Abstract
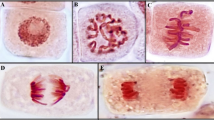
Paraquat is the most widely used herbicide and the third most sold pesticide in the world, applied in more than 120 countries despite being banned in the European Union. It is a risk to ecosystems. The genotoxic effect of paraquat was evaluated using the Lens culinaris test. L. culinaris seeds were subjected to 6 concentrations of paraquat (0.1, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 1.5, 2, and 3 ppm) plus a control (distilled water). During 72 h, root development was measured every 24 h. After 3 days, root apices were analyzed to obtain the inhibition of the mitotic index, as well as the type and rate of chromosomal abnormalities present. A decrease in root growth of more than 50% (72 h of exposure) and an inhibition of the mitotic index of 2.9 times in the treatment with 3 ppm compared to the control were observed. The 2 ppm concentration presented all the anomalies found with a frequency of 84 ± 2.5 of micronuclei, 106 ± 3.5 of nuclear lesions, 14 ± 4.7 of nucleus absence, 8 ± 2.7 of telophase bridges, 7 ± 2.7 of binucleated cells, among others. It is also recommended to establish comparisons of L. culinaris with multiple biomarkers since it is presented as a practical and economic alternative.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelsalam N, Megeed A, Ali HM, Salem MZM, Al-Hayali M, Elshikh MS (2018) Genotoxicity effects of silver nanoparticles on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) root tip cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 155:76–85
Acar A, Çavuşoğlu K, Türkmen Z, Çavuşoğlu K, Yalçın E (2015) The Investigation of Genotoxic, Physiological and Anatomical Effects of Paraquat Herbicide on Allium cepa L. CYTOLOGIA 80(3):343–351. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.80.343
Amondham W, Parkpian P, Polprasert C, Delaune RD, Jugsujinda A (2006) Paraquat adsorption, degradation, and remobilization in tropical soils of Thailand. J. Environ. Sci. Health B. 41:485–507
Asita AO, Mokhobo MM (2013) Clastogenic and cytotoxic effects of four pesticides used to control insect pest of stored products on root meristems of Allium cepa. Canadian Center of Science and Education. 3(2):133–145
Berry C, La Vecchia C, Nicotera P (2010) Paraquat and Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Differ. 17:1115–1125
Boesten J (2016) Proposal for field-based definition of soil bound pesticide residues. Science of The Total Environment. 544:114–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.122
Bortolotto LF, Barbosa FR, Silva G, Bitencourt TA, Beleboni R.O, Baek SJ, et al (2016). Cytotoxicity of transchalcone and licochalcone A against breast cancer cells is due to apoptosis induction and cell cycle arrest. Biomed. Pharmacother. 85, 425-433. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.047.
Caloni F, Cortinovis C, Rivolta M, Davanzo F (2016) Sospecha de envenenamiento de animales domésticos por pesticidas. Science of The Total Environment. 539:331–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.005
Causil L, Coronado J, Vega M, Verbel L (2017) Efecto citotoxico del hipoclorito de sodio (NaClO), en células apicales de raíces de cebolla (Allium cepa L.). Rev. Colomb. Ciencias Hortícolas. 11(1), 97-104. Doi: 10.17584/rcch.2017v11i1.5662
Cochemé HM, Murphy MP (2008) Complex I is the major site of mitochondrial superoxide production by paraquat. J. Biol. Chem. 283(4):1786–1798. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M708597200
El-Abidin Salam A, Hussein E, El-Itriby A, Anwar W, Mansour S (1993) The mutagenicity of Gramoxone (paraquat) on different eukaryotic systems. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology 319(2):89–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1218(93)90067-n
Faizah AA (2014) Cytotoxic and genotoxic potency screening of WIDE-SPEC pesticide on Allium cepa L. root meristem cells. Journal of Natural Sciences Research 4:24
Ferguson BS, Kelsey DE, Fan T, Bushway R (1993) Pesticide testing by enzyme immunoassay at trace levels in environmental and agricultural samples. Science of The Total Environment. 132 (2-3), 415-428. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(93)90148-Y
Fernández M, Ibáñez M, Picó Y, Mañes J (1998) Spatial and temporal trends of paraquat, diquat, and difenzoquat contamination in water from marsh areas of the valencian community (Spain). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 35:377–384
Fiskesjo G (1988) The Allium test-an alternative in environmental studies: the relative toxicity of metal ions. Mutat. Res. 197:243–260
Flores M, Barbachano M (1992) Effects of herbicides Gramoxone, Diuron and Totacol® on growth and nodulation of three strains of Rhizobium meliloti. Science of The Total Environment. 123-124:249–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(92)90150-Q
Franqueira D, Orosa M, Torres E, Herrero C, Cid A (2000) Potential use of flow cytometry in toxicity studies with microalgae. Science of The Total Environment. 247(2-3):119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(99)00483-0
Haijie L, Hao Q, Mingyuan Y, Yujie C, Qiliang D, Shuo W (2021) Carbon tubes from biomass with prominent adsorption performance for paraquat. Chemosphere. 262:127797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127797
Hoffman D, Eastin W (1982) Efectos del lindano, paraquat, toxafeno y ácido 2,4,5-triclorofenoxiacético en el desarrollo del embrión de ánade real. Arco. Reinar. Contam. Toxicol. 11, 79-86 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055190
Huitao L, Qiqi Z, Songxue W, Tongliang H, Xiaoheng L, Chaobo N, Yinghui F, Linxi L, Qingquan L, Ren-Shan G (2019) Paraquat exposure delays stem/progenitor Leydig cell regeneration in the adult rat testis. Chemosphere. 231:60–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.104
James OE, Adeleke MT (2016) Cytotoxicity of two common pesticides using Allium cepa (onion). Assay current studies in comparative education, science and technology. 3(2):211–221
Jovtchev G, Gateva S, Stergios M, Kulekova S (2010) Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of paraquat in Hordeum vulgare and human lymphocytes in vitro. Environ Toxicol. 25(3):294–303. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20503
Karaismailoglu MC (2017) Assessments on the potential genotoxic effects of fipronil insecticide on Allium cepa somatic cells. Caryologia. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.2017.1371992
Khannah N, Sonia S (2013) Allium cepa root chromosomal aberration assay: a review. Indian J. Pharm. Biol. Res. 1(3)
Lazalde-Ramos BP, Zamora-Pérez AL, Sosa-Macías M, Galaviz-Hernández C, Zúñiga-González GM (2017) Micronuclei and nuclear anomalies in Mexico's indigenous population. Salud Publica Mex. 59(5), 532-539. Doi: 10.21149/8318.
Liman R, Acikbas Y, Ciğerci İ (2019) Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of cerium oxide micro and nanoparticles by Allium and Comet tests. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 168:408–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.088
Ma J, Li Y, Li W, Li X (2018) Hepatotoxicity of paraquat on common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Science of The Total Environment. 616-617:889–898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.231
Mallo-Castaño J, Castañón-López L, Herrero-Mendoza B, Robles-Garcíaa B, Goded Rambaudb F (2005) Síndrome de Leigh con déficit de los complejos I, III y IV de la cadena respiratoria mitocondrial. Anales de pediatría. 62(2):161–165. https://doi.org/10.1157/13071315
Marin-Morales MA, Ventura-Camargo B, Miyuki-Hoshina M (2013) Toxicity of Herbicides: Impact on Aquatic and Soil Biota and Human Health, book chapter. Doi. https://doi.org/10.5772/55851
Meng Z, Zhang L (1992) Cytogenetic damage induced by sodium bisulfate. Mutation Research. 298:63–69
Novaes RD, Goncalves RV, Cupertino MC, Santos EC, Bigonha SM, Fernandes G, Maldonado I, Natali AJ (2016) Acute paraquat exposure determines dose dependent oxidative injury of multiple organs and metabolic dysfunction in rats: impact on exercise tolerance. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 97:114–124
Oikari A, Kukkonen J, Virtanen V (1992) Toxicidad aguda de productos químicos para Daphnia magna en aguas húmicas. Science of The Total Environment. 117-118, 367-377. Doi: 10.1016 / 0048-9697 (92) 90103-a
Ping KW, Darah I, Yusuf U, Yeng C, Sasidharan S (2012) Genotoxicity of Euphorbia hirata: An Allium cepa assay. Molecules. 17:7782–7791
Prado R, Rioboo C, Herrero A (2009) The herbicide paraquat induces alterations in the elemental and biochemical composition of non-target microalgal species. Chemosphere.76, 1440-1444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.06.003
Prajitha V, Thoppil J (2016) Genotoxic and antigenotoxic potential of the aqueous leaf extracts of Amaranthus spinosus Linn. using Allium cepa assay. South Afr. J. Bot. 102:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2015.06.018
Rizhsky L, Liang H, Mittler R (2003) The water–water cycle is essential for chloroplast protection in the absence of stress. J. Biol. Chem. 278:38921–38925
Sabeeh W (2011) Test of geuotoxicity of herbicid paraquat using chromosome aberration in anaphase- telophase in Alium cepa. Tikrit Journal of Pure Science 16:168–176
Salazar S, Maldonado, H (2019) Evaluation of cytotoxic potential of chlorpyrifos using Lens culinaris Med as efficient bioindicator. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 183, 109528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109528
Salazar S, Quintero J (2020a) Cytotoxic evaluation of glyphosate, using Allium cepa L. as bioindicator. Science of the Total Environment. 700, 134452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134452.
Salazar S, Quintero J (2020b) Determination of malathion’s toxic effect on Lens culinaris Medik cell cycle. Heliyon 6(9):e04846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04846
Salazar MA, Valderrama R, Quintero Caleño JD (2018) Efecto de la colchicina sobre la morfología foliar y los estomas de Kalanchoe daigremontiana Raym.-Hamet & H.Perrier (Crassulaceae). Revista Colombiana de Ciencias Hortícolas 12(1):212–222. https://doi.org/10.17584/rcch.2018v12i1.7059
Salazar S, Quintero J. Rojas J (2020a) Cytogenotoxic effect of propanil using the Lens culinaris Med and Allium cepa L test. Chemosphere. 249, 126193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126193
Salazar SA, Botello E, Quintero J (2020b) Optimización de la prueba de tetrazolio para evaluar la viabilidad en semillas de Solanum lycopersicum L. Ciencia & Tecnología Agropecuaria. 21(3), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.21930/rcta.vol21_num3_art:1344
Salazar-Mercado SA, Torres-León CA, Rojas-Suárez JP (2019) Cytotoxic evaluation of sodium hypochlorite, using Pisum sativum L as effective bioindicator. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe. 173, 71-76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.027.
Shao CY, Howe CJ, Porter AJ, Glover LA (2002) Novel cyanobacterial biosensor for detection of herbicides. App Environ Microbiol. 68:5026–5033
Sipari N, Lihavainen J, Shapiguzov A, Kangasjärvi J, Keinänen M (2020) Primary metabolite responses to oxidative stress in early-senescing and paraquat resistant Arabidopsis thaliana RCD1 (radical-induced cell death 1). Frontiers in Plant. 11:194. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00194
Spark KM, Swift RS (2002) Effect of soil composition and dissolved organic matter on pesticide sorption. Science of The Total Environment. 298(1-3):147–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00213-9
Tigre R, Silva N, Santos M, Honda N, Falcao EP, Pereira E (2012) Allelopathic and bioherbicidal potential of Cladonia verticillaris on the germination and growth of Lactuca sativa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 84, 125-132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.06.026.
Tütüncü E, Yalçin E, Acar A, Yapar K, Çavuşoğlu K (2019) Investigation of the toxic effects of a carbamate insecticide methiocarb in Allium cepa L. Cytologia. 84(2):113–117. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.84.113
Tyagi N, Singh R (2020) Estrés oxidativo inducido por paraquat e inflamación pulmonar. En: Chakraborti S., Parinandi N., Ghosh R., Ganguly N., Chakraborti T. (eds) Estrés oxidativo en enfermedades pulmonares. Springer Singapur.
US EPA (Ed.) (1989) Drinking Water Health Advisory: Pesticides. Lewis, Chelsea, MI. Li, P., Nijhawan, D., Budihardjo, I., Srinivasula, S.M., Ahmad, M., Alnemri, E.S., Wang, X.D., 1997. Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91, 479-489.
Verma S, Srivastava A (2018). Morphotoxicity and cytogenotoxicity of pendimethalin in the test plant Allium cepa L. - A biomarker based study. Chemosphere. 206, 248-254. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.177
Xiao H, Wang C, Yuan H, Christopher J (2018) El paraquat afecta la bioenergética mitocondrial, la expresión del sistema de dopamina y la actividad locomotora en el pez cebra ( Danio rerio ). Chemosphere. 191: 106-117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.032
Availability of data and materials
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy restrictions.
Funding
This study was funded by the University Francisco de Paula Santander
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Seir Antonio Salazar Mercado: methodology, writing, original draft preparation. Jesús David Quintero Caleño: supervision, conceptualization, investigation and data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This section is “not applicable” for this study as the study does not involve any human participants nor their data or biological material.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from individual or guardian participants.
Consent to publish
This section is “not applicable” for this study as the manuscript did not include any data from individuals.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mercado , S.A.S., Caleño , J.D.Q. Use of Lens culinaris Med test as environmental bioindicator to identify the cytogenotoxic effect of paraquat pesticide. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 51321–51328 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14352-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14352-0