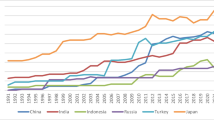
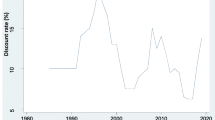
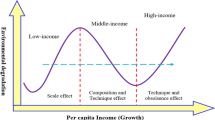
Abstract
This study aims to re-examine the impacts of monetary and fiscal policy on environmental quality in ASEAN countries from 1990 to 2019. We utilized the panel and time series NARDL approach to explore the long-run and short-run estimates at a regional level and country level. ASEAN regional-wise analysis shows that contractionary monetary policy reduces the CO2 emissions, while expansionary monetary policy enhances CO2 emissions in the long run. The long-run coefficient further confirms that expansionary fiscal policy mitigates CO2 emissions in ASEAN. The impact of expansionary monetary and fiscal policy on CO2 emissions is positive and significant, while contractionary monetary and fiscal policy have an insignificant impact on CO2 emissions in the short run. ASEAN country-wise analysis also reported the country-specific estimates for the short and long run. Some policies can redesign in light of these novel findings in ASEAN economies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets/materials used and/or analyzed for the present manuscript are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adewuyi AO (2016) Effects of public and private expenditures on environmental pollution: a dynamic heterogeneous panel data analysis. Renew Sust Energ Rev 65:489–506
Ahmad M, Ul Haq Z, Khan Z, Khattak SI, Rahman ZU, Khan S (2019) Does the inflow of remittances cause environmental degradation? Empirical evidence from China. Economic research-Ekonomska istraživanja 32(1):2099–2121
Annicchiarico B, Di Dio F (2017) GHG emissions control and monetary policy. Environ Resour Econ 67(4):823–851
Aslam B, Hu J, Hafeez M, Ma D, AlGarni TS, Saeed M, Abdullah MA, Hussain S (2021a) Applying environmental Kuznets curve framework to assess the nexus of industry, globalization, and CO2 emission. Environ Technol Innov 21:101377
Aslam B, Hu J, Majeed MT, Andlib Z, Ullah S (2021b) Asymmetric macroeconomic determinants of CO 2 emission in China and policy approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–14
Balcilar M, Ciftcioglu S, Gungor H (2016) The effects of financial development on Investment in Turkey. Singap Econ Rev 61(4):1650002–16500018
Chan YT (2020) Are macroeconomic policies better in curbing air pollution than environmental policies? A DSGE approach with carbon-dependent fiscal and monetary policies. Energy Policy 141:111454–111468
Chen C, Pan D (2020) The OptimalMix ofMonetary and Climate Policy. MPRA Paper No 97718
Chishti MZ, Ullah S, Ozturk I, Usman A (2020) Examining the asymmetric effects of globalization and tourism on pollution emissions in South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:27721–27737
Chishti MZ, Ahmad M, Rehman A, Khan MK (2021) Mitigations pathways towards sustainable development: assessing the influence of fiscal and monetary policies on carbon emissions in BRICS economies. J Clean Prod 292:126035
Dar JA, Asif M (2017) Is financial development good for carbon mitigation in India? A regime shift-based cointegration analysis. Carbon Management 8(5-6):435–443
Dongyan L (2009) Fiscal and tax policy support for energy efficiency retrofit for existing residential buildings in China’s northern heating region. Energy Policy 37(6):2113–2118
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377
Halkos GE, Paizanos EΑ (2013) The effect of government expenditure on the environment: an empirical investigation. Ecol Econ 91:48–56
Halkos GE, Paizanos EΑ (2016) The effects of fiscal policy on CO2 emissions: evidence from the USA. Energy Policy 88:317–328
Harper S (2013) Population–environment interactions: European migration, population composition and climate change. Environ Resour Econ 55(4):525–541
He L, Shen J, Zhang Y (2018) Ecological vulnerability assessment for ecological conservation and environmental management. J Environ Manag 206:1115–1125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.11.059
He L, Shao F, Ren L (2020) Sustainability appraisal of desired contaminated groundwater remediation strategies: an information-entropy-based stochastic multi-criteria preference model. Environ Dev Sustain 23:1759–1779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00650-z
He X, Zhang T, Xue Q, Zhou Y, Wang H, Bolan NS, Jiang R, Tsang DCW (2021) Enhanced adsorption of Cu(II) and Zn(II) from aqueous solution by polyethyleneimine modified straw hydrochar. Sci Total Environ 778:146116–146116
International Monetary Fund (2019) International Featured Standards 2019. International Monetary Fund Publications
Jalil A, Feridun M (2011) The impact of growth, energy and financial development on the environment in China: a cointegration analysis. Energy Econ 33(2):284–291
Katircioglu S, Katircioglu S (2018) Testing the role of fiscal policy in the environmental degradation: the case of Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(6):5616–5630
Khattak SI, Ahmad M, Khan ZU, Khan A (2020) Exploring the impact of innovation, renewable energy consumption, and income on CO2 emissions: new evidence from the BRICS economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–16
Li J, Hu Z, Shi V, Wang Q (2021a) Manufacturer’s encroachment strategy with substitutable green products. Int J Prod Econ 235:108102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2021.108102
Li X, Yu Z, Salman A, Ali Q, Hafeez M, Aslam MS (2021b) The role of financial development indicators in sustainable development-environmental degradation nexus. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–12
Liu Y, Han L, Yin Z, Luo K (2017) A competitive carbon emissions scheme with hybrid fiscal incentives: the evidence from a taxi industry. Energy Policy 102:414–422
Liu J, Yi Y, Wang X (2020) Exploring factors influencing construction waste reduction: a structural equation modeling approach. J Clean Prod 123185:123185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123185
Lopez R E, Palacios A (2010) Have government spending and energy tax policies contributed to make Europe environmentally cleaner? Working paper no 1667-2016-136345
Lopez R, Galinato GI, Islam A (2011) Fiscal spending and the environment: theory and empirics. J Environ Econ Manag 62(2):180–198
Lv Z, Xu T (2019) Trade openness, urbanization and CO2 emissions: dynamic panel data analysis of middle-income countries. The Journal of International Trade & Economic Development 28(3):317–330
McAusland C (2008) Trade, politics, and the environment: Tailpipe vs. smokestack. J Environ Econ Manag 55(1):52–71
Mirzaei M, Bekri M (2017) Energy consumption and CO2 emissions in Iran, 2025. Environ Res 154:345–351
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Rausch S (2013) Fiscal consolidation and climate policy: an overlapping generation’s perspective. Energy Econ 40:S134–S148
Shahbaz M, Mallick H, Mahalik MK, Sadorsky P (2016) The role of globalization on the recent evolution of energy demand in India: implications for sustainable development. Energy Econ 55:52–68
Shin Y, Yu B, Greenwood-Nimmo M (2014) Modelling asymmetric cointegration and dynamic multipliers in a nonlinear ARDL framework. In: Festschrift in honor of Peter Schmidt. Springer, New York, pp 281–314
Sun G, Yuan C, Hafeez M, Raza S, Jie L, Liu X (2020) Does regional energy consumption disparities assist to control environmental degradation in OBOR: an entropy approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(7):7105–7119
Tian P, Lu H, Feng W, Guan Y, Xue Y (2020) Large decrease in streamflow and sediment load of Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau driven by future climate change: a case study in Lhasa River Basin. Catena (Giessen) 187:104340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104340
Ullah S, Majeed MT, Chishti MZ (2020) Examining the asymmetric effects of fiscal policy instruments on environmental quality in Asian economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(30):38287–38299
Ullah S, Ozturk I, Sohail S (2021) The asymmetric effects of fiscal and monetary policy instruments on Pakistan’s environmental pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(6):7450–7461
Usman A, Ullah S, Ozturk I, Chishti MZ, Zafar SM (2020) Analysis of asymmetries in the nexus among clean energy and environmental quality in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(17):20736–20747
Wang S, Li G, Fang C (2018) Urbanization, economic growth, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions: empirical evidence from countries with different income levels. Renew Sust Energ Rev 81:2144–2159
Yuelan P, Akbar MW, Hafeez M, Ahmad M, Zia Z, Ullah S (2019) The nexus of fiscal policy instruments and environmental degradation
Zhao X, Gu B, Gao F, Chen S (2020) Matching model of energy supply and demand of the integrated energy system in coastal areas. J Coast Res 103(sp1):983. https://doi.org/10.2112/SI103-205.1
Zhao W, Hafeez M, Maqbool A, Ullah S, Sohail S (2021) Analysis of income inequality and environmental pollution in BRICS using fresh asymmetric approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–11
Zuo X, Dong M, Gao F, Tian S (2020) The modeling of the electric heating and cooling system of the integrated energy system in the coastal area. J Coast Res 103(sp1):1022. https://doi.org/10.2112/SI103-213.1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The idea was given by Nafeesa Mughal and Maryam Kashif. Maryam Kashif, Asma Arif, John William Grimaldo Guerrero, Wilson C. Nabua, and Gniewko Niedbala have done the data acquisitions and analysis and written the whole draft. Nafeesa Mughal and Maryam Kashif read and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
I am free to contract any of the people involved in the research to seek further clarification and information.
Consent to publish
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mughal, N., Kashif, M., Arif, A. et al. Dynamic effects of fiscal and monetary policy instruments on environmental pollution in ASEAN. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 65116–65126 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15114-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15114-8