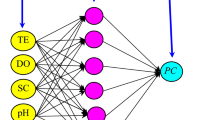
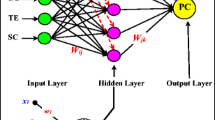
Abstract
Precise monitoring of cyanobacteria concentration in water resources is a daunting task. The development of reliable tools to monitor this contamination is an important research topic in water resources management. Indirect methods such as chlorophyll-a determination, cell counting, and toxin measurement of the cyanobacteria are tedious, cumbersome, and often lead to inaccurate results. The quantity of phycocyanin (PC) pigment is considered more appropriate for cyanobacteria monitoring. Traditional approaches for PC estimation are time-consuming, expensive, and require high expertise. Recently, some studies have proposed the application of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to predict the amount of PC concentration. Nonetheless, most of these researches are limited to standalone modeling schemas such as artificial neural network (ANN), multilayer perceptron (MLP), and support vector machine (SVM). The independent schema provides imprecise results when faced with highly nonlinear systems and data uncertainties resulting from environmental disturbances. To alleviate the limitations of the existing models, this study proposes the first application of a hybrid AI model that integrates the potentials of relevance vector machine (RVM) and flower pollination algorithm (RVM-FPA) to predict the PC concentration in water resources. The performance of the hybrid model is compared with the standalone RVM model. The prediction performance of the proposed models was evaluated at two stations (stations 508 and 478) using different statistical and graphical performance evaluation methods. The results showed that the hybrid models exhibited higher performance at both stations compared to the standalone RVM model. The proposed hybrid RVM-FPA can therefore serve as a reliable predictive tool for PC concentration in water resources.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding or first author (Dr. Saad Sh. Sammen, Saad123engineer@yahoo.com, or Quoc Bao Pham, phambaoquoc@duytan.edu.vn) upon reasonable request.
References
Abba SI, Hadi SJ, Sammen SS, Salih SQ, Abdulkadir RA, Pham QB, Yaseen ZM (2020) Evolutionary computational intelligence algorithm coupled with self-tuning predictive model for water quality index determination. J Hydrol 587:124974
Aghelpour P, Mohammadi B, Biazar SM (2019) Long-term monthly average temperature forecasting in some climate types of Iran, using the models SARIMA, SVR, and SVR-FA. Theor Appl Climatol 138(3-4):1471–1480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-02905-w
Ahmed AN, Othman FB, Afan HA, Ibrahim, RK, Fai CM, Hossain MS, …, Elshafie A (2019) Machine learning methods for better water quality prediction. J Hydrol 578(August), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124084
Ansari M, Othman F, El-Shafie A (2020) Optimized fuzzy inference system to enhance prediction accuracy for influent characteristics of a sewage treatment plant. Sci Total Environ 722:137878
Anter AM, Gupta D, Castillo O (2020) A novel parameter estimation in dynamic model via fuzzy swarm intelligence and chaos theory for faults in wastewater treatment plant. Soft Comput 24(1):111–129
Arun G, Mahesh P (2009) Application of support vector machines in scour prediction on grade-control structures. Eng Appl Artif Intell 22:216–223
Azimi H, Bonakdari H, Ebtehaj I (2019) Design of radial basis function-based support vector regression in predicting the discharge coefficient of a side weir in a trapezoidal channel. Appl Water Sci 9:78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0961-5
Backer LC (2002) Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms: developing a public health response. Lake Reserv Manag 18:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/07438140209353926
Chen S, Gunn SR, Harris CJ (2001) The relevance vector machine technique for channel equalization application. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12(6):1529–1532
Chiroma H, Shuib NLM, Muaz SA, Abubakar AI, Ila LB, Maitama JZ (2015) A review of the applications of bio-inspired flower pollination algorithm. Proc Comp Sci 62(Scse):435–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.08.438
Codd GA, Morrison LF, Metcalf JS (2005) Cyanobacterial toxins: risk management for health protection. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 203:264–272
Dekker AG (1993) Detection of the optical water quality parameters for eutrophic waters by high resolution remote sensing. PhD thesis, Free University, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Ebtehaj I, Bonakdari H, Zaji AH (2017) A new hybrid decision tree method based on two artificial neural networks for predicting sediment transport in clean pipes. Alex Eng J 57:1783–1795
Falconer I, Bartram J, Chorus I, Kuiper-Goodman T, Utkilen H, Burch M, Codd GA (1999) Safe levels and safe practices. In: Chorus I, Bartram J (eds) Toxic Cyanobacteria in water, a guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management. Spon Press, London, pp 161–182
Fatemeh BB, Ehteram M, Panahi F, Sammen SS, Othman FB, EL-Shafie A (2020) Estimation of total dissolved solids (TDS) using new hybrid machine learning models. J Hydrol 587:124989
Frohlich MW (2003) An evolutionary scenario for the origin of flowers. Nat Rev Genet 4(7):559–566. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1114
Ghorbani MA, Zadeh HA, Isazadeh M, Terzi O (2016) A comparative study of artificial neural network (MLP, RBF) and support vector machine models for river flow prediction. Environ Earth Sci 75(6):476
Gregor J, Maršálekab B, Šípkovác H (2007) Detection and estimation of potentially toxic cyanobacteria in raw water at the drinking water treatment plant by in vivo fluorescence method. Water Res 41:228–234
Hadi SJ, Abba SI, Sammen SSh, Salih SQ, Al-ansari N, & Yaseen ZM (2019). Non-linear input variable selection approach integrated with non-tuned data intelligence model for streamflow pattern simulation, 1–16.
Heddam S (2016) Multilayer perceptron neural network-based approach for modeling phycocyanin pigment concentrations: case study from lower Charles River buoy, USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(17):17210–17225
Heddam S, Kisi O (2017) Extreme learning machines: a new approach for modeling dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration with and without water quality variables as predictors. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(20):16702–16724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9283-z
Heddam S, Sanikhani H, Kisi O (2019) Application of artificial intelligence to estimate phycocyanin pigment concentration using water quality data: a comparative study. Appl Water Sci 9:164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1044-3
Hunter PD, Tyler AN, Garvalho L, Godd GA, Maberly SC (2010) Hyperspectral remote sensing of cyanobacterial pigments as indicators for cell populations and toxins in eutrophic lakes. Remote Sens Environ 114:2705–2718
Jahani B, Mohammadi B (2019) A comparison between the application of empirical and ANN methods for estimation of daily global solar radiation in Iran. Theor Appl Climatol 137(1-2):1257–1269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2666-3
Kang JH, Song J, Yoo SS, Lee BJ, Ji HW (2020) Prediction of odor concentration emitted from wastewater treatment plant using an artificial neural network (ANN). Atmosphere 11(8):784
Kong Y, Lou I, Zhang Y, Lou CU, Mok KM (2014) Using an online phycocyanin fluorescence probe for rapid monitoring of cyanobacteria in Macau freshwater reservoir. Hydrobiologia 741:33–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1759-3
Le CF, Li YM, Zha Y, Sun DY (2009) Specific absorption coefficient and the phytoplankton package effect in Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 619:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-0089579-6
Le CF, Li YM, Zha Y, Wang Q, Zhang H, Yin B (2011) Remote sensing of phycocyanin pigment in highly turbid inland waters in Lake Taihu, China. Int J Remote Sens 32(23):8253–8269. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2010.533210
Leondes CT (1998) Neural Network Systems Techniques and Applications. Academic Press, New York
Li L, Sengpiel RE, Pascual DL, Tedesco LP, Wilson JS, Soyeux E (2010) Using hyperspectral remote sensing to estimate chlorophyll-a and phycocyanin in a mesotrophic reservoir. Int J Remote Sens 31(15):4147–4162. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161003789549
Lin JY, Cheng CT, Chau KW (2006) Using support vector machines for long-term discharge prediction. Hydrol Sci J 51:599–612
Lord JM (2011) Flower and fruit. Morphology, ontogeny, phylogeny, function, ecology. N Z J Bot 49(1):141–142. https://doi.org/10.1080/0028825x.2011.548764
McQuaid N, Zamyadi A, Prevost M, Bird DF, Dorner S (2011) Use of in vivo phycocyanin fluorescence to monitor potential microcystin producing cynobacterial biovolume in a drinking water source. J Environ Monit 13:455–463. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0em00163e
Mingfeng J, Jiang S, Zhu L, Wang Y, Huang W, Zhang H (2013) Study on parameter optimization for support vector regression in solving the inverse ECG problem. Com Math Methods Med 2013:158056, 9 pages. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/158056
Moazenzadeh R, Mohammadi B (2019) Assessment of bio-inspired metaheuristic optimisation algorithms for estimating soil temperature. Geoderma 353:152–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.06.028
Moazenzadeh R, Mohammadi B, Shamshirband S, Chau KW (2018) Coupling a firefly algorithm with support vector regression to predict evaporation in northern Iran. Eng Appl Comp Fluid Mech 12(1):584–597. https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2018.1482476
Mohammadi B, Mehdizadeh S (2020) Modeling daily reference evapotranspiration via a novel approach based on support vector regression coupled with whale optimization algorithm. Agric Water Manag 237:106145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106145
Mohammadi B, Linh NTT, Pham QB, Ahmed AN, Vojteková J, Guan Y, Abba SI, El-Shafie A (2020a) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system coupled with shuffled frog leaping algorithm for predicting river streamflow time series. Hydrol Sci J 65:1738–1751. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2020.1758703
Mohammadi B, Guan Y, Aghelpour P, Emamgholizadeh S, Zolá RP, Zhang D (2020b) Simulation of Titicaca Lake water level fluctuations using hybrid machine learning technique integrated with Grey wolf optimizer algorithm. Water 12(11):3015
Najafzadeh M, Tafarojnoruz A, Lim SY (2017) Prediction of local scour depth downstream of sluice gates using data-driven models. ISH J Hydraul Eng 23:195–202
Nourani V, Andalib G (2015) Wavelet based artificial intelligence approaches for prediction of hydrological time series. Artifice Life Compute Intel, Springer, New York, pp 422–435
Paerl HW, Huisman J (2009) Climate change: a catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environ Microbiol 1:27–37
Pham QB, Yang TC, Kuo CM, Tseng HW, Yu PS (2019) Combing random forest and least square support vector regression for improving extreme rainfall downscaling. Water 11(3):451
Pham QB, Afan HA, Mohammadi B, Ahmed AN, Linh NTT, Vo ND et al (2020) Hybrid model to improve the river streamflow forecasting utilizing multi-layer perceptron-based intelligent water drop optimization algorithm. Soft Comput 24:18039–18056
Pham QB, Mohammadpour R, Linh NTT, Mohajane M, Pourjasem A, Sammen SS, Anh DT (2021) Application of soft computing to predict water quality in wetland. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(1):185–200
Ruiz-Verdú A, Simis SG, de Hoyos C, Gons HJ, Peña-Martinez R (2007) An evaluation of algorithms for the remote sensing of cyanobacterial biomass. Remote Sens Environ 112:3996–4008
Sammen SS, Mohamed TA, Ghazali AH, el-Shafie AH, Sidek LM (2017) Generalized regression neural network for prediction of peak outflow from dam breach. Water Resour Manag 31:549–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1547-8
Samui P (2014) Vector machine techniques for modeling of seismic liquefaction data. Ain Shams Eng J 5(2):355–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2013.12.004
Schalles JF, Yacobi YZ (2000) Remote detection and seasonal pattern of phycocyanin, carotenoid, and chlorophyll pigments in eutrophic waters. Arch Hydrobiol Spec Issues Adv Limnol 55:153–168
Schölkopf B, Smola AJ (1998) Learning with kernels [Ph.D. thesis]. GMD, Birlinghoven
Sharaf N, Bresciani M, Giardino C, Faour G, Slim K, Fadel A (2019) Using Landsat and in situ data to map turbidity as a proxy of cyanobacteria in a hypereutrophic Mediterranean reservoir. Ecol Inform 50:197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoin.f.2019.02.001
Sharafati A, Asadollah SBHS, Hosseinzadeh M (2020) The potential of new ensemble machine learning models for effluent quality parameters prediction and related uncertainty. Process Saf Environ Prot 140:68–78
Shi K, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Li N, Qin B, Zhu G, Zhou Y (2019) Phenology of phytoplankton blooms in a trophic lake observed from long-term MODIS data. Environ Sci Technol 53(5):2324–2331
Simis GH, Peters SW, Gons HJ (2005) Remote sensing of the cyanobacterial pigment phycocyanin in turbid inland water. Limnol Oceanogr 50(11):237–245
Simis SG, Ruiz-Verdú A, Domínguez-Gómez AJ, Peña-Martinez R, Peters SW, Gons HJ (2007) Influence of phytoplankton pigment composition on remote sensing of cyanobacterial biomass. Remote Sens Environ 106:414–427
Simis SG, Huot Y, Babin M, Seppala J, Metsamaa L (2012) Optimization of variable fluorescence measurements of phytoplankton communities with cyanobacteria. Photosynth Res 112:13–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s1112.0-012-9729-6
Sivapragasam C, Muttil N, Muthukumar S, Arun VM (2010) Prediction of algal blooms using genetic programming. Mar Pollut Bull 60:1849–1855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpo.lbul.2010.05.020
Song KS, Li L, Li S, Tedesco L, Li LH, Hall B (2012) Hyperspectral remote sensing of total phosphorus (TP) in three central Indiana water supply reservoirs. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(4):1481–1502
Song K, Li L, Tedesco L, Clercin N, Hall B, Li S, Shi K, Liu D, Sun Y (2013a) Remote estimation of phycocyanin (PC) for inland waters coupled with YSI PC fluorescence probe. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:5330–5340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1527-y
Song K, Li L, Li Z, Tedesco L, Hall B, Shi K (2013b) Remote detection of cyanobacteria through phycocyanin for water supply source using three-band model. Ecol Inform 15:22–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoin.f.2013.02.006
Song K, Li L, Tedesco L, Li S, Hall B, Du J (2014) Remote quantification of phycocyanin in potable water sources through an adaptive model. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 95:68–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprs.jprs.2014.06.008
Stumpf RP, Wynne TT, Baker DB, Fahnenstiel GL (2012) Interannual variability of cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Erie. PLoS One 7(8):e42444
Sun D, Li Y, Wang Q, le C, Lv H, Huang C, Gong S (2012) A novel support vector regression model to estimate the phycocyanin concentration in turbid inland waters from hyperspectral reflectance. Hydrobiologia 680:199–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-011-0918-7
Tipping ME, Faul A (2014) Fast Marginal Likelihood Maximization for Sparse Bayesian Models. Proc Ninth Int Workshop Artif Intell Stat 1:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13398-014-0173-7.2
Tsujinishi D, Abe S (2003) Fuzzy least squares support vector machines for multiclass problems. Neural Netw 16(5–6):785–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-6080(03)00110-2
Tzikas DG, Wei L, Likas A, Yang Y, Galatsanos NP (2006) A tutorial on relevance vector machines for regression and classification with applications. Eurasip News Lett 17(2):4–23
Vaheddoost B, Guan Y, Mohammadi B (2020) Application of hybrid ANN-whale optimization model in evaluation of the field capacity and the permanent wilting point of the soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07868-4
WHO (1998) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. In: Health criteria and other supporting information, Addendum to volume 2, 2nd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wynne TT, Stumpf RP, Tomlinson MC, Dyble J (2010) Characterizing a cyanobacterial bloom in western Lake Erie using satellite imagery and meteorological data. Limnol Oceanogr 55(5):2025–2036
Yan Y, Bao Z, Shao J (2018) Phycocyanin concentration retrieval in inland waters: a comparative review of the remote sensing techniques and algorithms. J Great Lakes Res 44:748–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2018.05.004
Yang X (2012) Flower pollination algorithm for global optimization. In: In Unconventional computation and natural computation. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 240–249
Yogameena B, Veeralakshmi S, Komagal E, Raju S, Abhaikumar V (2009) RVM-based human action classification in crowd through projection and star skeletonization. Eurasip J Image Video Process 2009:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/164019
Yaqub M, Asif H, Kim S, Lee W (2020) Modeling of a full-scale sewage treatment plant to predict the nutrient removal efficiency using a long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network. J Water Proc Eng 37:101388
Yousif AA, Sulaiman SO, Diop L, Ehteram M, Shahid S, Al-Ansari N, Yaseen ZM (2019) Open channel sluice gate scouring parameters prediction: different scenarios of dimensional and non-dimensional input parameters. Water 11(2):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020353
Zahrahtul AZ, Ani S (2012) Streamflow forecasting at ungaged sites using support vector machines. Appl Math Sci 60:3003–3014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Quoc Bao Pham: conceptualization, formal analysis, writing, editing, review, and supervision. Saad Sh. Sammen: data collection, writing and reviewing the manuscript, conceptual and supervision. Babak Mohammadi: modeling, writing, and reviewing the manuscript. S.I. Abba and R.A. Abdulkadir: manuscript writing, data, and visualization. Shamsuddin Shahid: formal analysis, writing, and reviewing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
This manuscript has not been published or presented elsewhere in part or in entirety and is not under consideration by another journal.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pham, Q.B., Sammen, S.S., Abba, S.I. et al. A new hybrid model based on relevance vector machine with flower pollination algorithm for phycocyanin pigment concentration estimation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 32564–32579 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12792-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12792-2