Abstract
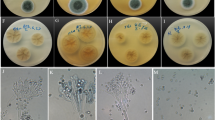
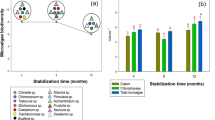
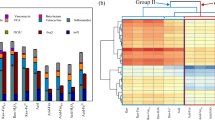
Bench- and pilot-scale successive multi-batch trials were conducted to investigate the performance and sustainability of fungal conditioning with Penicillium simplicissimum NJ12 for improving sludge dewatering. The dominant factors affecting the sludge dewaterability improvement by P. simplicissimum NJ12 were also identified. Fungal treatment with P. simplicissimum NJ12 at a volume fraction of 5% of the inoculum greatly improved the sludge dewaterability. This improvement was characterized by sharp decreases in the specific resistance to filtration from 1.97 × 1013 to 3.52 × 1011 m/kg and capillary suction time from 32 to 12 s within 3 days. Stepwise multiple linear regression analysis showed that a marked decrease (58.8%) in the protein content in slime extracellular polymeric substances and an increase in the zeta potential of the sludge (from −35 to −10 mV) were the most important factors that improved the dewaterability of sludge after fungal treatment. Consecutive processes of fungal treatment could be realized by recirculating the fungal-treated sludge with a recycling rate of 1:2 (Vbiotreated sludge/Vtotal sludge). The treatment effectiveness was maintained only over three successive cycles, but replenishment with fresh P. simplicissimum NJ12 would be provided periodically at set batch intervals. These findings demonstrate the possibility of P. simplicissimum NJ12-assisted fungal treatment for enhancing sludge dewatering.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MZ, Fakhru’l-Razi A (2003) Enhanced settleability and dewaterability of fungal treated domestic wastewater sludge by liquid state bioconversion process. Water Res 37:1118–1124
Alam MZ, Fakhru’l-Razi A, Molla AH (2003) Biosolids accumulation and biodegradation of domestic wastewater treatment plant sludge by developed liquid state bioconversion process using a batch fermenter. Water Res 37:3569–3578
Appels L, Houtmeyers S, Degrève J, Van Impe J, Dewil R (2013) Influence of microwave pre-treatment on sludge solubilization and pilot scale semicontinuous anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 128:598–603
Bala Subramanian S, Yan S, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY (2008) A new, pellet-forming fungal strain: its isolation, molecular identification, and performance for simultaneous sludge-solids reduction, flocculation, and dewatering. Water Environ Res 80:840–852
Bala Subramanian S, Yan S, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY (2010) SSPRSD using a filamentous fungal strain Penicillium expansum BS30 isolated from wastewater sludge. J Environ Eng 136:719–730
Cai MQ, Hu JQ, Wells G, Seo Y, Spinney R, Ho SH, Dionysiou DD, Su J, Xiao RY, Wei ZS (2018) Understanding mechanisms of synergy between acidification and ultrasound treatments for activated sludge dewatering: from bench to pilot-scale investigation. Environ Sci Technol 52:4313–4323
Chen Y, Yang H, Gu G (2001) Effect of acid and surfactant treatment on activated sludge dewatering and settling. Water Res 35:2615–2620
Christensen ML, Keiding K, Nielsen PH, Jørgensen MK (2015) Dewatering in biological wastewater treatment: a review. Water Res 82:14–24
Chroumpi T, Makela MR, de Vries RP (2020) Engineering of primary carbon metabolism in filamentous fungi. Biotechnol Adv 43:107551–107573
Fakhru’l-Razi A, Molla AH (2007) Enhancement of bioseparation and dewaterability of domestic wastewater sludge by fungal treated dewatered sludge. J Hazard Mater 147:350–356
Fakhru’l-Razi A, Alam MZ, Idris A, Abd-Aziz S, Molla AH (2002) Filamentous fungi in Indah Water Konsortium (IWK) sewage treatment plant for biological treatment of domestic wastewater sludge. J Environ Sci Health A 37:309–320
Faye MCAS, Zhang KK, Peng S, Zhang YR (2019) Sludge dewaterability: the variation of extracellular polymeric substances during sludge conditioning with two natural organic conditioners. J Environ Manag 251:109559–109568
Frølund B, Palmgren R, Keiding K, Nielsen PH (1996) Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res 30:1749–1758
Guibaud G, Tixier N, Baudu M (2005) Hysteresis area, a rheological parameter used as a tool to assess the ability of filamentous sludge to settle. Process Biochem 40:2671–2676
He DQ, Wang LF, Jiang H, Yu HQ (2015) A Fenton-like process for the enhanced activated sludge dewatering. Chem Eng J 272:128–134
Jernejc K, Legiša M (2004) A drop of intracellular pH stimulates citric acid accumulation by some strains of Aspergillus niger. J Biotechnol 112:289–297
Kacprzak M, Neczaj E, Okoniewska E (2005) The comparative mycological analysis of wastewater and sewage sludges from selected wastewater treatment plants. Desalination 185:363–370
Khanal SK, Grewell D, Sung S, Van Leeuwen J (2007) Ultrasound applications in wastewater sludge pretreatment: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 37:277–313
Li YY, Dong LM, Li YY, Zheng XY, Zhang C, Ding N (2019a) Enhancement of biological fermented sludge dewaterability by inoculation of filamentous fungi Mucor circinelloides XY-Z and Penicillium oxalicum LY-1. Dry Technol 37:1678–1687
Li SM, Li RW, Tang YN, Chen G (2019b) Microwave-induced heavy metal removal from dewatered biosolids for cost-effective composting. J Clean Prod 241:118342–118350
Liang JL, Zhang L, Ye MY, Guan ZJ, Huang JJ, Liu JY, Li L, Huang SS, Sun SY (2020) Evaluation of the dewaterability, heavy metal toxicity and phytotoxicity of sewage sludge in different advanced oxidation processes. J Clean Prod 265:121839–121848
Liu H, Yang S, Shi JS, Xu XY, Liu HB, Fu B (2016a) Towards understanding the dewatering mechanism of sewage sludge improved by bioleaching processing. Sep Purif Technol 165:53–59
Liu J, Yang Q, Wang DB, Li XM, Zhong Y, Li X, Deng YC, Wang LQ, Yi KX, Zeng GM (2016b) Enhanced dewaterability of waste activated sludge by Fe(II)-activated peroxymonosulfate oxidation. Bioresour Technol 206:134–140
Liu H, Shi JS, Xu XY, Zhan XM, Fu B, Li YF (2017) Enhancement of sludge dewaterability with filamentous fungi Talaromyces flavus S1 by depletion of extracellular polymeric substances or mycelium entrapment. Bioresour Technol 245:977–983
Low EW, Chase HA (1999) Reducing production of excess biomass during wastewater treatment. Water Res 33:1119–1132
Maqbool T, Cho J, Hur J (2019) Improved dewaterability of anaerobically digested sludge and compositional changes in extracellular polymeric substances by indigenous persulfate activation. Sci Total Environ 674:96–104
Molla AH, Fakhru’l-Razi A (2012) Mycoremediation-a prospective environmental friendly technique of bioseparation and dewatering of domestic wastewater sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1612–1619
More TT, Yan S, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY (2010) Potential use of filamentous fungi for wastewater sludge treatment. Bioresour Technol 101:7691–7700
Murugesan K, Selvam A, Wong JWC (2014) Flocculation and dewaterability of chemically enhanced primary treatment sludge by bioaugmentation with filamentous fungi. Bioresour Technol 168:198–203
Neyens E, Baeyens J, Dewil R (2004) Advanced sludge treatment affects extracellular polymeric substances to improve activated sludge dewatering. J Hazard Mater 106:83–92
Sheng GP, Yu HQ, Li XY (2010) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review. Biotechnol Adv 28:882–894
Wang ZY, Zheng GY, Zhou LX (2015) Degradation of slime extracellular polymeric substances and inhibited sludge flocs destruction contribute to sludge dewaterability enhancement during fungal treatment of sludge using filamentous fungus Mucor sp. GY-1. Bioresour Technol 192:514–521
Wang HF, Hu H, Wang HJ, Zeng RJ (2019) Combined use of inorganic coagulants and cationic polyacrylamide for enhancing dewaterability of sewage sludge. J Clean Prod 211:387–395
Wei LL, Xia XH, Zhu FY, Li QY, Xue M, Li JJ, Sun B, Jiang JQ, Zhao QL (2020) Dewatering efficiency of sewage sludge during Fe2+-activated persulfate oxidation: effect of hydrophobic/hydrophilic properties of sludge EPS. Water Res 181:115903–115914
Wu BR, Dai XH, Chai XL (2020) Critical review on dewatering of sewage sludge: influential mechanism, conditioning technologies and implications to sludge re-utilizations. Water Res 180:115912–115929
Xiao K, Chen Y, Jiang X, Tyagi VK, Zhou Y (2016) Characterization of key organic compounds affecting sludge dewaterability during ultrasonication and acidification treatments. Water Res 105:470–478
Yu GH, He PJ, Shao LM, He PP (2008) Stratification structure of sludge flocs with implications to dewaterability. Environ Sci Technol 42:7944–7949
Zhang WJ, Xiao P, Liu YY, Xu SW, Xiao F, Wang DS, Chow Christopher WK (2014a) Understanding the impact of chemical conditioning with inorganic polymer flocculants on soluble extracellular polymeric substances in relation to the sludge dewaterability. Sep Purif Technol 132:430–437
Zhang H, Yang JK, Yu WB, Luo S, Peng L, Shen XX, Shi YF, Zhang SN, Song J, Ye N, Li Y, Yang CZ, Liang S (2014b) Mechanism of red mud combined with Fenton’s reagent in sewage sludge conditioning. Water Res 59:239–247
Zhang WJ, Cao BD, Wang DS, Ma T, Xia H, Yu DH (2016) Influence of wastewater sludge treatment using combined peroxyacetic acid oxidation and inorganic coagulants re-flocculation on characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Water Res 88:728–739
Acknowledgements
We thank the editor and reviewers for their valuable and constructive comments and suggestions.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21677077) and the Program for Student Innovation through Research and Training (No. 202010307038Z).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, N.T., D.F., and L.X.Z.; methodology, N.T. and D.F.; investigation, N.T., X.W., F.Z., Z.L.P., and J.Q.W.; data curation, N.T., X.W., F.Z., Z.L.P., and J.Q.W.; writing the original draft, N.T.; supervision, D.F.; reviewing and editing, D.F. and L.X.Z. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gerald Thouand
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 785 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, N., Wu, X., Zhang, F. et al. Enhancement of sewage sludge dewaterability by fungal conditioning with Penicillium simplicissimum NJ12: from bench- to pilot-scale consecutive multi-batch investigations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 62255–62265 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15170-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15170-0