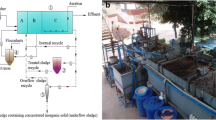
Abstract
A bioenhancement strategy for improving the anaerobic degradation efficiency of ship domestic sewage under microaerobic conditions was proposed in this study. Strains Stenotrophomonas sp. MSPP05 and Prevotella sp. MSPP07 with high organic-degrading efficiency and extracellular hydrolase yield were used for the bioenhancement of activated sludge. In batch experiments, the removal rates of chemical oxygen demand and total nitrogen reached 94.5% and 66.9% after 72 h of degradation. The activities of dehydrogenase, extracellular amylase, and protease in the treatment group were 1.2, 1.4, and 2.0 times higher than those in the control group. Microbial community analysis showed that exogenous enhanced strains competed with original microorganisms and became dominant. One-stage continuous stirred tank reactor with bioenhanced activated sludge ran steadily for 90 days with average effluent COD and TN concentrations of 87.5 and 14.6 mg/L. The feasibility of improving organic-degrading efficiency through bioenhancement by using exogenous hydrolase-producing strains was confirmed under microaerobic conditions. This work provided a theoretical basis for improving treatment effects and developing a new technique for ship domestic sewage treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bashandy SR, Abd-Alla MH, Dawood MFA (2020) Alleviation of the toxicity of oily wastewater to canola plants by the N2-fixing, aromatic hydrocarbon biodegrading bacterium Stenotrophomonas maltophilia-SR1. Appl Soil Ecol 154:103654
Chen Q, Wu WQ, Qi DC, Ding YH, Zhao ZH (2020) Review on microaeration-based anaerobic digestion: State of the art, challenges, and prospectives. Sci Total Environ 710:136388
Cupp-Enyard C (2008) Sigma’s non-specific protease activity assay-casein as a substrate. J Vis Exp 19:899
Díaz I, Lopes AC, Pérez SI, Fdz-Polanco M (2011) Determination of the optimal rate for the microaerobic treatment of several H2S concentrations in biogas from sludge digesters. Water Sci Technol 64:233–238
Dorador C, Meneses D, Urtuvia V, Demergasso C, Vila I, Witzel KP, Imhoff JF (2009) Diversity of Bacteroidetes in high-altitude saline evaporitic basins in northern Chile. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 114:G00D05
Filipovic L, Romic M, Sikora S, Babic KH, Filipovic L, Gerke HH, Romic D (2020) Response of soil dehydrogenase activity to salinity and cadmium species. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:530–536
Gargouri B, Contreras MM, Ammar S, Segura-Carretero A, Bouaziz M (2017) Biosurfactant production by the crude oil degrading Stenotrophomonas sp. B-2: chemical characterization, biological activities and environmental applications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:3769–3779
Green MR, Sambrook J (2012) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (Fourth Edition). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York.
Hassanshahian M, Ahmadinejad M, Tebyanian H, Kariminik A (2013) Isolation and characterization of alkane degrading bacteria from petroleum reservoir waste water in Iran (Kerman and Tehran provenances). Mar Pollut Bull 73:300–305
Hou F, Liu JN, Zhang YH, Zhao C, Xiao XD, Zou JL, Li Q, Hu S, Wang H, Jiang BJ (2020) Synthesis of metallic copper modified g-C3N4 by molecular self-assembly structure and its combined catalytic performance with activated sludge. J Hazard Mater 388:121754
Hu RH (2020) “Zero discharge and total degradation” Marine Domestic Sewage Treatment Equipment and Its Application Prospects. China Ship Survey 12:68–71
Inaba T, Su T, Aoyagi T, Aizawa H, Sato Y, Suh C, Lee JH, Hori T, Ogata A, Habe H (2020) Microbial community in an anaerobic membrane bioreactor and its performance in treating organic solid waste under controlled and deteriorated conditions. J Environ Manag 269:110786
Jenkins, D., Richard, M.G., Daigger, G., 2003. Manual on the causes and control of activated sludge bulking, foaming and other solids separation problems. Lewis Publishing, Boca Raton, FL.
Jiang L, Chen X, Qin M, Cheng SH, Wang YX, Zhou WZ (2019) On-board saline black water treatment by bioaugmentation original marine bacteria with Pseudoalteromonas sp. SCSE709-6 and the associated microbial community. Bioresour Technol 273:496–505
Kumar SS, Sangeeta R, Soumya S, Ranjan RP, Bidyut B, Kumar DMP (2014) Characterizing novel thermophilic amylase producing bacteria from Taptapani hot spring, Odisha, India. Jundishapur J Microb 7(12):e11800
Lim JW, Wang JY (2013) Enhanced hydrolysis and methane yield by applying microaeration pretreatment to the anaerobic co-digestion of brown water and food waste. Waste Manag 33:813–819
Lim JW, Chiam JA, Wang JW (2014) Microbial community structure reveals how microaeration improves fermentation during anaerobic co-digestion of brown water and food waste. Bioresour Technol 171:132–138
Liu L, Li N, Tao C, Zhao Y, Gao J, Huang Z, Zhang J, Gao J, Zhang J, Cai M (2020) Nitrogen removal performance and bacterial communities in zeolite trickling filter under different influent C/N ratios. Environ Sci Pollut Res, on publish.
Luo YR, Tian Y, Huang X, Yan CL, Hong HS, Lin GH, Zheng TL (2009) Analysis of community structure of a microbial consortium capable of degrading benzo(a)pyrene by DGGE. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1159–1116
Mesquita DP, Amaral AL, Ferreira EC (2011) Identifying different types of bulking in an activated sludge system through quantitative image analysis. Chemosphere 85:643–652
Nguyen D, Khanal SK (2018) A little breath of fresh air into an anaerobic system: how microaeration facilitates anaerobic digestion process. Bioresour Technol 36:1971–1983
Nguyen PHL, Kuruparan P, Visvanathan C (2007) Anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste as a treatment prior to landfill. Bioresour Technol 98:380–387
Van Staden JF, Mulaudzi LV (2000) Flow injection spectrophotometric assay of α-amylase activity. Anal Chim Acta 421:19–25
Wang HT, Hsu JT (2005) Optimal protease production condition for Prevotella ruminicola 23 and characterization of its extracellular crude protease. Anaerobe 11:155–162
Wang ZG, Sun LH, Cheng J, Liu CL, Tang XF, Zhang HF, Liu Y (2015) The optimization of fermentation conditions and enzyme properties of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia for protease production. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 63(2):292–299
Xie J, Hu WR, Pei HY, Dun MN, Qi F (2008) Detection of amount and activity of living algae in fresh water by dehydrogenase activity (DHA). Environ Monit Assess 146:473–478
Xu S, Selvam A, Wong JW (2014) Optimization of micro-aeration intensity in acidogenic reactor of a two-phase anaerobic digester treating food waste. Waste Manag 34:363–369
Zhang RC, Xu XJ, Chen C, Shao B, Zhou X, Yuan Y, Lee DJ, Ren NQ (2019) Bioreactor performance and microbial community analysis of autotrophic denitrification under micro-aerobic condition. Sci Total Environ 647:914–922
Zhu YB, Zhao R, Xiao AF, Li LJ, Jiang ZD, Chen F, Ni H (2016) Characterization of an alkaline β-agarase from Stenotrophomonas sp. NTa and the enzymatic hydrolysates. Int J Biol Macromol 86:525–534
Availability of data and material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
This work was supported by the China MSA project (grant number 80817006), which is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qing Chen integrated the data and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. Wanqing Wu and Linghua Zhang provided the research idea and instruments. Fang Wei performed the determination of chemical indexes. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PNG 41 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Wu, W., Zhang, L. et al. Shifts in enzymatic activities and microbial community structures in the bioenhanced treatment of ship domestic sewage under microaerobic conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 51242–51250 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14232-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14232-7