Abstract
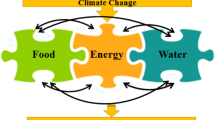
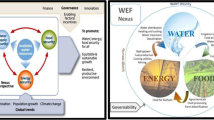
In recent decades, global forecasts show that the demands for freshwater, energy, and food have been affected by population growth, economic development, international trade, and increasing urbanization and food diversity. Moreover, cultural changes and other phenomena have adversely affected the water, energy, and food (WEF) resources demand. Consequently, climate change adverse impact, which is an undesirable phenomenon, will be increased at a staggering rate. Numerous studies have emphasized that the lack of integrated and systematic management strategies threaten these indispensable resources’ ability to meet growing demand. In many countries, the security of WEF resources, which is related to each other, has become three non-traditional security challenges that overshadow these communities’ development. Before realizing the importance of interactions between these three vital resources, the management strategies were typically used for one source, which was completely independent of the other two. Since these strategies did not consider the interactions between the three systems, the applied strategies’ results were sometimes contradictory. Also, due to the lack of attention to these three sectors’ vital connections, the competition level among these systems has been increased. Therefore, in recent years, the study of the complex interactions and connections between these resources has led to the emergence of a new term called WEF nexus in the scientific communities. Most studies about the WEF nexus have only described the current situation or, ideally, analyzed several predetermined scenarios. However, the adopted approach should be able to analyze different scenarios and be efficient and robust enough to develop a variety of strategies and utilize them for macro-policies. In this study, after reviewing the complex interactions between the WEF systems, it was tried to introduce a novel paradigm for the WEF nexus, which concentrates on expanding the possible space of WEF nexus.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors declare that the data are not available and can be presented upon the requested of the readers.
References
Arain H, Han L, Meo MS (2019) Nexus of FDI, population, energy production, and water resources in South Asia: a fresh insight from dynamic common correlated effects (DCCE). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(26):27128–27137
Asian Development Bank (2013) Thinking about water differently: managing the water–food–energy nexus. Mandaluyong City, Philippines: Asian Development Bank
Bazilian M, Rogner H, Howells M, Hermann S, Arent D, Gielen D, Steduto P, Mueller A, Komor P, Tol RSJ, Yumkella KK (2011) Considering the energy, water and food nexus: towards an integrated modelling approach. Energy Policy 39(12):7896–7906
Broca SS (2002) Food insecurity, poverty and agriculture: A concept paper. Working Paper No. 02-15, Agricultural and Development Economics Division, FAO (Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations), Rome
Chang Y, Li G, Yao Y, Zhang L, Yu C (2016) Quantifying the water-energy-food nexus: current status and trends. Energies 9(2):65–73
Daher BT, Mohtar RH (2015) Water–energy–food (WEF) Nexus Tool 2.0: guiding integrative resource planning and decision-making. Water Int 40(5-6):748-771
Dodds F, Bartram J (eds) (2016) The water, food, energy and climate nexus: challenges and an agenda for action. Routledge, Abingdon
El-Gafy I (2017) Water–food–energy nexus index: analysis of water–energy–food nexus of crop’s production system applying the indicators approach. Appl Water Sci 7(6):2857–2868
Endo A, Tsurita I, Burnett K, Orencio PM (2017) A review of the current state of research on the water, energy, and food nexus. J Hydrol Reg Stud 11:20–30
Fathollahi-Fard AM, Ahmadi A, Mirzapour Al-e-Hashem SMJ (2020) Sustainable closed-loop supply chain network for an integrated water supply and wastewater collection system under uncertainty. J Environ Manag 275:111277–111286
Finley JW, Seiber JN (2014) The nexus of food, energy, and water. J Agric Food Chem 62(27):6255–6262
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2003) Strengthening coherence in FAO’s initiatives to fight hunger. http://www.fao.org/docrep/MEETING/007/J0710E.HTM
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2014a) The water-energy-food nexus A new approach in support of food security and sustainable agriculture. Retrieved from http://www.fao.org/3/a-bl496e.pdf
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2014b) Walking the nexus talk: Assessing the water-energy-food nexus in the context of the sustainable energy for all initiative. In Environment and natural resources management working paper 58. Retrieved from http://www.fao.org/3/a-i3959e.pdf
Franke NA, Boyacioglu H, Hoekstra AY (2013) Grey water footprint accounting: tier 1 supporting guidelines. Unesco-Ihe, Delft
Garschagen M, Hagenlocher M, Kloos J, Pardoe J, Lanzendörfer M, Mucke P, Radtke K, Rhyner J, Walter B, Welle T, Birkmann J (2016) World risk report 2016. Bündnis Entwicklung Hilft and United Nations University Institute of Environment and Human Security (UNU-EHS), Bonn
Hadian S, Madani K (2015) A system of systems approach to energy sustainability assessment: are all renewables really green? Ecol Indic 52:194–206
Hanjra MA, Qureshi ME (2010) Global water crisis and future food security in an era of climate change. Food Policy 35(5):365–377
Hardy L, Garrido A, Juana L (2012) Evaluation of Spain’s water-energy nexus. Int J Water Resour Dev 28(1):151–170
Hoff H (2011) Understanding the nexus. Background paper for the Bonn2011 nexus conference: The water, energy and food security nexus solutions for the green economy. Stockholm, Stockholm Environment Institute
International Energy Agency (2016) Energy and Air Pollution: World Energy Outlook Special Report 2016
IRENA (The International Renewable Energy Agency) (2015) Renewable energy and the water, energy and food nexus. Retrieved from: http://www.pseau.org/outils/ouvrages/irena_renewable_energy_and_the_water_energy_and_food_nexus_2015.pdf
Khan S, Hanjra MA (2009) Footprints of water and energy inputs in food production–global perspectives. Food Policy 34(2):130–140
Li M, Fu Q, Singh VP, Liu D, Li T (2019) Stochastic multi-objective modeling for optimization of water-food-energy nexus of irrigated agriculture. Adv Water Resour 127:209–224
Meneguzzo F, Zabini F, Albanese L, Crisci A (2019) Novel affordable, reliable and efficient technologies to help addressing the water-energy-food nexus. Eur J Sustain Dev 8(4):1–15
Mohtar RH, Daher B (2012) Water, energy, and food: The ultimate nexus. Encyclopedia of agricultural, food and biological engineering (pp. 1–15). (2nd ed.). Abingdon, UK: Taylor & Francis. https://doi.org/10.1081/E-EAFE2-120048376
Mohtar RH, Daher B (2016) Water-energy-food nexus framework for facilitating multi-stakeholder dialogue. Water Int 41(5):655–661
Molden D (2007) Water for Food, Water for Life: a Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture. Earthscan, London
Pingali P, Alinovi L, Sutton J (2005) Food security in complex emergencies: enhancing food system resilience. Disasters 29:S5–S24
Ravar Z, Zahraie B, Sharifinejad A, Gozini H, Jafari S (2020) System dynamics modeling for assessment of water–food–energy resources security and nexus in Gavkhuni basin in Iran. Ecol Indic 108:105682
Sachs I, Silk D (1990). Food and energy: strategies for sustainable development. United Nations University Press, Tokyo
Scardigno A (2020) New solutions to reduce water and energy consumption in crop production: a water–energy–food nexus perspective. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health 13:11–15
Secretariat, OPEC (2014) World oil outlook: Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries. Vienna, Austria
Sharghi E, Nourani V, Najafi H, Molajou A (2018) Emotional ANN (EANN) and wavelet-ANN (WANN) approaches for Markovian and seasonal based modeling of rainfall-runoff process. Water Resour Manag 32(10):3441–3456
Sharghi E, Nourani V, Najafi H, Gokcekus H (2019) Conjunction of a newly proposed emotional ANN (EANN) and wavelet transform for suspended sediment load modeling. Water Supply 19(6):1726–1734
Slorach PC, Jeswani HK, Cuéllar-Franca R, Azapagic A (2020) Environmental sustainability in the food-energy-water-health nexus: a new methodology and an application to food waste in a circular economy. Waste Manag 113:359–368
Smajgl A, Ward J, Pluschke L (2016) The water–food–energy nexus–realising a new paradigm. J Hydrol 533:533–540
Stephan RM, Mohtar RH, Daher B, Embid Irujo A, Hillers A, Ganter JC, Karlberg L, Martin L, Nairizi S, Rodriguez DJ, Sarni W (2018) Water–energy–food nexus: a platform for implementing the sustainable development goals. Water Int 43(3):472–479
Van der Hoeven M (2013) World energy outlook 2012. International Energy Agency, Tokyo, Japan
Yang J, Yamazaki A (2013) Water and energy nexus: a literature review. Water West- Stanford Univ 1:146
Zaman K, Shamsuddin S, Ahmad M (2017) Energy-water-food nexus under financial constraint environment: good, the bad, and the ugly sustainability reforms in sub-Saharan African countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(15):13358–13372
Zhang X, Vesselinov VV (2017) Integrated modeling approach for optimal management of water, energy and food security nexus. Adv Water Resour 101:1–10
Zhang J, Campana PE, Yao T, Zhang Y, Lundblad A, Melton F, Yan J (2018) The water-food-energy nexus optimization approach to combat agricultural drought: a case study in the United States. Appl Energy 227:449–464
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Amir Molajou: conceptualization; original draft; visualization; writing and editing.
Abbas Afshar: supervisor; conceptualization; review and editing.
Mina Khosravi: review an editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors declare that they agree with the participation of this paper in this journal.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that they agree with the publication of this paper in this journal.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Molajou, A., Afshar, A., Khosravi, M. et al. A new paradigm of water, food, and energy nexus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 107487–107497 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13034-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13034-1