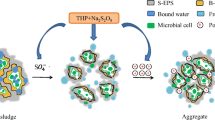
Abstract
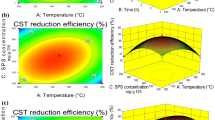
Sewage sludge (SS) dewatering is a key step in sludge disposal, which plays an important role in reducing sludge volume, facilitating transportation and subsequent treatment. In this paper, a facile hydrothermal-alkaline treatment for SS was proposed, which can be used for sludge dewatering and humic acid (HA) recycling at the same time. Response surface methodology (RSM) was used to determine the optimal conditions, and a mathematical model was established to accurately predict the changes of sludge water content and the extraction rate of HA. Under the optimal conditions of 170 °C/42 min/0.05 (for hydrothermal temperature, hydrothermal time, and mass ratio of KOH to wet sludge, respectively), the water content decreased to 46.7% and the extraction rate of HA (with a purity of 96.2%) was 89.1%. The improvement of the dewatering performance effectively facilitates the subsequent disposal of the sludge. The hydrothermal-alkaline method not only realizes the efficient dehydration of the sludge, but also obtains HA from the sludge extract. The obtained HA has potential economic value in the fields of agriculture, biological medicine, environment, and the like.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels L, Baeyens J, Degrèveet J, Dewil R (2008) Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog Energy Combust 34:755–781
Aranganathan L, Rajasree SRR, Suman TY (2019) Comparison of molecular characteristics of Type A humic acids derived from fish waste and sugarcane bagasse co-compost influenced by various alkaline extraction protocols. Microchem J 149:104038
Cassini ST, Andrade MCE, Abreu TA, Keller R, Goncalves RF (2006) Alkaline and acid hydrolytic processes in aerobic and anaerobic sludges: effect on total EPS and fractions. Water Sci Technol 5:51–58
Chen N, Tao SY, Xiao KK, Liang SY, Yang JK, Zhang LZ (2020) A one-step acidification strategy for sewage sludge dewatering with oxalic acid. Chemosphere 238:124598
Cheng X, Zhang HB, Hu JL, Feng LF, Gu XP, Jean-Pierre C (2018) Characterization of broad molecular weight distribution polyethylene with multi-detection gel permeation chromatography. Polym Test 67:213–217
Cristina G, Camelin E, Ottone C, Fraterrigo Garofalo S, Jorquera L, Castro M, Fino D, Schiappacasse MC, Tommasi T (2020) Recovery of humic acids from anaerobic sewage sludge: extraction, characterization and encapsulation in alginate beads. Int J Biol Macromol 164:277–285
Deng W, Ma J, Xiao J, Wang X, Su Y (2017) Orthogonal experimental study on hydrothermal treatment of municipal sewage sludge for mechanical dewatering followed by thermal drying. J Clean Prod 209:236–249
Dewil R, Baeyens J, Appels L (2007) Enhancing the use of waste activated sludge as bio-fuel through selectively reducing its heavy metal content. J Hazard Mater 144:703–707
Ding F, He Z, Liu S, Zhang S, Zhao F, Li Q, Stoffella PJ (2016) Heavy metals in composts of China: historical changes, regional variation, and potential impact on soil quality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:3194–3209
El Hayany B, El Fels L, Ouhdouch Y, Hafidi M (2021) Fate of pathogenic microorganisms during lagooning sludge composting and exploration of bacteriophages as indicator of hygienization. Environ Technol Innov 21:101268
Figueiredo CCD, Chagas JKM, Da Silva J, Paz-Ferreiro J (2019) Short-term effects of a sewage sludge biochar amendment on total and available heavy metal content of a tropical soil. Geoderma 344:31–39
Ghafarzadeh M, Abedini R, Rajabi R (2017) Optimization of ultrasonic waves application in municipal wastewater sludge treatment using response surface method. J Clean Prod 150:361–370
He MC, Shi YH, Lin CY (2008) Characterization of humic acids extracted from the sediments of the various rivers and lakes in China. J Environ Sci (China) 20:1294–1299
Janoš P, Tokarová V (2002) Characterization of coal-derived humic substances with the aid of low-pressure gel permeation chromatography. Fuel 81:1025–1031
Kang KH, Shin HS, Parka H (2002) Characterization of humic substances present in landfill leachates with different landfill ages and its implications. Water Res 36:4023–4032
Kelessidis A, Stasinakis AS (2012) Comparative study of the methods used for treatment and final disposal of sewage sludge in European countries. Waste Manag 32:1186–1195
Kholodov VA, Yaroslavtseva NV, Konstantinov AI, Perminova IV (2015) Preparative yield and properties of humic acids obtained by sequential alkaline extractions. Eurasian Soil Sci 48:1101–1109
Kim H, Chon K, Lee YG, Kim YK, Jang A (2020) Enhanced mechanical deep dewatering of dewatered sludge by a thermal hydrolysis pre-treatment: effects of temperature and retention time. Environ Res 188:109746
Lamar RT, Olk DC, Mayhew L, Bloom PR (2014) A new standardized method for quantification of humic and fulvic acids in humic ores and commercial products. J AOAC Int 97:721–730
Li H, Jin YY, Nie YF (2009) Application of alkaline treatment for sludge decrement and humic acid recovery. Bioresour Technol 100:6278–6283
Li H, Li Y, Zou SX, Li CC (2014) Extracting humic acids from digested sludge by alkaline treatment and ultrafiltration. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 16:93–100
Li CX, Wang XD, Zhang GY, Yu GW, Lin JJ, Wang Y (2017) Hydrothermal and alkaline hydrothermal pretreatments plus anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge for dewatering and biogas production: bench-scale research and pilot-scale verification. Water Res 117:49–57
Liu GY, Wright MM, Zhao QL, Brown RC (2015) Hydrocarbon and ammonia production from catalytic pyrolysis of sewage sludge with acid pretreatment. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:1819–1826
Lu D, Wu D, Qian T, Jiang J, Cao S, Zhou Y (2020) Liquid and solids separation for target resource recovery from thermal hydrolyzed sludge. Water Res 171:115476
Maryam A, Zeshan BM, Sabeeh M, Khan SJ (2021) Enhancing methane production from dewatered waste activated sludge through alkaline and photocatalytic pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 325:124677
Mazaheri H, Lee KT, Bhatia S, Mohamed AR (2010) Subcritical water liquefaction of oil palm fruit press fiber in the presence of sodium hydroxide: an optimisation study using response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 101:9335–9341
Nasir S, Sarfaraz TB, Verheyen TV, Chaffee AL (2011) Structural elucidation of humic acids extracted from Pakistani lignite using spectroscopic and thermal degradative techniques. Fuel Process Technol 92:983–991
Neyens E, Baeyens J (2003a) A review of thermal sludge pre-treatment processes to improve dewaterability. J Hazard Mater 98:51–67
Neyens E, Baeyens J (2003b) A review of classic Fenton’s peroxidation as an advanced oxidation technique. J Hazard Mater 98:33–50
Novak J, Kozler J, Janos P, Cezikova J, Tokarova V, Madronova L (2001) Humic acids from coals of the North-Bohemian coal field: I. Preparation and characterisation. React Funct Polym 47:101–109
Ooi TY, Yong EL, Din MFM, Rezania S, Aminudin E, Chelliapan S, Rahman AA, Park J (2018) Optimization of aluminium recovery from water treatment sludge using Response Surface Methodology. J Environ Manag 228:13–19
Park M, Kim N, Lee S, Yeon S, Seo JH, Park D (2019) A study of solubilization of sewage sludge by hydrothermal treatment. J Environ Manag 250:109490
Quist-Jensen CA, Wybrandt L, Lokkegaard H, Antonsen SB, Jensen HC, Nielsen AH, Christensen ML (2018) Acidification and recovery of phosphorus from digested and non-digested sludge. Water Res 146:307–317
Rao JLUM, Satyanarayana T (2007) Improving production of hyperthermostable and high maltose-forming α-amylase by an extreme thermophile Geobacillus thermoleovorans using response surface methodology and its applications. Bioresour Technol 98:345–352
Sarlaki E, Paghaleh AS, Kianmehr MH, Vakilian KA (2019) Extraction and purification of humic acids from lignite wastes using alkaline treatment and membrane ultrafiltration. J Clean Prod 235:712–723
Schnell M, Horst T, Quicker P (2020) Thermal treatment of sewage sludge in Germany: A review. J Environ Manag 263:110367
Venkatesan AK, Done HY, Halden RU (2015) United States National Sewage Sludge Repository at Arizona State University-a new resource and research tool for environmental scientists, engineers, and epidemiologists. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1577–1586
Wang LP, Li AM, Chang YZ (2017) Relationship between enhanced dewaterability and structural properties of hydrothermal sludge after hydrothermal treatment of excess sludge. Water Res 112:72–82
Wang HF, Hu H, Wang HJ, Zeng RJ (2018) Impact of dosing order of the coagulant and flocculant on sludge dewatering performance during the conditioning process. Sci Total Environ 643:1065–1073
Wang LP, Chang YZ, Li AM (2019a) Hydrothermal carbonization for energy-efficient processing of sewage sludge: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 108:423–440
Wang Y, Guo L, Zhang JW, She ZL, Jin CJ, Gao MC, Zhao YG (2019b) Optimization of operating conditions for the acidification metabolites production with waste sludge using response surface methodology (RSM). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:30303–30312
Wang H, Yang ZJ, Li X, Liu YS (2020) Distribution and transformation behaviors of heavy metals and phosphorus during hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:17109–17122
Wu B, Dai X, Chai X (2020) Critical review on dewatering of sewage sludge: Influential mechanism, conditioning technologies and implications to sludge re-utilizations. Water Res 180:115912
Yan YX, Qin L, Gao JL, Nan RQ, Gao JQ (2020) Protein extraction and sludge dewatering performance of ultrasound-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis of excess sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:18317–18328
Yang G, Wang J (2017) Fermentative hydrogen production from sewage sludge. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 47:1219–1281
Yang SS, Guo WQ, Zhou XJ, Meng ZH, Liu B, Ren NQ (2011) Optimization of operating parameters for sludge process reduction under alternating aerobic/oxygen-limited conditions by response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 102:9843–9851
Zhao H, Zhang PY, Zhang GM, Cheng R (2016) Enhancement of ultrasonic disintegration of sewage sludge by aeration. J Environ Sci (China) 42:163–167
Zhou HB, Meng HB, Zhao LX, Shen YQ, Cheng HS, Song LQ (2018) Effect of biochar and humic acid on the copper, lead, and cadmium passivation during composting. Bioresour Technol 258:279–286
Zingaretti D, Lominchar MA, Verginelli I, Santos A, Baciocchi R (2020) Humic acids extracted from compost as amendments for Fenton treatment of diesel-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:22225–22234
Acknowledgements
The author would like to acknowledge Prof. Su XT for his continuous help and support. The authors acknowledge the research and testing platforms provided by the South China University of Technology and China-Singapore International Joint Research Institute.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U1901216) and the Guangdong Science and Technology Program (2020B121201003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Investigation, experiment design, and data collection were performed by CQ, XS, ZL, and JY. WX and YW provided study materials. The first draft of the manuscript was written by CQ and all authors commented and revised on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1036 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, C., Xu, W., Wang, Y. et al. Hydrothermal alkaline conversion of sewage sludge: optimization of process parameters and characterization of humic acid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 57695–57705 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14711-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14711-x