Abstract
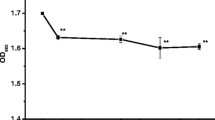
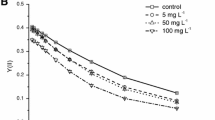
To elucidate the mechanism of succinic acid (SA) inhibition of Microcystis aeruginosa, the chlorophyll fluorescence transients, photosynthesis, photosynthetic electron transport activity, and gene expression of M. aeruginosa were evaluated under various doses of SA. The results demonstrated that, after treatment with 60 mg L−1 SA for 1 h, the chlorophyll fluorescence transients and related parameters changed significantly, indicating that the function and structure of photosynthetic apparatuses of Microcystis were seriously damaged. The initial quantum efficiency α, maximum net photosynthetic rate Pnmax, dark respiration rate Rd, and gross photosynthetic rate decreased to 57%, 49%, 49%, and 46%, respectively, relative to the control. Furthermore, photosystem II (PSII) activity (H2O→p-BQ) and the electron transport activity of H2O→MV and DPC→MV significantly decreased. Real-time PCR analysis revealed that, following incubation with 60 mg L−1 SA for 24 h, the expression level of core protein genes (psbA, psaB, psbD, and psbO) of the photosynthesis centers photosystem I (PSI) and PSII decreased significantly. However, the transcription of gene nblA encoding phycobilisome degradation protein was elevated. The downregulation of the rbcL gene, which encodes the large subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco), resulted in the suppression of CO2 fixation and assimilation. High concentration (60 mg L−1) of SA resulted in damage to oxygen-evolving complex (OEC) and reaction center of PSII, blocking photosynthetic electron transport, thereby lowering the rate photosynthesis and inhibiting the growth of Microcystis. We concluded that inhibition of photosynthesis is an important mechanism of SA inhibition in M. aeruginosa.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Amorim CA, Moura AN (2020) Effects of the manipulation of submerged macrophytes, large zooplankton, and nutrients on a cyanobacterial bloom: a mesocosm study in a tropical shallow reservoir. Environ Pollut 265:114997
Canton MC, Holguin FO, Boeing WJ (2019) Alkaloid gramine to control algal invaders: algae inhibition and gramine persistence. Bioresource Technol Rep 7:100304
Che X, Ding R, Li Y, Zhang Z, Gao H, Wang W (2018) Mechanism of long-term toxicity of CuO NPs to microalgae. Nanotoxicology. 12:923–939
Chen Q, Zhu B, Sun D, Liu W, Sun X, Duan S (2020) The effect of protocatechuic acid on the phycosphere in harmful algal bloom species Scrippsiella trochoidea. Aquat Toxicol 227:105591
Cheng L, He Y, Tian Y, Liu B, Zhang Y, Zhou Q, Wu Z (2017) Comparative biotoxicity of N-phenyl-1-naphthylamine and N-phenyl-2-naphthylamine on cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa. Chemosphere. 176:183–191
Dong J, Chang M, Li C, Dai D, Gao Y (2019) Allelopathic effects and potential active substances of Ceratophyllum demersum L. on Chlorella vulgaris Beij. Aquat Ecol 53:651–663
Gao YN, Ge FJ, Zhang LP, He Y, Lu ZY, Zhang YY, Liu BY, Zhou QH, Wu ZB (2017) Enhanced toxicity to the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa by low-dosage repeated exposure to the allelochemical N-phenyl-1-naphthylamine. Chemosphere. 174:732–738
Han M, Wang R, Ding N, Liu X, Zheng N, Fu B, Sun L, Gao P (2018) Reactive oxygen species-mediated caspase-3 pathway involved in cell apoptosis of Karenia mikimotoi induced by linoleic acid. Algal Res 36:48–56
Hou X, Huang J, Tang J, Wang N, Zhang L, Gu L, Sun Y, Yang Z, Huang Y (2019) Allelopathic inhibition of juglone (5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone) on the growth and physiological performance in Microcystis aeruginosa. J Environ Manag 232:382–386
Hua Q, Liu Y, Yan Z, Zeng G, Liu S, Wang W, Tan X, Deng J, Tang X, Wang Q (2018) Allelopathic effect of the rice straw aqueous extract on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:953–959
Huang H, Xiao X, Ghadouani A, Wu J, Nie Z, Peng C, Xu X, Shi J (2015) Effects of natural flavonoids on photosynthetic activity and cell integrity in Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxins. 7:66–80
Kong W, Huang S, Liu X, Tang T (2018) Establishment and application of a non-destructive method for measurement of constructed wetlands plant. Chin J Environ Eng 12:356–364
Li J, Hu J, Cao L, Yuan Y (2020a) Growth, physiological responses and microcystin-production/-release dynamics of Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to various luteolin doses. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 196:110540
Li J, Liu Y, Zhang P, Zeng G, Cai X, Liu S, Yin Y, Hu X, Hu X, Tan X (2016) Growth inhibition and oxidative damage of Microcystis aeruginosa induced by crude extract of Sagittaria trifolia tubers. J Environ Sci 43:40–47
Li N, Tong M, Glibert PM (2020b) Effect of allelochemicals on photosynthetic and antioxidant defense system of Ulva prolifera. Aquat Toxicol 224:105513
Liu L, Zhang S, Dai W, Bi X, Zhang D (2019) Comparing effects of berberine on the growth and photosynthetic activities of Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Water Sci Technol 80:1155–1162
Liu R, Ran X, Bai F, Xu J, Yang S, Shi J, Wu Z (2015) Use of chlorophyll a fluorescence to elucidate the toxicity target of N-phenyl-2-naphthylamine on photosynthetic system of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria). Phycologia. 54:12–19
Lu Y, Wang J, Yu Y, Shi L, Kong F (2014) Changes in the physiology and gene expression of Microcystis aeruginosa under EGCG stress. Chemosphere. 117:164–169
Mao F, He Y, Gin KY (2020) Antioxidant responses in cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa caused by two commonly used UV filters, benzophenone-1 and benzophenone-3, at environmentally relevant concentrations. J Hazard Mater 396:122587
Markou G, Depraetere O, Muylaert K (2016) Effect of ammonia on the photosynthetic activity of Arthrospira and Chlorella: a study on chlorophyll fluorescence and electron transport. Algal Res 16:449–457
Men Y, Hu H, Li F (2007) Effects of the novel allelochemical ethyl 2-methylacetoacetate from the reed (Phragmitis australis Trin) on the growth of several common species of green algae. J Appl Phycol 19:521–527
Ni L, Rong S, Gu G, Hu L, Wang P, Li D, Yue F, Wang N, Wu H, Li S (2018) Inhibitory effect and mechanism of linoleic acid sustained-release microspheres on Microcystis aeruginosa at different growth phases. Chemosphere. 212:654–661
Paunov M, Koleva L, Vassilev A, Vangronsveld J, Goltsev V (2018) Effects of different metals on photosynthesis: cadmium and zinc affect chlorophyll fluorescence in durum wheat. Int J Mol Sci 19:787–799
Qian H, Pan X, Shi S, Yu S, Jiang H, Lin Z, Fu Z (2011) Effect of nonylphenol on response of physiology and photosynthesis-related gene transcription of Chlorella vulgaris. Environ Monit Assess 182:61–69
Qian H, Xu J, Lu T, Zhang Q, Qu Q, Yang Z, Pan X (2018) Responses of unicellular alga Chlorella pyrenoidosa to allelochemical linoleic acid. Sci Total Environ 625:1415–1422
Qian Y, Li X, Tian R (2019) Effects of aqueous extracts from the rhizome of Pontederia cordata on the growth and interspecific competition of two algal species. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 168:401–407
Rivas-Ubach A, Poret-Peterson AT, Peñuelas J, Sardans J, Pérez-Trujillo M, Legido-Quigley C, Oravec M, Urban O, Elser JJ (2018) Coping with iron limitation: a metabolomic study of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Acta Physiol Plant 40:1–13
Shao J, Liu D, Gong D, Zeng Q, Yan Z, Gu J (2013) Inhibitory effects of sanguinarine against the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa NIES-843 and possible mechanisms of action. Aquat Toxicol 142-143:257–263
Shao J, Wu X, Li R (2009) Physiological responses of Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 to nonanoic acid stress. Environ Toxicol 24:610–617
Takahashi S, Badger MR (2011) Photoprotection in plants: a new light on photosystem II damage. Trends Plant Sci 16:53–60
Wang H, Kong H, Zhang L (2017) Determination of polyphenol content and antialgal activities of typical emergent plants. Saf Environ Eng 24:75–78
Wang J, Chen Z, Chen H, Wen Y (2018) Effect of hydrogen peroxide on Microcystic aeruginosa: role of cytochromes P450. Sci Total Environ 626:211–218
Wang J, Liu Q, Feng J, Lv J, Xie S (2016a) Effect of high-doses pyrogallol on oxidative damage, transcriptional responses and microcystins synthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa TY001 (Cyanobacteria). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 134:273–279
Wang J, Liu Q, Feng J, Lv J, Xie S (2016b) Photosynthesis inhibition of pyrogallol against the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa TY001. Pol J Environ Stud 25:2601–2608
Wu X, Wu H, Wang S, Wang Y, Zhang R, Hu X, Ye J (2018) Effect of propionamide on the growth of Microcystis flos-aquae colonies and the underlying physiological mechanisms. Sci Total Environ 630:526–535
Xu L, Tian R (2019) Effects of succinic acid, an allelopathic substance of Pontederi cordata, on the growth and competition of Microcystis aeruginosa and Scenedesmus obliquus. Chin J Ecol 38:770–777
Ye Z, Ling Y, Yu Q, Duan H, Kang H, Huang G, Duan S, Chen X, Liu Y, Zhou S (2020) Quantifying light response of leaf-scale water-use efficiency and its interrelationships with photosynthesis and stomatal conductance in C3 and C4 species. Front Plant Sci 11:374
Yuan R, Li Y, Li J, Ji S, Wang S, Kong F (2020) The allelopathic effects of aqueous extracts from Spartina alterniflora on controlling the Microcystis aeruginosa blooms. Sci Total Environ 712:136332
Zhang C, Ling F, Yi Y, Zhang H, Wang G (2014) Algicidal activity and potential mechanisms of ginkgolic acids isolated from Ginkgo biloba exocarp on Microcystis aeruginosa. J Appl Phycol 26:323–332
Zhao P, Liu S, Huang W, He L, Li J, Zhou J, Zhou J (2020a) Influence of eugenol on algal growth, cell physiology of cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa and its interaction with signaling molecules. Chemosphere. 255:126935
Zhao P, Wang Y, Huang W, He L, Lin Z, Zhou J, He Q (2020b) Toxic effects of terpinolene on Microcystis aeruginosa: physiological, metabolism, gene transcription, and growth effects. Sci Total Environ 719:137376
Zhong X, Li Y, Che X, Zhang Z, Li Y, Liu B, Li Q, Gao H (2019) Significant inhibition of photosynthesis and respiration in leaves of Cucumis sativus L. by oxybenzone, an active ingredient in sunscreen. Chemosphere. 219:456–462
Zhu J, Liu B, Wang J, Gao Y, Wu Z (2010) Study on the mechanism of allelopathic influence on cyanobacteria and chlorophytes by submerged macrophyte (Myriophyllum spicatum) and its secretion. Aquat Toxicol 98:196–203
Zhu X, Dao G, Tao Y, Zhan X, Hu H (2021) A review on control of harmful algal blooms by plant-derived allelochemicals. J Hazard Mater 401:123403
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31670698). We also thank the LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31670698).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YDC and RNT conceived and designed the study; YDC, YZ, and CZ performed the experiments; YDC, YZ, and JPX contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vitor Vasconcelos
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 50 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Yd., Zhu, Y., Xin, Jp. et al. Succinic acid inhibits photosynthesis of Microcystis aeruginosa via damaging PSII oxygen-evolving complex and reaction center. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 58470–58479 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14811-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14811-8