Abstract
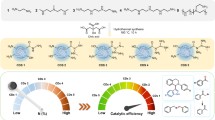
Graphene oxide sheets (GO) were coupled with carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to enhance the photoactivity of anatase under visible and solar irradiation. The carbon nanotube surface was functionalized in the acidic reflux condition before coupling with GO and decoration of anatase by the sol–gel method. A modified kinetic model was appropriately applied to predict the breakthrough in the methylene blue degradation yield and determine the constant rate which was clearly affected by coupling architecture. The nanocomposite fabricated by the same proportions of GO and CNTs, 3.33%, exhibited the maximal degradation yield, 96.5%, in the dye solution with the initial concentration of 3.0 mg l−1. The characterizations based on X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) revealed that the functionalized CNTs could create the appropriate space between the graphene sheets for uniformly interconnection of anatase via oxygen-containing groups onto the material surfaces. This enhancement in the degradation efficiency could be ascribed to the unique architecture, leading to a decrease in bandgap energy, 2.2 eV, which facilitated the electron-hole separation. Besides of breakthrough in the photoreaction rate, the adequate architecture led to an efficient reduction in the content of carbon-based materials. Also, the performance of mentioned nanocomposite under sunlight photons was effectively higher than that under UV irradiation. The hybrid nanocomposite provided a large number of active sites for photoreactions to facilitate the treatment of wastewater under solar irradiation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi M, Motlagh HR, Jaafarzadeh N, Mostoufi A, Saeedi R, Barzegar G, Jorfi S (2017) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline and real pharmaceutical wastewater using MWCNT/TiO2 nano-composite. J Environ Manag 186:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.09.088
Ai L, Jiang J (2012) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution with self-assembled cylindrical graphene–carbon nanotube hybrid. Chem Eng J 192:156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.03.056
Ashkarran AA, Fakhari M, Hamidinezhad H, Haddadi H, Nourani MR (2015) TiO2 nanoparticles immobilized on carbon nanotubes for enhanced visible-light photo-induced activity. J Mater Res Technol 4(2):126–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2014.10.005
Barik AJ, Gogate PR (2016) Degradation of 4-chloro 2-aminophenol using a novel combined process based on hydrodynamic cavitation, UV photolysis and ozone. Ultrason Sonochem 30:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2015.07.001
Bellamkonda S, Thangavel N, Hafeez HY, Neppolian B, Rao GR (2019) Highly active and stable multi-walled carbon nanotubes-graphene-TiO2 nanohybrid: an efficient non-noble metal photocatalyst for water splitting. Catal Today 321:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.10.023
Bozic M, Vivod V, Vogrincic R, Ban I, Jaksa G, Hribernik S, Fakin D, Kokol V (2016) Enhanced catalytic activity of the surface modified TiO2-MWCNT nanocomposites under visible light. J Colloid Interface Sci 465:93–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.11.051
Byrne C, Subramanian G, Pillai SC (2018) Recent advances in photocatalysis for environmental applications. J Environ Chem Eng 6(3):3531–3555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.07.080
Choi J, Park H, Hoffmann MR (2010) Effects of single metal-ion doping on the visible-light photoreactivity of TiO2. J Phys Chem C 114(2):783–792. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp908088x
Collivignarelli MC, Abba A, Miino MC, Damiani S (2019) Treatments for color removal from wastewater: state of the art. J Environ Manag 236:727–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.11.094
Dong Y, Tang D, Li C (2014) Photocatalytic oxidation of methyl orange in water phase by immobilized TiO2-carbon nanotube nanocomposite photocatalyst. Appl Surf Sci 296:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.12.128
Fatima M, Farooq R, Lindström RW, Saeed M (2017) A review on biocatalytic decomposition of azo dyes and electrons recovery. J Mol Liq 246:275–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.09.063
Fiyadh SS, Alsaadi MA, Jaafar WZB, Alomar MK, Fayaed SS, Mohd NSB, Hin LS, Elshafie A (2019) Review on heavy metal adsorption processes by carbon nanotubes. J Clean Prod 230:783–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.154
Fu J, Kyzas GZ (2014) Wet air oxidation for the decolorization of dye wastewater: an overview of the last two decades. Chin J Catal 35(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(12)60724-4
Fu Z, Zhang S, Fu Z (2019) Preparation of multicycle GO/TiO2 composite photocatalyst and study on degradation of methylene blue synthetic wastewater. Appl Sci 9(16):3282. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163282
Fujishima A, Rao TN, Tryk DA (2000) Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol C 1(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1389-5567(00)00002-2
Galveza HEG, Beltrana CGA, Sancheza JLA, Maciasb AH, Fontechac AMG, Luqued PA, Beltrana AC (2019) Graphene role in improved solar photocatalytic performance of TiO2-RGO nanocomposite. Chem Phys 521:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2019.01.013
Ghorbani M, Salem S (2021) Solar treatment of sewage discharged from industrial estate for reduction of chemical oxygen demand over Degussa P-25 titania. Chemosphere 265:129123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129123
Huang Y, Chen D, Hu X, Qian Y, Li D (2018) Preparation of TiO2/carbon nanotubes/reduced graphene oxide composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity for the degradation of rhodamine B. Nanomaterials 8(6):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8060431
Hunge Y, Yadav A, Dhodamani A, Suzuki N, Terashima C, Fujishima A, Mathe V (2020) Enhanced photocatalytic performance of ultrasound treated GO/TiO2 composite for photocatalytic degradation of salicylic acid under sunlight illumination. Ultrason Sonochem 61:104849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104849
Imtiaz S, Siddiq M, Kausar A, Muntha ST, Ambreen J, Bibi I (2018) A review featuring fabrication, properties and applications of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) reinforced polymer and epoxy nanocomposites. Chin J Polym Sci 36(4):445–461 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10118-018-2045-7
Kausar A, Iqbal M, Javed A, Aftab K, Bhatti HN, Nouren S (2018) Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: a review. J Mol Liq 256:395–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.034
Koli VB, Dhodamani AG, Delekar SD, Pawar SH (2017) In situ sol-gel synthesis of anatase TiO2-MWCNTs nanocomposites and their photocatalytic applications. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 333:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.10.008
Koo Y, Littlejohn G, Collins B, Yun Y, Shanov VN, Schulz M, Pai D, Sankar J (2014) Synthesis and characterization of Ag–TiO2–CNT nanoparticle composites with high photocatalytic activity under artificial light. Compos B Eng 57:105–111. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20170081
Li Q, Bian J, Zhang L, Zhang R, Wang G, Ng DH (2014) Synthesis of carbon materials–TiO2 hybrid nanostructures and their visible-light photocatalytic activity. ChemPlusChem 79(3):454–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/cplu.201300380
Liu WW, Chai SP, Mohamed AR, Hashim U (2014) Synthesis and characterization of graphene and carbon nanotubes: a review on the past and recent developments. J Ind Eng Chem 20(4):1171–1185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.08.028
Mohamed R, McKinney D, Sigmund W (2012) Enhanced nanocatalysts. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 73(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2011.09.001
Mora-Gomez J, Ortega E, Mestre S, Perez-Herranz V, Garcia-Gabaldon M (2019) Electrochemical degradation of norfloxacin using BDD and new Sb-doped SnO2 ceramic anodes in an electrochemical reactor in the presence and absence of a cation-exchange membrane. Sep Purif Technol 208:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.05.017
Muhich CL, Westcott JY, Fuerst T, Weimer AW, Musgrave CB (2014) Increasing the photocatalytic activity of anatase TiO2 through B, C and N doping. J Phys Chem C 118(47):27415–27427. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp508882m
Nagarajan S, Skillen SC, Fina F, Zhang G, Randorn C, Lawton LA, Irvine JTS, Robertson PKJ (2017) Comparative assessment of visible light and UV active photocatalysts by hydroxyl radical quantification. J Photochem Photobiol A 334:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.10.034
Natarajan S, Bajaj HC, Tayade RJ (2018) Recent advances based on the synergetic effect of adsorption for removal of dyes from waste water using photocatalytic process. J Environ Sci 65:201–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.03.011
Navarro P, Gabaldon JA, Gomez-Lopez VM (2017) Degradation of an azo dye by a fast and innovative pulsed light/H2O2 advanced oxidation process. Dyes Pigments 136:887–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2016.09.053
Nazari Y, Salem S (2017) Magnetisation of TiO2/reduced graphene oxide nano photocatalyst. Int Proc Chem Biol Environ Eng 102:50–56
Peralta E, Roa G, Hernandez-Servin JA, Romero R, Balderas P, Natividad R (2014) Hydroxyl radicals quantification by UV spectrophotometry. Electrochim Acta 129:137–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.02.047
Prasad C, Liu Q, Tang H, Yuvaraja G, Long J, Rammohan A, Zyryanov GV (2020) An overview of graphene oxide supported semiconductors based photocatalysts: properties, synthesis and photocatalytic applications. J Mol Liq 297:111826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111826
Salem S, Salem A, Rezaei M (2016) Facile decoration of TiO2 nanoparticles on graphene for solar degradation of organic dye. Solid State Sci 61:131–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2016.09.013
Sarkar AK, Saha A, Tarafder A, Panda AB, Pal S (2016) Efficient removal of toxic dyes via simultaneous adsorption and solar light driven photodegradation using recyclable functionalized amylopectin–TiO2–Au nanocomposite. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(3):1679–1688. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b01614
Sehar S, Naz I, Perveen I, Ahmed S (2019) Superior dye degradation using SnO2-ZnO hybrid heterostructure catalysts. Korean J Chem Eng 36(1):56–62 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11814-018-0159-9
Shafei A, Sheibani S (2019) Visible light photocatalytic activity of Cu doped TiO2-CNT nanocomposite powder prepared by sol–gel method. Mater Res Bull 110:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.10.035
Sharma M, Behl K, Nigam S, Joshi M (2018) TiO2-GO nanocomposite for photocatalysis and environmental applications: a green synthesis approach. Vacuum 156:434–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.08.009
Shanker U, Rani M, Jassal V (2017) Degradation of hazardous organic dyes in water by nanomaterials. Environ Chem Lett 15(4):623–642 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10311-017-0650-2
Shen T, Zhou X, Cao H, Zheng C, Liu Z (2015) TiO2(B)–CNT–graphene ternary composite anode material for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv 5(29):22449–22454. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA01337B
Rezaei M, Salem S (2016a) Optimal TiO2–graphene oxide nanocomposite for photocatalytic activity under sunlight condition: synthesis, characterization, and kinetics. Int J Chem Kinet 48(10):573–583. https://doi.org/10.1002/kin.21013
Rezaei M, Salem S (2016b) Photocatalytic activity enhancement of anatase–graphene nanocomposite for methylene removal: degradation and kinetics. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 167:41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.04.057
Wang C, Cao M, Wang P, Ao Y, Hou J, Qian J (2014) Preparation of graphene–carbon nanotube–TiO2 composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity for the removal of dye and Cr (VI). Appl Catal A Gen 473:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2013.12.028
Wang G, Zhang Q, Chen Q, Ma X, Xin Y, Zhu X, Ma D, Cui C, Zhang J, Xiao Z (2019) Photocatalytic degradation performance and mechanism of dibutyl phthalate by graphene/TiO2 nanotube array photoelectrodes. Chem Eng J 358:1083–1090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.039
Xiang Q, Yu J, Wong PK (2011) Quantitative characterization of hydroxyl radicals produced by various photocatalysts. J Colloid Interface Sci 357:163–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.01.093
Yadav HM, Kim JS (2016) Solvothermal synthesis of anatase TiO2-graphene oxide nanocomposites and their photocatalytic performance. J Alloys Compd 688(Part B):123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.133
Yao W, Li Y, Yan D, Ma M, He Z, Chai S, Su X, Chen F, Fu Q (2013) Fabrication and photocatalysis of TiO2-graphene sandwich nanosheets with smooth surface and controlled thickness. Chem Eng J 229:569–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.027
Yu J, Ma T, Liu S (2011) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of mesoporous TiO2 aggregates by embedding carbon nanotubes as electron-transfer channel. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:3491–3501. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CP01139H
Zhou Y, Lu J, Zhou Y, Liu Y (2019) Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: a review. Environ Pollut 252:352–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.072
Zhu Y, Murali S, Cai W, Li X, Suk JW, Potts JR, Ruoff RS (2010) Graphene and graphene oxide: synthesis, properties and applications. Adv Mater 22(35):3906–3924. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201001068
Zou H, Ma W, Wang Y (2015) A novel process of dye wastewater treatment by linking advanced chemical oxidation with biological oxidation. Arch Environ Prot 41(4):33–39. https://doi.org/10.1515/aep-2015-0037
Availability of data and materials
Data available on request from the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Saeedeh Zamani: experimentation and characterizations. Shiva Salem: supervision, conceptualization, methodology, characterizations, writing–reviewing, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the present study did not involve human and animal participants.
Consent to participate
The authors voluntarily agreed to participate in this research study.
Consent to publish
The authors agree to publish the article in the Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zamani, S., Salem, S. Couple of graphene oxide and functionalized carbon nanotubes for dye degradation enhancement of anatase under visible light and solar irradiation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 32763–32776 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12931-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12931-9