Abstract
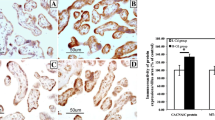
Cadmium (Cd), a toxic heavy metal, produces various forms of environmental contaminations and health problems in human. In this study, we aimed to examine the localization of several apoptotic markers in human placentas from pregnant women who were environmentally exposed to Cd. Twelve pregnant women participated in this analysis and they were divided into 2 groups according to their living areas: high-Cd (H-Cd) and low-Cd (L-Cd) groups. After delivery, the placentas were immediately harvested, and the placental width, length, and weight were measured. The placental Cd concentration was determined by using ICP-MS. The expression of three apoptotic markers, cleaved caspase-3, cleaved lamin A/C, and TUNEL, was examined in immunohistochemistry. In results, the placental Cd concentration in the H-Cd group was higher than that in the L-Cd group. In contrast, a significant decrease in the BW (birth weight):PW (placenta weight) ratio representing the placental nutrient transport function was found in the H-Cd group, and an inverse correlation between placental Cd concentration and BW:PW ratio was demonstrated. Additionally, significant elevations in the expression of cleaved caspase-3, cleaved lamin A/C proteins, and TUNEL were shown in the H-Cd placenta. Moreover, positive correlations were found between the placental Cd concentration and the expression of cleaved caspase-3 and TUNEL. Collectively, our findings suggest that the exposure of pregnant women to environmental Cd might induce Cd to be transferred to the body and then accumulated in the placenta, resulting in disturbance of the placental function and eventual apoptosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Akesson A et al (2005) Tubular and glomerular kidney effects in Swedish women with low environmental cadmium exposure. Environ Health Perspect 113:1627–1631. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8033
Botta C, Pellegrini G, Hässig M, Pesch T, Prähauser B, Wunderlin S, Guscetti F, Schneeberger M, Schmitt S, Basso W, Hilbe M, Schuler G, Borel N (2019) Bovine fetal placenta during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Vet Pathol 56:248–258. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985818806453
Broers JL, Bronnenberg NM, Kuijpers HJ, Schutte B, Hutchison CJ, Ramaekers FC (2002) Partial cleavage of A-type lamins concurs with their total disintegration from the nuclear lamina during apoptosis. Eur J Cell Biol 81:677–691. https://doi.org/10.1078/0171-9335-00282
Bush PG, Mayhew TM, Abramovich DR, Aggett PJ, Burke MD, Page KR (2000) A quantitative study on the effects of maternal smoking on placental morphology and cadmium concentration. Placenta 21:247–256. https://doi.org/10.1053/plac.1999.0470
Cockcroft DW, Gault MH (1976) Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16:31–41. https://doi.org/10.1159/000180580
Cunningham F, Leveno K, Bloom S, Hauth J, Rouse D, Spong C (2010) Chapter 3: implantation, embryogenesis, and placental development. In: Cunningham F, Leveno K, Bloom S, Hauth J, Rouse D, Spong C (eds) Williams obstetrics, 23rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 36–77
El-Baz MA, El-Deeb TS, El-Noweihi AM, Mohany KM, Shaaban OM, Abbas AM (2015) Environmental factors and apoptotic indices in patients with intrauterine growth retardation: a nested case-control study. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 39:589–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2015.01.009
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337
Erboga M, Kanter M (2016) Effect of cadmium on trophoblast cell proliferation and apoptosis in different gestation periods of rat placenta. Biol Trace Elem Res 169:285–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0439-8
Ganer Herman H, Miremberg H, Schreiber L, Bar J, Kovo M (2017) The association between disproportionate birth weight to placental weight ratio, clinical outcome, and placental histopathological lesions. Fetal Diagn Ther 41:300–306. https://doi.org/10.1159/000448949
Gloria-Bottini F, Neri A, Coppeta L, Magrini A, Bottini E (2016) Correlation between birth weight and placental weight in healthy and diabetic puerperae Taiwanese. J Obstet Gynecol 55:697–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tjog.2015.03.013
Hashimoto K, Majumdar R, Tsuji Y (2017) Nuclear lamins and progerin are dispensable for antioxidant Nrf2 response to arsenic and cadmium. Cell Signal 33:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.02.012
Huppertz B (2008) The anatomy of the normal placenta. J Clin Pathol 61:1296–1302. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.2008.055277
Hwangbo Y, Weaver VM, Tellez-Plaza M, Guallar E, Lee BK, Navas-Acien A (2011) Blood cadmium and estimated glomerular filtration rate in Korean adults. Environ Health Perspect 119:1800–1805. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1003054
Järup L, Hellström L, Alfvén T, Carlsson MD, Grubb A, Persson B, Pettersson C, Spång G, Schütz A, Elinder CG (2000) Low level exposure to cadmium and early kidney damage: the OSCAR study. Occup Environ Med 57:668–672. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.57.10.668
Kippler M, Tofail F, Gardner R, Rahman A, Hamadani JD, Bottai M, Vahter M (2012) Maternal cadmium exposure during pregnancy and size at birth: a prospective cohort study. Environ Health Perspect 120:284–289. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1103711
Kivinen K, Kallajoki M, Taimen P (2005) Caspase-3 is required in the apoptotic disintegration of the nuclear matrix. Exp Cell Res 311:62–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.08.006
Klaassen CD, Liu J, Diwan BA (2009) Metallothionein protection of cadmium toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.03.026
Lee CK, Lee JT, Yu SJ, Kang SG, Moon CS, Choi YH, Kim JH, Kim DH, Son BC, Lee CH, Kim HD, Ahn JH (2009) Effects of cadmium on the expression of placental lactogens and Pit-1 genes in the rat placental trophoblast cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 298:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2008.09.028
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang Y(L), Castro AF III, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, van Lente F, Greene T, Coresh J, for the CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) (2009) A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 150:604–612. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-150-9-200905050-00006
Lyengar GV, Rapp A (2001) Human placenta as a “dual” biomarker for monitoring fetal and maternal environment with special reference to potentially toxic trace elements. Part 3: toxic trace elements in placenta and placenta as a biomarker for these elements. Sci Total Environ 280:221–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(01)00827-0
Mukherjee R et al (2010) Melatonin protects against alterations in hippocampal cholinergic system, trace metals and oxidative stress induced by gestational and lactational exposure to cadmium. EXCLI J 9:119–132
Myllynen P, Pasanen M, Pelkonen O (2005) Human placenta: a human organ for developmental toxicology research and biomonitoring. Placenta 26:361–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2004.09.006
Nan Y, Yi SJ, Zhu HL, Xiong YW, Shi XT, Cao XL, Zhang C, Gao L, Zhao LL, Zhang J, Xu DX, Wang H (2020) Paternal cadmium exposure increases the susceptibility to diet-induced testicular injury and spermatogenic disorders in mouse offspring. Chemosphere 246:125776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125776
Navas-Acien A, Tellez-Plaza M, Guallar E, Muntner P, Silbergeld E, Jaar B, Weaver V (2009) Blood cadmium and lead and chronic kidney disease in US adults: a joint analysis. Am J Epidemiol 170:1156–1164. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwp248
Nordberg GF, Nogawa K, Nordberg M (2015) Chapter 32—cadmium. In: Nordberg GF, Fowler BA, Nordberg M (eds) Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, Fourth edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 667–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-59453-2.00032-9
Pekovic V, Gibbs-Seymour I, Markiewicz E, Alzoghaibi F, Benham AM, Edwards R, Wenhert M, von Zglinicki T, Hutchison CJ (2011) Conserved cysteine residues in the mammalian lamin A tail are essential for cellular responses to ROS generation. Aging Cell 10:1067–1079. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00750.x
Phuapittayalert L, Norkaew T, Supanpaiboon W, Chuenchoojit S, Hipkeao W, Swaddiwudhipong W, Sakulsak N (2013) Increasing of syncytial knot and fibrinoid deposit in high-Cd accumulated human placentas. Int J Morphol 31:1210–1215
Phuapittayalert L, Saenganantakarn P, Supanpaiboon W, Cheunchoojit S, Hipkaeo W, Sakulsak N (2016) Increasing CACNA1C expression in placenta containing high Cd level: an implication of Cd toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:24592–24600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7841-4
Salavati N, Gordijn SJ, Sovio U, Zill-E-Huma R, Gebril A, Charnock-Jones DS, Scherjon SA, Smith GCS (2018) Birth weight to placenta weight ratio and its relationship to ultrasonic measurements, maternal and neonatal morbidity: a prospective cohort study of nulliparous women. Placenta 63:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2017.11.008
Satarug S, Boonprasert K, Gobe GC, Ruenweerayut R, Johnson DW, Na-Bangchang K, Vesey DA (2019) Chronic exposure to cadmium is associated with a marked reduction in glomerular filtration rate. Clin Kidney J 12:468–475. https://doi.org/10.1093/ckj/sfy113
Selvaratnam J, Guan H, Koropatnick J, Yang K (2013) Metallothionein-I- and -II-deficient mice display increased susceptibility to cadmium-induced fetal growth restriction. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 305:E727–E735. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00157.2013
Simmons RW, Pongsakul P, Saiyasitpanich D, Klinphoklap S (2005) Elevated levels of cadmium and zinc in paddy soils and elevated levels of cadmium in rice grain downstream of a zinc mineralized area in Thailand: implications for public health. Environ Geochem Health 27:501–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-005-7857-z
Somsuan K, Phuapittayalert L, Srithongchai Y, Sonthi P, Supanpaiboon W, Hipkaeo W, Sakulsak N (2019) Increased DMT-1 expression in placentas of women living in high-Cd-contaminated areas of Thailand. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:141–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3598-2
Suwatvitayakorn P, Ko MS, Kim KW, Chanpiwat P (2019) Human health risk assessment of cadmium exposure through rice consumption in cadmium-contaminated areas of the Mae Tao sub-district, Tak, Thailand. Environ Geochem Health 42:2331–2344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00410-7
Swaddiwudhipong W, Limpatanachote P, Mahasakpan P, Krintratun S, Padungtod C (2007) Cadmium-exposed population in Mae Sot District, Tak Province: 1. Prevalence of high urinary cadmium levels in the adults. J Med Assoc Thail 90:143–148
Taricco E, Radaelli T, Nobile de Santis MS, Cetin I (2003) Foetal and placental weights in relation to maternal characteristics in gestational diabetes. Placenta 24:343–347. https://doi.org/10.1053/plac.2002.0913
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Exp Suppl 101:133–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Wolf CM, Wang L, Alcalai R, Pizard A, Burgon PG, Ahmad F, Sherwood M, Branco DM, Wakimoto H, Fishman GI, See V, Stewart CL, Conner DA, Berul CI, Seidman CE, Seidman JG (2008) Lamin A/C haploinsufficiency causes dilated cardiomyopathy and apoptosis-triggered cardiac conduction system disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol 44:293–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.11.008
Yu R, He L, Cai R, Li B, Li Z, Yang K (2017) Heavy metal pollution and health risk in China. Glob Health J 1:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2414-6447(19)30059-4
Zhu HL et al (2019) Activation of autophagy inhibits cadmium-triggered apoptosis in human placental trophoblasts and mouse placenta. Environ Pollut (Barking, Essex: 1987 254:112991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.11299
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Witaya Swaddiwudhipong and staffs of Mae Sot General Hospital for the collaboration and sample collection. Additionally, we are grateful to Professor Dr. Thomas Brunner, Department of Biology, University of Konstanz in supply of sections of the liver and small intestine from mice pre-injected with 6μg TNF-α used as specimens for positive control in this study. Finally, we appreciate the School of Medical Science, University of Phayao for the generous support. We acknowledge the Overseas resident Professor Hisatake Kondo in Khon Kaen University for editing the manuscript.
Funding
This study was granted by the School of Medical Science, University of Phayao (Project Nos. MS612001 and MS612002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Nathamon Tanasrivaroottanun performed the placental tissue processing and sectioning. Wisa Supanpaiboon conducted the metal analysis. Wiphawi Hipkaeo and Natthiya Sakulsak designed the methodology. Laorrat Phuapittayalert investigated the immunohistochemistry technique, TUNEL assay, data analysis, and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the University of Phayao Human Ethnic Committee, University of Phayao, Thailand (No. 2/073/59). All participants have read the information sheet and signed a consent form before engaging in the experiment.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phuapittayalert, L., Tanasrivaroottanun, N., Hipkaeo, W. et al. Increased expression of apoptotic markers in human full-term placenta after exposure to elevated environmental cadmium levels during pregnancy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 51795–51807 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14431-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14431-2