Abstract
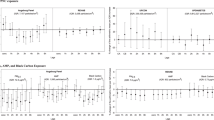
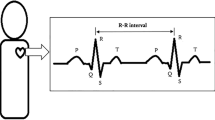
As an indicator of cardiac autonomic function, heart rate variability (HRV) has been proven to decrease after short-term exposure to particulate matters (PM) based on controlled animal studies. In this study, we conducted a systematic review to investigate short-term effects of exposure with different particle sizes on HRV in humans. Both crossover and controlled studies of human which were published prior to February 2020 were searched on four electronic databases. The HRV parameters included standard deviation of normal-to-normal intervals (SDNN), root mean square of successive normal-to-normal intervals (RMSSD), percent of normal-to-normal intervals that differ by more than 50 milliseconds (PNN50), low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and LF/HF. This review included 14 studies with 300 participants. The short-term effects of PM exposure on HRV in humans are inconclusive. For time-domain parameters, one study showed higher SDNN values with 2-h exposure to PM, whereas another one showed lower SDNN values. One study found RMSSD increased after PM exposure. One study found PNN50 decreased after PM exposure. For frequency-domain parameters, two studies showed LF increased with 2-h exposure to PM, and two studies showed an increase of LF/HF after PM exposure. Four studies showed lower HF values after PM exposure, whereas two studies showed higher HF values. Five studies did not find statistically significant results for any HRV parameters. We could not conclude that short-term exposure to PM can influence autonomic nervous function. The inconsistent changes of HRV in response to PM exposure may have complex mechanisms, which remains to be elucidated.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Acharya UR, Joseph KP, Kannathal N et al. (2006) Heart rate variability: a review. Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing 44(12): 1031erate
Aubert AE, Seps B, Beckers F (2003) Heart rate variability in athletes. Sports Med 33(12):889–919
Bai L, Wang J, Ma X, Lu H (2018) Air pollution forecasts: an overview. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(4):780
Bilchick KC, Fetics B, Djoukeng R et al (2020) Prognostic value of heart rate variability in chronic congestive heart failure (Veterans Affairs’ Survival Trial of Antiarrhythmic Therapy in Congestive Heart Failure). Am J Cardiol 90(1):24ay
Brook RD, Bard RL, Morishita M, Dvonch JT, Wang L, Yang HY, Spino C, Mukherjee B, Kaplan MJ, Yalavarthi S, Oral EA, Ajluni N, Sun Q, Brook JR, Harkema J, Rajagopalan S (2014) Hemodynamic, autonomic, and vascular effects of exposure to coarse particulate matter air pollution from a rural location. Environ Health Perspect 122(6):624–630
Buteau S, Goldberg MS (2016) A structured review of panel studies used to investigate associations between ambient air pollution and heart rate variability. Environmental Reasearch 148(207):148
Byrd JB, Morishita M, Bard RL et al (2016) Acute increase in blood pressure during inhalation of coarse particulate matter air pollution from an urban location. Journal of the American Society of Hypertension 10(2):133–139.e4
Cesaroni G, Forastiere F, Stafoggia M, Andersen ZJ, Badaloni C, Beelen R, Caracciolo B, de Faire U, Erbel R, Eriksen KT, Fratiglioni L, Galassi C, Hampel R, Heier M, Hennig F, Hilding A, Hoffmann B, Houthuijs D, Jockel KH, Korek M, Lanki T, Leander K, Magnusson PKE, Migliore E, Ostenson CG, Overvad K, Pedersen NL, P JJ, Penell J, Pershagen G, Pyko A, Raaschou-Nielsen O, Ranzi A, Ricceri F, Sacerdote C, Salomaa V, Swart W, Turunen AW, Vineis P, Weinmayr G, Wolf K, de Hoogh K, Hoek G, Brunekreef B, Peters A (2014) Long term exposure to ambient air pollution and incidence of acute coronary events: prospective cohort study and meta-analysis in 11 European cohorts from the ESCAPE Project. BMJ 348:f7412
Chen X, Huang YY, Yun F, Chen TJ, Li J (2015) Effect of changes in sympathovagal balance on the accuracy of heart rate variability obtained from photoplethysmography. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 10(6):2311–2318
Devlin RB, Ghio AJ, Kehrl H, Sanders G, Cascio W (2003) Elderly humans exposed to concentrated air pollution particles have decreased heart rate variability. The European Respiratory Journal Supplement 40:–76 sdecr
Devlin RB, Smith CB, Schmitt MT et al (2014) Controlled exposure of humans with metabolic syndrome to concentrated ultrafine ambient particulate matter causes cardiovascular effects. Toxicol Sci 140(1):610
Dong JG (2016) The role of heart rate variability in sports physiology. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 11(5):1531–1536
Fakhri AA, Ilic LM, Wellenius GA, Urch B, Silverman F, Gold DR, Mittleman MA (2009) Autonomic effects of controlled fine particulate exposure in young healthy adults: effect modification by ozone. Environ Health Perspect 117(8):1287–1292
Graff DW, Cascio WE, Rappold A, Zhou H, Huang YCT, Devlin RB (2009) Exposure to concentrated coarse air pollution particles causes mild cardiopulmonary effects in healthy young adults. Environ Health Perspect 117(7):1089 10
Hayano J, Sakakibara Y, Yamada A et al (1991) Accuracy of assessment of cardiac vagal tone by heart rate variability in normal subjects. Am J Cardiol 90(1):24you
Heusser K, Tank J, Holz O, May M, Brinkmann J, Engeli S, Diedrich A, Framke T, Koch A, Großhennig A, Jan Danser AH, Sweep FCGJ, Schindler C, Schwarz K, Krug N, Jordan J, Hohlfeld JM (2019) Ultrafine particles and ozone perturb norepinephrine clearance rather than centrally generated sympathetic activity in humans. Sci Rep 9(1):3641
Huang YCT, Rappold AG, Graff DW, Ghio AJ, Devlin RB (2012) Synergistic effects of exposure to concentrated ambient fine pollution particles and nitrogen dioxide in humans. Inhal Toxicol 24(12):790–797
Huang F, Luo Y, Guo Y et al (2016) Particulate matter and hospital admissions for stroke in Beijing, China: modification effects by ambient temperature. J Am Heart Assoc 5(7):e003437
Huang F, Wang P, Pan X, Wang Y, Ren S (2020) Effects of short-term exposure to particulate matters on heart rate variability: a systematic review and meta-analysis based on controlled animal studies. Environ Pollut 256:113306
Kemp AH, Quintana DS (2013) The relationship between mental and physical health: insights from the study of heart rate variability. Int J Psychophysiol 89(3):288–296
Lelieveld J, KlingmingmJ K, Pozzer A et al (2019) Cardiovascular disease burden from ambient air pollution in Europe reassessed using novel hazard ratio functions. Eur Heart J 40(20):159024(12)
Liu Z, Wang F, Li W et al (2018) Does utilizing WHO’s interim targets further reduce the riskm ambient air pollution in Europe reassessed using novel hazard ratio functions. Eur Heart J 40(20):159024(12)–790 797ogy 24(1)
Orellano P, Reynoso J, Quaranta N, Bardach A, Ciapponi A (2020) Short-term exposure to particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3) and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Int 142:105876
Pieters N, Plusquin M, Cox B, Kicinski M, Vangronsveld J, Nawrot TS (2012) An epidemiological appraisal of the association between heart rate variability and particulate air pollution: a meta-analysis. Heart 98(15):1127–1135
Roth GA, Johnson C, Abajobir A, Abd-Allah F, Abera SF, Abyu G, Ahmed M, Aksut B, Alam T, Alam K, Alla F, Alvis-Guzman N, Amrock S, Ansari H, Ärnlöv J, Asayesh H, Atey TM, Avila-Burgos L, Awasthi A, Banerjee A, Barac A, Bärnighausen T, Barregard L, Bedi N, Belay Ketema E, Bennett D, Berhe G, Bhutta Z, Bitew S, Carapetis J, Carrero JJ, Malta DC, Castañeda-Orjuela CA, Castillo-Rivas J, Catalá-López F, Choi JY, Christensen H, Cirillo M, Cooper L Jr, Criqui M, Cundiff D, Damasceno A, Dandona L, Dandona R, Davletov K, Dharmaratne S, Dorairaj P, Dubey M, Ehrenkranz R, el Sayed Zaki M, Faraon EJA, Esteghamati A, Farid T, Farvid M, Feigin V, Ding EL, Fowkes G, Gebrehiwot T, Gillum R, Gold A, Gona P, Gupta R, Habtewold TD, Hafezi-Nejad N, Hailu T, Hailu GB, Hankey G, Hassen HY, Abate KH, Havmoeller R, Hay SI, Horino M, Hotez PJ, Jacobsen K, James S, Javanbakht M, Jeemon P, John D, Jonas J, Kalkonde Y, Karimkhani C, Kasaeian A, Khader Y, Khan A, Khang YH, Khera S, Khoja AT, Khubchandani J, Kim D, Kolte D, Kosen S, Krohn KJ, Kumar GA, Kwan GF, Lal DK, Larsson A, Linn S, Lopez A, Lotufo PA, el Razek HMA, Malekzadeh R, Mazidi M, Meier T, Meles KG, Mensah G, Meretoja A, Mezgebe H, Miller T, Mirrakhimov E, Mohammed S, Moran AE, Musa KI, Narula J, Neal B, Ngalesoni F, Nguyen G, Obermeyer CM, Owolabi M, Patton G, Pedro J, Qato D, Qorbani M, Rahimi K, Rai RK, Rawaf S, Ribeiro A, Safiri S, Salomon JA, Santos I, Santric Milicevic M, Sartorius B, Schutte A, Sepanlou S, Shaikh MA, Shin MJ, Shishehbor M, Shore H, Silva DAS, Sobngwi E, Stranges S, Swaminathan S, Tabarés-Seisdedos R, Tadele Atnafu N, Tesfay F, Thakur JS, Thrift A, Topor-Madry R, Truelsen T, Tyrovolas S, Ukwaja KN, Uthman O, Vasankari T, Vlassov V, Vollset SE, Wakayo T, Watkins D, Weintraub R, Werdecker A, Westerman R, Wiysonge CS, Wolfe C, Workicho A, Xu G, Yano Y, Yip P, Yonemoto N, Younis M, Yu C, Vos T, Naghavi M, Murray C (2017) Global, regional, and national burden of cardiovascular diseases for 10 causes, 1990 to 2015. J Am Coll Cardiol 70(1):1–25
Rowan WH 3rd, Campen MJ, Wichers LB, Watkinson WP (2007) Heart rate variability in rodents: uses and caveats in toxicological studies. Cardiovasc Toxicol 7(1):28: y
Samet JM, Rappold A, Graff D et al (2009) Concentrated ambient ultrafine particle exposure induces cardiac changes in young healthy volunteers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 179(11):103488–103429
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology (1996) Heart rate variability. Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Circulation 93(5):1043–1065
Thayer JF, Yamamoto SS, Brosschot JF (2010) The relationship of autonomic imbalance, heart rate variability and cardiovascular disease risk factors. Int J Cardiol 141(2):122–131
Tobaldini E, Bollati V, Prado M, Fiorelli EM, Pecis M, Bissolotti G, Albetti B, Cantone L, Favero C, Cogliati C, Carrer P, Baccarelli A, Bertazzi PA, Montano N (2018) Acute particulate matter affects cardiovascular autonomic modulation and IFN-gamma methylation in healthy volunteers. Environ Res 161:97–103
Tsuji H, Mg L, Venditti FJ Jr et al (1996) Impact of reduced heart rate variability on risk for cardiac events. The Framingham Heart Study Circulation 94(11):2850ironm
Vora R, Zareba W, Utell MJ, Pietropaoli AP, Chalupa D, Little EL, Oakes D, Bausch J, Wiltshire J, Frampton MW (2014) Inhalation of ultrafine carbon particles alters heart rate and heart rate variability in people with type 2 diabetes. Particle and Fibre Toxicology 11:31
Weichenthal S (2012) Selected physiological effects of ultrafine particles in acute cardiovascular morbidity. Environ Res 115:26–36
World Health Organization (2016) Ambient air pollution: a global assessment of exposure and burden of disease. World Health Organization, Geneva
Zareba W, Couderc JP, Oberdorster G et al (2009) ECG parameters and exposure to carbon ultrafine particles in young healthy subjects. Inhal Toxicol 21(3):223Heal
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81773512) and the Scientific Research Common Program of Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (grant number KM201810025008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HF, YZ, and YL performed the literature search, HF and YL performed the data analysis and drafted the work, PW, YW, and LZ critically revised the work, and YL performed funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, F., Zhao, Y., Wang, P. et al. Short-term exposure to particulate matter on heart rate variability in humans: a systematic review of crossover and controlled studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 35528–35536 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14494-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14494-1