Abstract
Internal combustion engines are the inevitable prime movers in the contemporary engineering era. The suitability of proper bio-fuel and their blends plays a vital role in engine behaviour. This study aims to select smart fuel opus depending on Aegle marmelos (AM) fuel properties with nano additive blends for diesel engines by using intelligent hybrid decision-making tools. Physicochemical properties of CuO and novel graphene nano sheets added bio-oil combinations were studied. The assessment of an appropriate blend depends on the analysis of fuel properties. The Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process (FAHP) integrated with Grey relational analysis (GRA) was employed for optimum fuel blend selection. The FAHP model was used to identify the criteria weights, whereas GRA was hired to rank alternative fuel blends. Pairwise analysis and ranking of the alternatives were compared to get the optimum fuel blend through FAHP and GRA amalgamation. The addition of nanoparticles enhanced engine performance and reduced emission. The obtained ascending order of preference of the bio-oil blends from FAHP and GRA analysis is AC15G15>AG30>AC30>A10>A20. From FAHP, GRA, and engine test results, it is observed that AC15G15 opus is the most suitable fuel blend for diesel engines. Lower fuel consumption (0.37 kg/kW hr) and emissions (CO level of 0.21%, which is 0.34% for diesel, HC value of 134 ppm, which is 184 ppm for diesel) of AC15G15 aids in contributing towards a green and clean environment.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHP:
-
analytical hierarchy process
- AM:
-
Aegle marmelos
- ANOVA:
-
analysis of variance
- ASTM:
-
American society for testing and materials
- A10:
-
AM 10% + diesel 90%
- A20:
-
AM 20% + diesel 80%
- AC30:
-
AM 20% + diesel 80% + CuO 30 ppm
- AG30:
-
AM 20% + diesel 80% + GON 30 ppm
- AC15G15:
-
AM 20% + diesel 80% + CuO 15 ppm + GON 15 ppm
- BSFC:
-
brake specific fuel consumption
- BTE:
-
brake thermal efficiency
- CI:
-
consistency index
- CN:
-
cetane number
- CO:
-
carbon monoxide
- CO2 :
-
carbon dioxide
- CR:
-
consistency ratio
- CuO:
-
copper oxide
- CV:
-
calorific value
- D:
-
density
- DF:
-
degrees of freedom
- FAHP:
-
Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process
- GON:
-
graphene oxide nano sheet
- GRA:
-
grey relational analysis
- GRC (δi):
-
grey relational coefficient
- GRG (ɸi):
-
grey relational grade
- HC:
-
hydro carbons
- i:
-
test number
- IC:
-
internal combustion
- k:
-
comparability sequence
- KV:
-
kinematic viscosity
- MCDM:
-
multi-criteria decision making
- mf:
-
membership function
- n:
-
matrix size
- NOx:
-
oxides of nitrogen
- OA:
-
orthogonal array
- ‘P’ value:
-
probability value
- ppm:
-
parts per million
- RCI:
-
random consistency index
- TFN:
-
triangular fuzzy numbers
- w:
-
Eigen vector
- WC:
-
water content
- λmax:
-
Eigen value
-
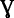 :
: -
distinctive coefficient
References
Babu KA, Venkataramaiah P, Yerrathota S (2018) Material Selection for Preparation of Aluminium Hybrid Mmcs. Mater Today: Proc 5:12209–12222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.02.198
Baranitharan P (2020) Exergy analysis of a diesel engine fuelled with Aegle marmelos de-oiled seed cake pyrolysis oil opus. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 39(5):e13426. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13426
Bhuvanesh Kumar M, Parameshwaran R (2018) Fuzzy integrated QFD, FMEA framework for the selection of lean tools in a manufacturing organisation. Prod Plan Control 29(5):403–417. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2018.1434253
Chinnasamy C, Tamilselvam P, Ranjith R (2019) Influence of aluminum oxide nanoparticle with different particle sizes on the working attributes of diesel engine fueled with blends of diesel and waste plastic oil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:29962–29977. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06139-1
Deshmukh S, Sunnapwar V (2019) Fuzzy analytic hierarchy process (FAHP) for green supplier selection in Indian Industries. Proc Int Conf Intell Manuf Auto:679–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2490-1_63
Devarajan Y, Nagappan B, Subbiah G (2019) A comprehensive study on emission and performance characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with nanoparticle-blended biodiesel. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(11):10662–10672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04446-1
Erdoğan S, Balki MK, Aydın S, Sayin C (2019) The best fuel selection with hybrid multiple-criteria decision making approaches in a CI engine fueled with their blends and pure biodiesels produced from different sources. Renew Energy 134:653–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.11.060
Fu P, Bai X, Yi W, Li Z, Li Y, Wang L (2017) Assessment on performance, combustion and emission characteristics of diesel engine fuelled with corn stalk pyrolysis bio-oil/diesel emulsions with Ce0.7Zr0.3O2 nanoadditive. Fuel Process Technol 167:474–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.07.032
Gitinavard H, Shirazi MA, Zarandi MHF (2020) Sustainable feedstocks selection and renewable products allocation: a new hybrid adaptive utility-based consensus model. J Environ Manag 264:110428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110428
Hosseini SH, Taghizadeh-Alisaraei A, Ghobadian B, Abbaszadeh-Mayvan A (2017) Performance and emission characteristics of a CI engine fuelled with carbon nanotubes and diesel-biodiesel blends. Renew Energy 111:201–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.04.013
Jain SK, Agrawal GD, Gupta K, Misra R (2020) Optimization of performance parameters of stationary VCR diesel engine using hybrid FTOPSIS-FAHP approach. Int J Ambient Energy:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2020.1712246
Julong D (1989) Introduction to grey system theory. J Grey Syst 1(1):1–24
Kavimani V, Prakash KS (2017) Tribological behaviour predictions of r-GO reinforced Mg composite using ANN coupled Taguchi approach. J Phys Chem Solids 110:409–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2017.06.028
Kavimani V, Prakash KS, Thankachan T (2017) Surface characterization and specific wear rate prediction of r-GO/AZ31 composite under dry sliding wear condition. Surfac Interf 6:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2017.01.004
Krishnamoorthi M, Malayalamurthi R, Sakthivel R (2019) Optimization of compression ignition engine fueled with diesel-chaulmoogra oil-diethyl ether blend with engine parameters and exhaust gas recirculation. Renew Energy 134:579–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.11.062
Kumaravel S, Murugesan A, Vijayakumar C, Thenmozhi M (2019) Enhancing the fuel properties of tyre oil diesel blends by doping nano additives for green environments. J Clean Prod 240:118128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118128
Madhu P, Kumar CN, Anojkumar L, Matheswaran M (2018) Selection of biomass materials for bio-oil yield: a hybrid multi-criteria decision making approach. Clean Techn Environ Policy 20(6):1377–1384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-018-1545-z
Mahad N, Yusof N, Ismail N (2019) The application of fuzzy analytic hierarchy process (FAHP) approach to solve multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) problems. J Phys: Conf Series IOP Publ 1358:012081. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1358/1/012081
Manigandan S, Sarweswaran R, Devi PB, Sohret Y, Kondratiev A, Venkatesh S, Vimal MR, Joshua JJ (2020) Comparative study of nanoadditives TiO2, CNT, Al2O3, CuO, and CeO2 on reduction of diesel engine emission operating on hydrogen fuel blends. Fuel 262:116336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116336
Mathimani T, Baldinelli A, Rajendran K, Prabakar D, Matheswaran M, van Leeuwen RP, Pugazhendhi A (2019) Review on cultivation and thermochemical conversion of microalgae to fuels and chemicals: process evaluation and knowledge gaps. J Clean Prod 208:1053–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.096
Paramasivam B, Kasimani R, Rajamohan S (2018) Characterization of pyrolysis bio-oil derived from intermediate pyrolysis of Aegle marmelos de-oiled cake: study on performance and emission characteristics of CI engine fueled with Aegle marmelos pyrolysis oil-blends. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(33):33806–33819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3319-x
Peer MS, Peer MN (2019) Experimental investigation on engine characteristics fueled with waste HDPE oil and study on NO x emission variation using thermal imager. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(4):3436–3446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3830-0
Pradhan D, Bendu H, Singh R, Murugan S (2017) Mahua seed pyrolysis oil blends as an alternative fuel for light-duty diesel engines. Energy 118:600–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.10.091
Purushothaman P, Masimalai S, Subramani V (2021) Effective utilization of mahua oil blended with optimum amount of Al2 O3 and TiO2 nanoparticles for better performance in CI engine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:11893–11903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07926-x
Quesada L, Pérez A, Godoy V, Peula F, Calero M, Blázquez G (2019) Optimization of the pyrolysis process of a plastic waste to obtain a liquid fuel using different mathematical models. Energy Convers Manag 188:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.03.054
Rajamohan S, Kasimani R (2018) Analytical characterization of products obtained from slow pyrolysis of Calophyllum inophyllum seed cake: study on performance and emission characteristics of direct injection diesel engine fuelled with bio-oil blends. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(10):9523–9538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1241-x
Rajamohan S, Marshal JJ, Suresh S (2021) Derivation of synthetic fuel from waste plastic: investigation of engine operating characteristics on DI diesel engine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:11976–11987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08625-3
Rajeswari B, Amirthagadeswaran KS (2017) Experimental investigation of machinability characteristics and multiresponseoptimization of end milling in aluminium composites using RSM based grey relational analysis. Measurement 105:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.04.014
Sachuthananthan B, Krupakaran R, Balaji G (2019) Exploration on the behaviour pattern of a DI diesel engine using magnesium oxide nano additive with plastic pyrolysis oil as alternate fuel. Int J Ambient Energy 42:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2018.1563812
Sakthivel G, Sivaraja C, Ikua BW (2019) Prediction OF CI engine performance, emission and combustion parameters using fish oil as a biodiesel by fuzzy-GA. Energy 166:287–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.10.023
Satty TL (2001) Fundamentals of the analytic hierarchy process. In: The analytic hierarchy process in natural resource and environmental decision making. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 15–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-9799-9_2
Sidhu SS, Bains PS, Yazdani M, Zolfaniab SH (2018) Application of MCDM techniques on nonconventional machining of composites. In: Futuristic Compos, pp 127–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2417-8_6
Sivaraja C, Sakthivel G, Warke VR (2018) Selection of optimum fuel blend to empower the energy efficiency in IC engine using decision system. Energy Sourc A: Recov Utiliz Environ Effect 40(6):693–708. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2018.1454551
Sudhagar S, Sakthivel M, Mathew PJ, Daniel SAA (2017) A multi criteria decision making approach for process improvement in friction stir welding of aluminium alloy. Measurement 108:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.05.023
Tamilvanan A, Balamurugan K, Vijayakumar M (2019) Effects of nano-copper additive on performance, combustion and emission characteristics of Calophyllum inophyllum biodiesel in CI engine. J Therm Anal Calorim 136:317–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7743-4
Varatharajulu M, Duraiselvam M, Kumar KA, Kanniyan CG, Sathiyamurthy R (2020) Experimental investigation of the effect of independent parameters in the face milling of aluminum 6082 alloy. Trans Indian Inst Metals 74:659–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02161-x
Vellaiyan S (2019) Enhancement in combustion, performance, and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with diesel, biodiesel, and its blends by using nanoadditive. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(10):9561–9573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04356-2
Vellaiyan S, Subbiah A, Chockalingam P (2019) Multi-response optimization to obtain better performance and emission level in a diesel engine fueled with water-biodiesel emulsion fuel and nanoadditive. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(5):4833–4841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3979-6
Venugopal P, Kasimani R, Chinnasamy S (2018) Prediction and optimization of CI engine performance fuelled with Calophylluminophyllum diesel blend using response surface methodology (RSM). Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:24829–24844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04164-8
Vinodh S, Prasanna M, Prakash NH (2014) Integrated Fuzzy AHP–TOPSIS for selecting the best plastic recycling method: a case study. Appl Math Model 38:4662–4672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2014.03.007
Wang B, Song J, Ren J, Li K, Duan H (2019) Selecting sustainable energy conversion technologies for agricultural residues: a fuzzy AHP-VIKOR based prioritization from life cycle perspective. Resour Conserv Recycl 142:78–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.11.011
Wang Y, Xu L, Solangi YA (2020) Strategic renewable energy resources selection for Pakistan: Based on SWOT-Fuzzy AHP approach. Sustain Cities Soc 52:101861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101861
Yessian S, Varthanan PA (2020) Optimization of performance and emission characteristics of catalytic coated ic engine with biodiesel using Grey-taguchi Method. Sci Rep 10(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57129-9
Yoram W, Satty TL (1980) Marketing applications of the analytic hierarchy process. Manag Sci 26(7):641–658 https://www.jstor.org/stable/2630699
Zadeh LA (1978) Fuzzy sets as a basis for a theory of possibility. Fuzzy Sets Syst 1:3–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(78)90029-5
Zhang J, Zhou Q, Lin J, Li W, Tang Z, Duan C (2019) A fuzzy-based analytic hierarchy process for mechanical noise source identification of a diesel engine. Shock Vib 2019:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2854836
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Dr.Mini Shaji Thomas, Director, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli-620015, for her support.
Data and materials availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BP considered the research concept, designed the research methodology, and wrote the original draft of this manuscript. KS contributed to exploring the result outcomes, providing supervision for research performance, and editing this manuscript’s draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paramasivam, B., Somasundaram, K. Selection of smart fuel opus for diesel engine depending on their fuel characteristics: an intelligent hybrid decision-making approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 62216–62234 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14928-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14928-w





 :
: