Abstract
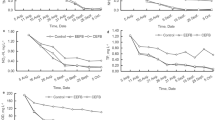
The ecological floating beds (EFB) are widely used in water quality restoration because of its low cost, high efficiency, and green characteristics. However, there is a potential impact of the EFB on the environment while water purification is not in progress. In this study, the life cycle assessment (LCA) and life cycle cost (LCC) methods were used to evaluate the overall environment of mixed-fill and biofilm enhanced EFB. The results show that the total environmental impact of the mixed-fill ecological floating beds (MEFB) is greater than that of the biofilm ecological floating beds (BEFB). In the raw material acquisition and operational stages, the environmental impact of the MEFB is smaller than that of the BEFB, while the environmental impact of the MEFB during the construction phase is much greater than that of the BEFB. The environmental impact of the construction stage of the MEFB accounts for 98.3% of the environmental impact of the entire life cycle. The operational stage of the MEFB was eco-friendly with regard to eutrophication potential, photochemical oxidation potential, ozone layer depletion potential, human toxicity potential, freshwater aquatic eco-toxicity potential, and terrestrial eco-toxicity potential environmental impact, and these effects of the operational stage of the MEFB account for 45.5% of the total environmental impact. The impact of the BEFB on the environment during raw material acquisition, construction, and operation accounts for 46.7%, 37.7%, and 15.6%, respectively, of the entire life cycle impact. Both two EFB technologies, the capital cost was the main expenditure with LCC, accounting for 60.4% and 52.9% of the MEFB and BEFB, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Abbreviations
- EFB:
-
ecological floating beds
- LCA:
-
life cycle assessment
- LCC:
-
life cycle cost
- MEFB:
-
mixed-fill ecological floating beds
- BEFB:
-
biofilm ecological floating beds
- LCIA:
-
life cycle inventory analysis
- PE:
-
person equivalent
- LCI:
-
life cycle inventory
- HDPE:
-
high-density polyethylene
- PVC:
-
polyvinyl chloride
- ADP:
-
abiotic depletion potential
- AP:
-
acidification potential
- EP:
-
eutrophication potential
- GWP:
-
global warming potential
- POCP:
-
photochemical oxidation potential
- ODP:
-
ozone layer depletion potential
- HTP:
-
human toxicity potential
- FAETP:
-
freshwater aquatic eco-toxicity potential
- TETP:
-
terrestrial eco-toxicity potential
References
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075
Alizadeh S, Zafari Klukhi H, Rostami F, Rouhbakhsh M, Avami A (2020) The eco-efficiency assessment of wastewater treatment plants in the city of Mashhad using emergy and life cycle analyses. J Clean Prod 249:119327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119327
Awad H, Alalm MG, El-Etriby HK (2019) Environmental and cost life cycle assessment of different alternatives for improvement of wastewater treatment plants in developing countries. Sci Total Environ 660:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.386
Cao W, Wang Y, Sun L, Jiang J, Zhang Y (2016) Removal of nitrogenous compounds from polluted river water by floating constructed wetlands using rice straw and ceramsite as substrates under low temperature conditions. Ecol Eng 88:77–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.12.019
Chen B, Yang S, Cao Q, Qian Y (2020) Life cycle economic assessment of coal chemical wastewater treatment facing the ‘Zero liquid discharge’ industrial water policies in China: Discharge or reuse? Energ. Policy 137:111107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111107
Corbella C, Puigagut J (2018) Improving domestic wastewater treatment efficiency with constructed wetland microbial fuel cells: Influence of anode material and external resistance. Sci Total Environ 631-632:1406–1414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.084
Corominas L, Foley J, Guest JS, Hospido A, Larsen HF, Morera S, Shaw A (2013) Life cycle assessment applied to wastewater treatment: State of the art. Water Res 47:5480–5492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.06.049
Dixon A, Simon M, Burkitt T (2003) Assessing the environmental impact of two options for small-scale wastewater treatment: comparing a reedbed and an aerated biological filter using a life cycle approach. Ecol Eng 20:297–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0925-8574(03)00007-7
Duan N, Liu XD, Dai J, Lin C, Xia XH, Gao RY, Wang Y, Chen SQ, Yang J, Qi J (2011) Evaluating the environmental impacts of an urban wetland park based on emergy accounting and life cycle assessment: A case study in Beijing. Ecol Model 222:351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2010.08.028
Flores L, García J, Pena R, Garfí M (2018) Constructed wetlands for winery wastewater treatment: A comparative Life Cycle Assessment. Sci Total Environ 659:1567–1576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.348
Fuchs VJ, Mihelcic JR, Gierke JS (2011) Life cycle assessment of vertical and horizontal flow constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment considering nitrogen and carbon greenhouse gas emissions. Water Res 45:2073–2081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.12.021
Gallego A, Hospido A, Moreira MT, Feijoo G (2008) Environmental performance of wastewater treatment plants for small populations. Resour Conserv Recycl 52:931–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2008.02.001
Garfí M, Flores L, Ferrer I (2017) Life Cycle Assessment of wastewater treatment systems for small communities: Activated sludge, constructed wetlands and high-rate algal ponds. J Clean Prod 161:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.116
Gerhardt KE, Gerwing PD, Greenberg BM (2017) Opinion: Taking phytoremediation from proven technology to accepted practice. Plant Sci 256:170–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.11.016
Guven H, Eriksson O, Wang Z, Ozturk I (2018) Life cycle assessment of upgrading options of a preliminary wastewater treatment plant including food waste addition. Water Res 145:518–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.08.061
Hospido A, Moreira MT, Feijoo G (2007) A comparison of municipal wastewater treatment plants for big centres of population in Galicia (Spain). Int J Life Cycle Assess 13:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1065/lca2007.03.314
Hu W, Guo Y, Tian J, Chen L (2019a) Eco-efficiency of centralized wastewater treatment plants in industrial parks: A slack-based data envelopment analysis. Resour Conserv Recycl 141:176–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.10.020
Hu Z, Li D, Guan D (2019b) Water quality retrieval and algae inhibition from eutrophic freshwaters with iron-rich substrate based ecological floating beds treatment. Sci Total Environ 712:135584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135584
ISO, 2006. ISO 14040: Environmental management–Life Cycle Assessment–Principles and Framework. Geneva.
Ita-Nagy D, Vázquez-Rowe I, Kahhat R, Quispe I, Chinga-Carrasco G, Clauser NM, Area MC (2020) Life cycle assessment of bagasse fiber reinforced biocomposites. Sci Total Environ 720:137586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137586
Johnson E (2003) Handbook on Life Cycle Assessment Operational Guide to the ISO Standards. Environ Impact Assess Rev 23:129–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0195-9255(02)00101-4
Karvonen J, Halder P, Kangas J, Leskinen P (2017) Indicators and tools for assessing sustainability impacts of the forest bioeconomy. For Ecosyst 4(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40663-017-0089-8
Lima NDDS, Nääs IDA, Garcia RG, Moura DJD (2019) Environmental impact of Brazilian broiler production process: Evaluation using life cycle assessment. J Clean Prod 237:117752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117752
Liu L, Wang S, Ji J, Xie Y, Shi X, Chen J (2019) Characteristics of microbial eukaryotic community recovery in eutrophic water by using ecological floating beds. Sci Total Environ 711:134551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134551
Lopsik K (2013) Life cycle assessment of small-scale constructed wetland and extended aeration activated sludge wastewater treatment system. Int J Environ Sci Te 10:1295–1308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0159-y
Lorenzo-Toja Y, Alfonsín C, Amores MJ, Aldea X, Marin D, Moreira MT, Feijoo G (2016) Beyond the conventional life cycle inventory in wastewater treatment plants. Sci Total Environ 553:71–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.073
Lucke T, Walker C, Beecham S (2019) Experimental designs of field-based constructed floating wetland studies: A review. Sci Total Environ 660:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.018
Mayer F, Bhandari R, Gäth SA, Himanshu H, Stobernack N (2020) Economic and environmental life cycle assessment of organic waste treatment by means of incineration and biogasification. Is source segregation of biowaste justified in Germany? Sci Total Environ:137731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137731
Mu D, Addy M, Anderson E, Chen P, Ruan R (2016) A life cycle assessment and economic analysis of the Scum-to-Biodiesel technology in wastewater treatment plants. Bioresour Technol 204:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.12.063
Muller S, Lesage P, Ciroth A, Mutel C, Weidema BP, Samson R (2014) The application of the pedigree approach to the distributions foreseen in ecoinvent v3. Int J Life Cycle Assess 21:1327–1337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-014-0759-5
Piao W, Kim Y, Kim H, Kim M, Kim C (2016) Life cycle assessment and economic efficiency analysis of integrated management of wastewater treatment plants. J Clean Prod 113:325–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.11.012
Rehman K, Imran A, Amin I, Afzal M (2018) Enhancement of oil field-produced wastewater remediation by bacterially-augmented floating treatment wetlands. Chemosphere 217:576–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.041
Resende JD, Nolasco MA, Pacca SA (2019) Life cycle assessment and costing of wastewater treatment systems coupled to constructed wetlands. Resour Conserv Recycl 148:170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.04.034
Rodríguez R, Espada JJ, Gallardo R, Molina R, López-Muñoz MJ (2018) Life cycle assessment and techno-economic evaluation of alternatives for the treatment of wastewater in a chrome-plating industry. J Clean Prod 172:2351–2362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.175
Rodriguez-Garcia G, Molinos-Senante M, Hospido A, Hernández-Sancho F, Moreira MT, Feijoo G (2011) Environmental and economic profile of six typologies of wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 45:5997–6010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.08.053
Samal K, Dash RR, Bhunia P (2018) A comparative study of macrophytes influence on performance of hybrid vermifilter for dairy wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 6(4):4714–4726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.07.018
Samal K, Kar S, Trivedi S (2019) Ecological floating bed (EFB) for decontamination of polluted water bodies: Design, mechanism and performance. J Environ Manag 251:109550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109550
Song J, Li Q, Dzakpasu M, Wang XC, Chang N (2020) Integrating stereo-elastic packing into ecological floating bed for enhanced denitrification in landscape water. Bioresour Technol 299:122601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122601
Sun S, Liu J, Zhang M, He S (2019) Simultaneous improving nitrogen removal and decreasing greenhouse gas emission with biofilm carriers addition in ecological floating bed. Bioresour Technol 292:121944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121944
The Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China (2002) Environmental quality standards for surface water (GB 3838-2002), Beijing, China
Tillman A-M, Svingby M, Lundström H (1998) Life cycle assessment of municipal waste water systems. Int J Life Cycle Assess 3:145–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02978823
Weragoda SK, Jinadasa KBSN, Zhang DQ, Gersberg RM, Tan SK, Tanaka N, Jern NW (2012) Tropical Application of Floating Treatment Wetlands. Wetlands 32(5):955–961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-012-0333-5
Wernet G, Bauer C, Steubing B, Reinhard J, Moreno-Ruiz E, Weidema B (2016) The ecoinvent database version 3 (part I): overview and methodology. Int J Life Cycle Assess 21:1218–1230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-016-1087-8
Wissel S, Wätzold F (2010) A Conceptual Analysis of the Application of Tradable Permits to Biodiversity Conservation. Conserv Biol 24:404–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2009.01444
Wu Q, Hu Y, Li S, Peng S, Zhao H (2016) Microbial Mechanisms of Using Enhanced Ecological Floating Beds for Eutrophic Water Improvement. Bioresour Technol 211:451–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.113
Yeh N, Yeh P, Chang Y-H (2015) Artificial floating islands for environmental improvement. Renew Sust Energ Rev 47:616–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.03.090
Yu S, Miao C, Song H, Huang Y, Chen W, He X (2019) Efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus removal by six macrophytes from eutrophic water. Int J Phytoremediat 21(7):643–651. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2018.1556582
Zhang L, Sun Z, Xie J, Wu J, Cheng S (2018) Nutrient removal, biomass accumulation and nitrogen-transformation functional gene response to different nitrogen forms in enhanced floating treatment wetlands. Ecol Eng 112:21–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.12.021
Zhang Y, Zhang C, Qiu Y, Li B, Pang H, Xue Y, Liu Y, Yuan Z, Hunag X (2020) Wastewater treatment technology selection under various influent conditions and effluent standards based on life cycle assessment. Resour Conserv Recycl 154:104562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104562
Zhao X, Yang J, Zhang X, Wang L, Ma F (2017) Evaluation of bioaugmentation using multiple life cycle assessment approaches: A case study of constructed wetland. Bioresour Technol 244:407–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.170
Zheng X, Como S, Magni P, Huang L (2019) Spatiotemporal variation in environmental features and elemental/isotopic composition of organic matter sources and primary producers in the Yundang Lagoon (Xiamen, China). Environ Sci Pollut R 26(13):13126–13137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04720-2
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0401102), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41361017), and the Natural Scientific Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20181BAB203021). We are also thankful to all our laboratory colleagues and research staff members for their constructive advice and help.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0401102), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41361017), the Natural Scientific Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20181BAB203021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaochen Yao: data curation, writing—original draft preparation and editing.
Guodi Zheng: development or design of methodology, writing—reviewing and editing.
Yun Cao: data curation, writing—original draft preparation.
Bao Yu: writing—original draft preparation and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Loubet
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, X., Zheng, G., Cao, Y. et al. Life cycle and economic assessment of enhanced ecological floating beds applied water purification. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 49574–49587 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14008-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14008-z