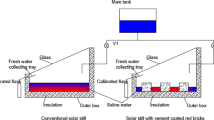
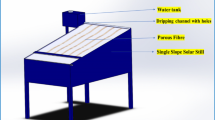
Abstract
In the current research, the energy and economic performance in single-slope solar still using ball marbles (BMSS) has been investigated and compared the results with conventional solar still (CSS) under the similar weather conditions of Karaikal (10.92° N, 79.83° E), India, during October 2020. The experiments have been conducted on both sunny and cloudy day to evaluate the performance of solar still. The BMSS has increased the evaporation rate and productivity when compared to CSS due to the sensible heat energy stored by the ball marbles in the absorber basin. The potable water yield of the BMSS is improved by 21.23% and 22.86%, respectively, during sunny and cloudy days. The maximum cumulative productivity obtained in the BMSS is 2950 mL/m2.day and 2150 mL/m2.day, respectively, on sunny and cloudy days. In economic analysis, the payback period (PBP) of the BMSS is 5.7 months, whereas the PBP of the CSS is 6.5 months, respectively. Furthermore, the cost per litre (CPL) potable water produced by BMSS is 8% lower than the CPL of CSS.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
annual cost
- AMC:
-
annual maintenance cost
- ASV:
-
annual salvage value
- BMSS:
-
ball marbles solar still
- CC:
-
capital cost
- CPL:
-
cost per litre
- CRF:
-
capital recovery factor
- CSS:
-
conventional solar still
- FAC:
-
fixed annual cost
- PBP:
-
payback period
- S:
-
salvage value
- SFF:
-
sinking fund factor
References
Arjunan TV, Aybar HŞ, Nedunchezhian N (2009) Status of solar desalination in India. Renew Sust Energ Rev 13:2408–2418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.03.006
Arunkumar T, Denkenberger D, Ahsan A, Jayaprakash R (2013) The augmentation of distillate yield by using concentrator coupled solar still with phase change material. Desalination 314:189–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.01.018
Attia MEH, Driss Z, Kabeel AE, et al (2021a) Phosphate bags as energy storage materials for enhancement of solar still performance. Environmental Science and Pollution Research
Attia MEH, Kabeel AE, Abdelgaied M, el-Maghlany WM, Driss Z (2021b) Enhancement of the performance of hemispherical distiller via phosphate pellets as energy storage medium. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12920-y
Aybar HS, Assefi H (2009) A review and comparison of solar distillation: direct and indirect type systems. Desalin Water Treat 10:321–331. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2009.931
Bait O, Si-Ameur M (2018) Enhanced heat and mass transfer in solar stills using nanofluids: a review. Sol Energy 170:694–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.06.020
Chamkha AJ, Rufuss DDW, Kabeel AE, Sathyamurthy R, Abdelgaid M, Manokar AM, Madhu B (2020) Augmenting the potable water produced from single slope solar still using CNT-doped paraffin wax as energy storage: an experimental approach. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02703-w
Dashtban M, Tabrizi FF (2011) Thermal analysis of a weir-type cascade solar still integrated with PCM storage. Desalination 279:415–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.06.044
Dhivagar R, Mohanraj M (2021a) Optimization of performance of coarse aggregate-assisted single-slope solar still via Taguchi Approach. Journal of Renewable 8:13–19
Dhivagar R, Mohanraj M (2021b) Performance improvements of single slope solar still using graphite plate fins and magnets. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:20499–20516. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11737-5
Dhivagar R, Sundararaj S (2018) A review on methods of productivity improvement in solar desalination. Appl Mech Mater 877:414–429. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.877.414
Dhivagar R, Sundararaj S (2019) Thermodynamic and water analysis on augmentation of a solar still with copper tube heat exchanger in coarse aggregate. J Therm Anal Calorim 136:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7746-1
Dhivagar R, Mohanraj M, Hidouri K, Belyayev Y (2020) Energy, exergy, economic and enviro-economic (4E) analysis of gravel coarse aggregate sensible heat storage-assisted single-slope solar still. J Therm Anal Calorim 145:475–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09766-w
Dhivagar R, Mohanraj M, Hidouri K, Midhun M (2021a) CFD modeling of a gravel coarse aggregate sensible heat storage assisted single slope solar still. Desalin Water Treat 210:54–69. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.26554
Dhivagar R, Mohanraj M, Raj P, Gopidesi RK (2021b) Thermodynamic analysis of single slope solar still using graphite plates and block magnets at seasonal climatic conditions. Water Sci Technol:1–17. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.156
Dsilva Winfred Rufuss D, Iniyan S, Suganthi L, Davies PA (2016) Solar stills: a comprehensive review of designs, performance and material advances. Renew Sust Energ Rev 63:464–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.05.068
Dumka P, Sharma A, Kushwah Y, Raghav AS, Mishra DR (2019) Performance evaluation of single slope solar still augmented with sand-filled cotton bags. Journal of Energy Storage 25:100888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2019.100888
Dumka P, Chauhan R, Mishra DR (2020) Experimental and theoretical evaluation of a conventional solar still augmented with jute covered plastic balls. Journal of Energy Storage 32:101874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101874
Durkaieswaran P, Murugavel KK (2015) Various special designs of single basin passive solar still - a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 49:1048–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.111
El-Sebaii AA, El-Bialy E (2015) Advanced designs of solar desalination systems: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 49:1198–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.161
Esfahani JA, Rahbar N, Lavvaf M (2011) Utilization of thermoelectric cooling in a portable active solar still - an experimental study on winter days. Desalination 269:198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.10.062
Fathy M, Hassan H, Salem Ahmed M (2018) Experimental study on the effect of coupling parabolic trough collector with double slope solar still on its performance. Sol Energy 163:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.01.043
Gad HE, Shams El-Din S, Hussien AA, Ramzy K (2015) Thermal analysis of a conical solar still performance: an experimental study. Sol Energy 122:900–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2015.10.016
Holman JP (2007) Experimental methods for engineers. The McGraw-Hill Companies
Kabeel AE, Abdelgaied M (2016) Improving the performance of solar still by using PCM as a thermal storage medium under Egyptian conditions. Desalination. 383:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.01.006
Kabeel AE, Abdelgaied M (2017) Observational study of modified solar still coupled with oil serpentine loop from cylindrical parabolic concentrator and phase changing material under basin. Sol Energy 144:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.01.007
Kabeel AE, El-Agouz SA, Sathyamurthy R, Arunkumar T (2018a) Augmenting the productivity of solar still using jute cloth knitted with sand heat energy storage. Desalination 443:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.05.026
Kabeel AE, El-Samadony YAF, El-Maghlany WM (2018b) Comparative study on the solar still performance utilizing different PCM. Desalination 432:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.01.016
Khalifa AJN, Hamood AM (2009) On the verification of the effect of water depth on the performance of basin type solar stills. Sol Energy 83:1312–1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2009.04.006
Khechekhouche A, Manokar AM, Sathyamurthy R, Essa FA, Sadeghzadeh M, Issakhov A (2021) Energy, exergy analysis, and optimizations of collector cover thickness of a solar still in El Oued Climate, Algeria. International Journal of Photoenergy 2021:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6668325
Kumar S, Tiwari GN (2009) Estimation of internal heat transfer coefficients of a hybrid (PV/T) active solar still. Sol Energy 83:1656–1667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2009.06.002
Manchanda H, Kumar M (2015) A comprehensive decade review and analysis on designs and performance parameters of passive solar still. Renewables: Wind, Water, and Solar 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40807-015-0019-8
Manokar AM, Winston DP, Mondol JD, Sathyamurthy R, Kabeel AE, Panchal H (2018) Comparative study of an inclined solar panel basin solar still in passive and active mode. Sol Energy 169:206–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.04.060
Modi KV, Modi JG (2019) Performance of single-slope double-basin solar stills with small pile of wick materials. Appl Therm Eng 149:723–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.12.071
Mohammed AH, Attalla M, Shmroukh AN (2021) Performance enhancement of single-slope solar still using phase change materials. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:17098–17108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12096-x
Muthu Manokar A, Kalidasa Murugavel K, Esakkimuthu G (2014) Different parameters affecting the rate of evaporation and condensation on passive solar still - a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 38:309–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.05.092
Natarajan SK, Kamran F, Ragavan N, Rajesh R, Jena RK, Suraparaju SK (2019a) Analysis of PEM hydrogen fuel cell and solar PV cell hybrid model. Materials Today: Proceedings 17:246–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.06.426
Natarajan SK, Kousik Suraparaju S, Elavarasan E, Arjun Singh K (2019b) Performance analysis of solar photovoltaic panel at Karaikal weather conditions. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 312. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/312/1/012007
Natarajan SK, Kumar A, Mohamed R, Rathna R, Mondal S, Suraparaju SK (2019c) Design and development of dual axis sun tracking system for floating PV plant. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 312. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/312/1/012001
Natarajan SK, Raviteja B, Sri Harshavardhan D et al (2019d) Numerical study of natural convection in flat receiver with and without secondary reflector for solar parabolic dish system. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 312. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/312/1/012020
Nayi KH, Modi KV (2020) Effect of cost-free energy storage material and saline water depth on the performance of square pyramid solar still: a mathematical and experimental study. J Therm Anal Calorim 144:1351–1368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09598-8
Panchal H, Patel P, Patel N, Thakkar H (2017) Performance analysis of solar still with different energy-absorbing materials. International Journal of Ambient Energy 38:224–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2015.1086683
Patel SK, Kumar B, Pal P, Dev R, Singh D (2020) Production of potable water from Gomti River by using modified double slope solar still with external mounted reflectors. Sol Energy 209:576–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2020.09.036
Raj G, Prabhansu D, Kumar R, Chandra P, Saurabh S (2020) Experimental study of solar still augmented with low-cost energy absorbing and releasing materials. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization and Environmental Effects 42:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1587054
Ravi Kumar K, Krishna Chaitanya NVV, Sendhil Kumar N (2021) Solar thermal energy technologies and its applications for process heating and power generation – a review. J Clean Prod 282:125296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125296
Sahota L, Tiwari GN (2016) Effect of Al2O3 nanoparticles on the performance of passive double slope solar still. Sol Energy 130:260–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2016.02.018
Sakthivel TG, Arjunan TV (2019) Thermodynamic performance comparison of single slope solar stills with and without cotton cloth energy storage medium. J Therm Anal Calorim 137:351–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7909-0
Sakthivel M, Shanmugasundaram S, Alwarsamy T (2010) An experimental study on a regenerative solar still with energy storage medium - Jute cloth. Desalination 264:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.06.074
Sampathkumar A, Natarajan SK (2021) Experimental investigation on productivity enhancement in single slope solar still using borassus flabellifer micro-sized particles. Mater Lett 299:130097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130097
Sathish Kumar TR, Jegadheeswaran S, Chandramohan P (2019) Performance investigation on fin type solar still with paraffin wax as energy storage media. J Therm Anal Calorim 136:101–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7882-7
Sathyamurthy R, El-Agouz E (2019) Experimental analysis and exergy efficiency of a conventional solar still with Fresnel lens and energy storage material. Heat Transfer - Asian Research 48:885–895. https://doi.org/10.1002/htj.21412
Selvaraj K, Natarajan A (2018) Factors influencing the performance and productivity of solar stills - a review. Desalination 435:181–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.09.031
Shalaby SM, El-Bialy E, El-Sebaii AA (2016) An experimental investigation of a v-corrugated absorber single-basin solar still using PCM. Desalination 398:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.07.042
Sharon H, Reddy KS (2015) A review of solar energy driven desalination technologies. Renew Sust Energ Rev 41:1080–1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.09.002
Singh HN, Tiwari GN (2004) Monthly performance of passive and active solar stills for different Indian climatic conditions. Desalination 168:145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2004.06.180
Singh DB, Tiwari GN, Al-Helal IM et al (2016) Effect of energy matrices on life cycle cost analysis of passive solar stills. Sol Energy 134:9–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2016.04.039
Suraparaju SK, Natarajan SK (2020) Performance analysis of single slope solar desalination setup with natural fibre. Desalin Water Treat 193:64–71. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25679
Suraparaju SK, Natarajan SK (2021a) Experimental investigation of single-basin solar still using solid staggered fins inserted in paraffin wax PCM bed for enhancing productivity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:20330–20343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11980-w
Suraparaju SK, Natarajan SK (2021b) Productivity enhancement of single-slope solar still with novel bottom finned absorber basin inserted in phase change material (PCM): techno-economic and enviro-economic analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13495-4
Suraparaju SK, Sampathkumar A, Natarajan SK (2021) Experimental and economic analysis of energy storage - based single - slope solar still with hollow - finned absorber basin. Heat Transfer:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/htj.22136
Tanaka H, Nakatake Y (2009) Increase in distillate productivity by inclining the flat plate external reflector of a tilted-wick solar still in winter. Sol Energy 83:785–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2008.12.001
UNESCO (2019) The United Nations World Water Development Report 2019: Leaving no one behind.
Vigneswaran VS, Kumaresan G, Dinakar BV, Kamal KK, Velraj R (2019) Augmenting the productivity of solar still using multiple PCMs as heat energy storage. Journal of Energy Storage 26:101019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2019.101019
Winfred Rufuss DD, Iniyan S, Suganthi L, Pa D (2017) Nanoparticles enhanced phase change material (NPCM) as heat storage in solar still application for productivity enhancement. Energy Procedia 141:45–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.11.009
Yadav S, Sudhakar K (2015) Different domestic designs of solar stills: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 47:718–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.03.064
Ziabari FB, Sharak AZ, Moghadam H, Tabrizi FF (2013) Theoretical and experimental study of cascade solar stills. Sol Energy 90:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2012.12.019
Units
mL millilitre
mm millimetre
cmcentimetre
m metre
L litre
°C degree Celsius
Other abbreviations
p.y potable water yield
λ latent heat of vaporization of water
Ab area of the absorber basin
G.R global solar radiation
∆t duration of the cumulative readings in sec
uη uncertainty of the efficiency
udw uncertainty in instantaneous productivity
I(t) radiation at a particular time
Wr total uncertainty
R function
w,x independent variables
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Subbarama Kousik Suraparaju—conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing (original draft).
Ramasamy Dhivagar—conceptualization, data curation, methodology, writing (original draft).
Sendhil Kumar Natarajan—conceptualization, validation, resources, writing (review and editing), supervision, project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(XLSX 15 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suraparaju, S.K., Ramasamy, D. & Natarajan, S.K. Augmentation of freshwater productivity in a single-slope solar still using ball marbles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 65974–65986 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15117-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15117-5