Abstract
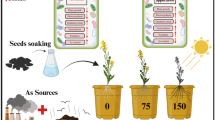
Phenol and its derivatives behave as mutagens, teratogens and carcinogens inducing adverse physiological effects and are considered environmental hazards. The present study focuses on high concentration phenol utilization by Aspergillus niger FP7 under various physicochemical parameters. The soil remediation potential of the culture for reducing phenol toxicity against Vigna radiata L. seed germination was also evaluated along with the extent of phenol utilization using high-performance liquid chromatography. Aspergillus niger FP7 showed phenol tolerance up to 1000 mg/l, beyond which there was a sharp reduction in phenol utilization. Supplementation of the mineral salt medium with glucose and peptone and application of a 100 rpm agitation rate enhanced phenol utilization (up to 88.3%). Phenol utilization efficiency decreased (up to 29.6%) when cadmium and mercury salts were present, but the same improved (59.4–75.5%) by the incorporation of cobalt, copper and zinc salts. Vigna radiata L. seeds sown in the non-augmented soil revealed a 3.27% germination index, and with fungal augmentation, the germination index improved (97.3%). The non-augmented soil demonstrated 3.1% phenol utilization, while for the augmented soil, the utilization was 79.3%. Based on the phytotoxicity study and chromatographic analysis, it could be inferred that Aspergillus niger FP7 significantly enhanced phenol utilization in soil. In the future, Aspergillus niger FP7 could be of potential use in bioremediation of sites polluted with high concentrations of phenol.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Al Hashemi W, Maraqa MA, Rao MV, Hossain MM (2015) Characterization and removal of phenolic compounds from condensate-oil refinery wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 54(3):660–671. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.884472
Al-Khalid T, El-Naas MH (2012) Aerobic biodegradation of phenols: a comprehensive review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42(16):1631–1690. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2011.569872
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Aracic S, Manna S, Petrovski S, Wiltshire JL, Mann G, Franks AE (2015) Innovative biological approaches for monitoring and improving water quality. Front Microbiol 6:826. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00826
Baldrian P, Gabriel J (2002) Copper and cadmium increase activity in Pleurotus ostreatus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 206(1):69–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb10988.x
Bhattacharya S, Das A, Mangai G, Vignesh K, Sangeetha J (2011) Mycoremediation of Congo red dye by filamentous fungi. Braz J Microbiol 42(4):1526–1536. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822011000400040
Bhattacharya S, Das A, Srividya S, Prakruti PA, Priyanka N, Sushmitha B (2020) Prospects of Stenotrophomonas pavanii DB1 in diesel utilization and reduction of its phytotoxicity on Vigna radiata. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:445–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02302-w
Campuzano S, Serra B, Pedrero M, de Villena FJM, Pingarrón JM (2003) Amperometric flow-injection determination of phenolic compounds at self-assembled monolayer-based tyrosinase biosensors. Anal Chim Acta 494(1-2):187–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00919-X
Carabajal M, Perullini M, Jobbágy M, Ullrich R, Hofrichter M, Levin L (2016) Removal of phenol by immobilization of Trametes versicolor in silica-alginate-fungus biocomposites and loofa sponge. CLEAN 44(2):180–188. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201400366
Chandrasekaran S, Pugazhendi A, Banu RJ, Ismail IMI, Qari HA (2018) Biodegradation of phenol by a moderately halophilic bacterial consortium. Environ Prog Sustain 37(5):1587–1593. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12834
Galhaup C, Goller S, Peterbauer CK, Strauss J, Haltrich D (2002) Characterization of the major laccase isoenzyme from Trametes pubescens and regulation of its synthesis by metal ions. Microbiology 148(Pt 7):2159–2169. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-148-7-2159
Gerginova M, Manasiev J, Yemendzhiev H, Terziyska A, Peneva N, Alexieva Z (2014) Biodegradation of phenol by Antarctic strains of Aspergillus fumigatus. Z Naturforschung C, J Biosci 68(9-10):384–393. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2013-9-1006
Gu Q, Wu Q, Zhang J, Guo W, Wu H, Sun M (2016) Community analysis and recovery of phenol-degrading bacteria from drinking water biofilters. Front Microbiol 7:495. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00495
Ibrahim AG, EL-Gamdi LSYA (2019) Characterization of fungi that able to degrade phenol from different contaminated areas in Saudi Arabia. J Biol Sci 19:210-217. https://doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2019.210.217
Kannan A, Upreti RK (2008) Influence of distillery effluent on germination and growth of mung bean (Vigna radiata) seeds. J Hazard Mater 153:609–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.004
Krastanov A, Alexieva Z, Yemendzhiev H (2013) Microbial degradation of phenol and phenolic derivatives. Eng Life Sci 13(1):76–87. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201100227
Krogmeier MJ, Bremner JM (1989) Effects of phenolic acids on seed germination and seedling growth in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 8(2):116–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00257754
Loh KC, Tan PP (2000) Effect of additional carbon sources on biodegradation of phenol. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 64(6):756–763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s0012800068
Ma Y, Li X, Mao H, Wang B, Wang P (2018) Remediation of hydrocarbon–heavy metal co-contaminated soil by electrokinetics combined with biostimulation. Chem Eng J 353:410–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.131
Melo JS, Kholi S, Patwardhan AW, D’Souza SF (2005) Effect of oxygen transfer limitations in phenol biodegradation. Process Biochem 40(20):625–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.01.049
Mikiashvili N, Wasser SP, Nevo E, Elisashvili V (2006) Effects of carbon and nitrogen sources on Pleurotus ostreatus ligninolytic enzyme activity. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22(9):999–1002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9132-6
Osma JF, Toca-Herrera JL, Rodríguez-Couto S (2010) Transformation pathway of Remazol Brilliant Blue R by immobilised laccase. Bioresour Technol 101(22):8509–8514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.074
Patel H, Gupte A (2016) Optimization of different culture conditions for enhanced laccase production and its purification from Tricholoma giganteum AGHP. Bioresour Bioprocess 3:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-016-0088-6
Prabu PC, Udayasoorian C (2005) Phenol metabolism by white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium isolated from Indian paper mill effluent enriched soil samples. Asian J Plant Sci 4(1):56–59. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajps.2005.56.59
Pradeep NV, Anupama S, Navya K, Shalini HN, Idris M, Hampannavar US (2015) Biological removal of phenol from wastewaters: a mini review. Appl Water Sci 5(2):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0176-8
Rao A, Zhang Y, Muend S, Rao R (2010) Mechanism of antifungal activity of terpenoid phenols resembles calcium stress and inhibition of the TOR pathway. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(12):5062–5069. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01050-10
Rubino FM (2015) Toxicity of glutathione-binding metals: a review of targets and mechanisms. Toxics 3(1):20–62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics3010020
Ruelle P (2000) The n-octanol and n-hexane/water partition coefficient of environmentally relevant chemicals predicted from the mobile order and disorder (MOD) thermodynamics. Chemosphere 40(5):457–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00268-4
Sharma N, Gupta VC (2012) Batch biodegradation of paper and pulp effluent by Aspergillus niger. Int J Chem Eng Appl 3(3):182–186. https://doi.org/10.7763/IJCEA.2012.V3.183
Sharma R, Prakash O, Sonawane MS, Nimonkar Y, Golellu PB, Sharma R (2016) Diversity and distribution of phenol oxidase producing fungi from soda lake and description of Curvularia lonarensis. Front Microbiol 7:1847. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01847
Singh S, Singh BR, Chandra R (2009) Biodegradation of phenol in batch culture by pure and mixed strains of Paenibacillus sp. and Bacillus cereus. Pol J Microbiol 58(4):319–325
Supriya CH, Neehar D (2014) Biodegradation of phenol by Aspergillus niger. IOSR J Pharm 4:11–17. https://doi.org/10.9790/3013-0407011017
Tebbouche L, Hank D, Zeboudj S, Namane A, Hellal A (2016) Evaluation of the phenol biodegradation by Aspergillus niger: application of full factorial design methodology. Desalin Water Treat 57(13):6124–6130. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1053991
Viswanath B, Rajesh B, Janardhan A, Kumar AP, Narasimha G (2014) Fungal laccases and their applications in bioremediation. Enzyme Res 2014:163242–163221. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/163242
Wolski EA, Barrera V, Castellari C, González JF (2012) Biodegradation of phenol in static cultures by Penicillium chrysogenum ERK1: catalytic abilities and residual phytotoxicity. Rev Argent Microbiol 44(2):113–121
Yordanova G, Godjevargova T, Nenkova R, Ivanova D (2013) Biodegradation of phenol and phenolic derivatives by a mixture of immobilized cells of Aspergillus awamori and Trichosporon cutaneum. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 27(2):3681–3688. https://doi.org/10.5504/BBEQ.2013.0003
Zhao D, Zhang X, Cui D, Zhao M (2012) Characterisation of a novel white laccase from the deuteromycete fungus Myrothecium verrucaria NF-05 and its decolourisation of dyes. PLoS One 7(6):e38817. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038817
Zhou M, Zhang J, Sun C (2017) Occurrence, ecological and human health risks, and seasonal variations of phenolic compounds in surface water and sediment of a potential polluted river basin in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(10):1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph1410114
Acknowledgements
We extend our sincere gratitude to the management of JAIN (Deemed-to-be University) for providing the research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SB designed the study and interpreted the data. AD contributed in writing the manuscript. KK, NP and JS performed the experiments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharya, S., Das, A., Krishnan, K. et al. Co-substrate-mediated utilization of high concentration of phenol by Aspergillus niger FP7 and reduction of its phytotoxicity on Vigna radiata L.. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 64030–64038 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13947-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13947-x