hill, New York
Bellver-Domingo A, Fuentes R, Hernandez-Sancho F (2019) Reclaimed water and irrigation: a cost-benefit analysis for desalination of WWTPs effluents. Desalin Water Treat 166:193–201. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24556
Beltran EM, Pablos MV, Torija CF, Porcel MA, Gonzalez-Doncel M (2020) Uptake of atenolol, carbamazepine and triclosan by crops irrigated with reclaimed water in a Mediterranean scenario. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191:110171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.escoenv.2020.110171
Chen Z, Ngo HH, Guo WS (2013) A critical review on the end uses of recycled water. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 43:1446–1516. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2011.647788
Chen WP, Lu SD, Pan N, Wang YC, Wu LS (2015) Impact of reclaimed water irrigation on soil health in urban green areas. Chemosphere 119:654–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.07.035
Chi YB, Yang PL, Ren SM, Yang J (2020) Finding the optimal fertilizer type and rate to balance yield and soil GHG emissions under reclaimed water irrigation. Sci Total Environ 729:138954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138954
Dolnicar S, Schäfer AI (2009) Desalinated versus recycled water: public perceptions and profiles of the accepters. J Environ Manag 90:888–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.02.003
Dolnicar S, Hurlimann A, Nghiem LD (2010) The effect of information on public acceptance - the case of water from alternative sources. J Environ Manag 91:1288–1293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.02.003
Dolnicar S, Hurlimann A, Grün B (2011) What affects public acceptance of recycled and desalinated water? Water Res 45:933–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.09.030
Dolnicar S, Hurlimann A, Gruen B (2014) What affects public acceptance of recycled and desalinated water? (vol 45, pg 933, 2011). Water Res 64:321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.07.027
Ellis SF, Savchenko OM, Messer KD (2019) What’s in a name? Branding reclaimed water. Environ Res 172:384–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.01.059
Fielding KS, Dolnicar S, Schultz T (2019) Public acceptance of recycled water. Int J Water Resour Dev 35:551–586. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2017.1419125
Garcia-Cuerva L, Berglund EZ, Binder AR (2016) Public perceptions of water shortages, conservation behaviors, and support for water reuse in the US. Resour Conserv Recycl 113:106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.06.006
Garrido Y, Marin A, Tudela JA, Truchado P, Allende A, Gil MI (2020) Chlorate accumulation in commercial lettuce cultivated in open field and irrigated with reclaimed water. Food Control 114:107283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107283
Goerlandt F, Li J, Reniers G (2020) The landscape of risk communication research: a scientometric analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093255
Hartley TW (2006) Public perception and participation in water reuse. Desalination 187:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.04.072
Hurlimann A, Dolnicar S (2010) When public opposition defeats alternative water projects - the case of Toowoomba Australia. Water Res 44:287–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.09.020
Liu ZQ, Xu YP, Yang XW, Huang R, Zhou QH, Cui FY (2017) Does the recycling of waste streams from drinking water treatment plants worsen the quality of finished water?, A case assessment in China. Water Sci Technol Supply 17:597–605. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2016.151
Liu G, Lu Y, Shi LL, Ren YR, Kong JY, Zhang MY, Chen MH, Liu WL (2020) TLR4-MyD88 signaling pathway is responsible for acute lung inflammation induced by reclaimed water. J Hazard Mater 396:122586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122586
Marks JS (2006) Taking the public seriously: the case of potable and non potable reuse. Desalination 187:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.04.074
McClaran N, Behe BK, Huddleston P, Fernandez RT (2020) Recycled or reclaimed? The effect of terminology on water reuse perceptions. J Environ Manag 261:110144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110144
Munakata N, Morton R, Tang CC, Barry JJ, Tremblay R, Friess PL, Maguin SR, 2012. Comparing traditional UF-RO-AOP to MBR-RO-AOP for treatment of recycled water for indirect potable reuse. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 243.
Nancarrow BE, Leviston Z, Po M, Porter NB, Tucker DI (2008) What drives communities’ decisions and behaviours in the reuse of wastewater. Water Sci Technol 57:485–491. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2008.160
Niu ZG, Zang X, Zhang JG (2014) Health risk assessment of exposure to organic matter from the use of reclaimed water in toilets. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:6687–6695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2583-7
Po, M; Nancarrow, BE; Leviston, Z; Porter, NB; Syme, GJ; Kaercher, J., 2005. Water for a healthy country predicting community behaviour in relation to wastewater reuse, CSIRO Water for a Healthy Country Flagship report.
Pype ML, Lawrence MG, Keller J, Gernjak W (2016) Reverse osmosis integrity monitoring in water reuse: the challenge to verify virus removal - a review. Water Res 98:384–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.04.040
Ross VL, Fielding KS, Louis WR (2014) Social trust, risk perceptions and public acceptance of recycled water: testing a social-psychological model. J Environ Manag 137:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.01.039
Rusinol M, Hundesa A, Cardenas-Youngs Y, Fernandez-Bravo A, Perez-Cataluna A, Moreno-Mesonero L, Moreno Y, Calvo M, Alonso JL, Figueras MJ, Araujo R, Bofill-Mas S, Girones R (2020) Microbiological contamination of conventional and reclaimed irrigation water: evaluation and management measures. Sci Total Environ 710:136298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136298
Santana MVE, Cornejo PK, Rodriguez-Roda I, Buttiglieri G, Corominas L (2019) Holistic life cycle assessment of water reuse in a tourist-based community. J Clean Prod 233:743–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.290
Sun J, Zhou Z, Huang J, Li G (2020) A bibliometric analysis of the impacts of air pollution on children. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041277
Trussell RS, Lai-Bluml G, Chaudhuri M, Johnson G (2019) Developing a regional recycled water program in Southern California. Water Pract Technol 14:570–578. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2019.042
United Nations, (2019) Water scarcity[Online]. https://www.unwater.org/water-facts/scarcity/. Accessed 13 May 2020
UN-Water, (2020) The United Nations world water development report 2020: water and climate change[Online]. https://www.unwater.org/publications/world-water-development-report-2020/. Accessed 13 Nov 2020
US Bureau of Reclamation 2004. Recycled Water Project Implementation Strategies. Tech Memorandum.
Wang Z, Li JS, Li YF (2017) Using reclaimed water for agricultural and landscape irrigation in China: a review. Irrig Drain 66:672–686. https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.2129
World Health Organization (2017) Potable Reuse: guidance for producing safe drinking-water. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241512770. Accessed 14 May 2020
Zhang CM, Xu PC, Wang XCC, Xu LM, (2020) Bacterial viability and diversity in a landscape lake replenished with reclaimed water: a case study in Xi’an, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:32796–32808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08910-1
Zhu ZF, Wang HR, Li AH (2019) On the factors influencing public knowledge and acceptance of reclaimed water from a survey of three cities in northern China. J Water Reuse Desalin 9:193–202. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2018.049
Dolnicar S, Schäfer AI (2009) Desalinated versus recycled water: Public perceptions and profiles of the accepters. J Environ Manage 90, 888–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.02.003
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the helpful comments from reviewers and editors.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.71874135) and the MOE (Ministry of Education in China) the Project of Humanities and Social Sciences (No. 18YJA630068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Xiaojun Liu and Li Li had the idea for the article, Li Li performed the literature search and data analysis and drafted the manuscript, and Xinyue Zhang critically revised the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Liu, X. & Zhang, X. Uncovering the research progress and hotspots on the public use of recycled water: a bibliometric perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 44845–44860 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15263-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15263-w