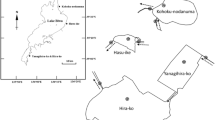
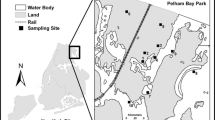
Abstract
Trophic status in surface waters has been mostly monitored by measuring soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP) and total phosphorus (TP). Additional to these common parameters, a two-dimensional ion chromatography mass spectrometry (2D-IC-MS) method was used to simultaneously measure soluble phosphate (Pi), pyrophosphate (PPi), and eleven phosphate-containing metabolites (P-metabolites) in Lake Ontario and its tributaries. From the additional P species, PPi, adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP), glucose 6-phosphate (G-P), D-fructose 6-phosphate (F-P), D-fructose 1,6-biphosphate (F-2P), D-ribulose 5-phosphate (R-P), D-ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (R-2P), and D-(-)-3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) were detected and quantified in the lake and river samples. The additional multivariate statistical analysis identified similarities between samples collected at different locations. The presence of R-P, R-2P, and F-2P in Lake Ontario tributaries seems to be mainly related to the Calvin cycle, while the lack of all these three P-metabolites and higher PGA levels than G-P in Toronto Harbour samples seems to be the result of depleted Calvin cycle, pentose phosphate, and glycolysis metabolic pathways.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in this paper is available on request from the corresponding author.
References
4500-P Phosphorus (2017) In: Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. https://doi.org/10.2105/smww.2882.093
Baldwin DS (2013) Organic phosphorus in the aquatic environment. Environ Chem 10:439–454. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN13151
Baykov AA, Anashkin VA, Salminen A, Lahti R (2017) Inorganic pyrophosphatases of Family II—two decades after their discovery. FEBS Lett 591:3225–3234. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12877
Boujelben N, Bouzid J, Elouear Z, Feki M, Jamoussi F, Montiel A (2008) Phosphorus removal from aqueous solution using iron coated natural and engineered sorbents. J Hazard Mater 151:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.05.057
Cade-Menun BJ, Navaratnam JA, Walbridge MR (2006) Characterizing dissolved and particulate phosphorus in water with 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 40:7874. https://doi.org/10.1021/es061843e
Cooper WT, Llewelyn JM, Bennett GL, Salters VJM (2005) Mass spectrometry of natural organic phosphorus. Talanta 66:348–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2004.12.028
Correll DL (1998) The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: a review. J Environ Qual 27:261–266. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1998.00472425002700020004x
Edge TA, Boyd RJ, Shum P, Thomas JL (2020) Microbial source tracking to identify fecal sources contaminating the Toronto Harbour and Don River watershed in wet and dry weather. J Great Lakes Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2020.09.002
Feng W, Zhu Y, Wu F, He Z, Zhang C, Giesy JP (2016a) Forms and lability of phosphorus in algae and aquatic macrophytes characterized by solution 31P NMR coupled with enzymatic hydrolysis. Sci Rep 6:37164. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37164
Feng W, Zhu Y, Wu F, Meng W, Giesy JP, He Z, Song L, Fan M (2016b) Characterization of phosphorus forms in lake macrophytes and algae by solution31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:7288–7297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5913-5
Feng W, Li C, Zhang C, Liu S, Song F, Guo W, He Z, Li T, Chen H (2019) Characterization of phosphorus in algae from a eutrophic lake by solution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Limnology 20:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-018-0562-2
Garrett RH, Grisham CM, Andreopoulos S, Willmore W, Gallouzi I-E (2013) Biochemistry, 1st Canadian Edition. Nelson Education, Toronto
He Z, Cade-Menun BJ, Toor GS, Fortuna A-M, Honeycutt CW, Sims JT (2007) Comparison of phosphorus forms in wet and dried animal manures by solution phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and enzymatic hydrolysis. J Environ Qual 36:1086. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2006.0549
Howell ET, Benoit N (2020) Nutrient footprints on the Toronto-Mississauga waterfront of Lake Ontario. J Great Lakes Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2020.11.009
Howell ET, Chomicki KM, Kaltenecker G (2012) Patterns in water quality on Canadian shores of Lake Ontario: correspondence with proximity to land and level of urbanization. J Great Lakes Res 38:32–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2011.12.005
Huang R, Tang Y (2015) Speciation dynamics of phosphorus during (hydro)thermal treatments of sewage sludge. Environ Sci Technol 49:14466–14474. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04140
Jansson M, Olsson H, Pettersson K (1988) Phosphatases; origin, characteristics and function in lakes. In: Phosphorus in Freshwater Ecosystems. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 157–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00024903
Lin P, Guo L (2016) Dynamic changes in the abundance and chemical speciation of dissolved and particulate phosphorus across the river-lake interface in southwest Lake Michigan. Limnol Oceanogr 61:771–789. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10254
Lin J, Zhao Y, Zhan Y, Wang Y (2020) Influence of coexisting calcium and magnesium ions on phosphate adsorption onto hydrous iron oxide. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:11303–11319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07676-w
Makarewicz JC, Booty WG, Bowen GS (2012) Tributary phosphorus loading to Lake Ontario. J Great Lakes Res 38:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2012.08.001
Packa V, Bostan V, Furdui VI, (2019a) Analysis of phosphorus species in water. In: Encyclopedia of Water. pp 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119300762.wsts0049
Packa V, Maedler S, Howell T, Bostan V, Diep N, Tooley R, Furdui VI (2019b) Unbiased measurement of phosphate and phosphorus speciation in surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 53:820–828. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b05089
Polakof S, Panserat S, Soengas JL, Moon TW (2012) Glucose metabolism in fish: a review. J Comp Physiol B 182:1015–1045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-012-0658-7
Poulton DJ, Griffiths M (1986) Toronto waterfront general water quality, 1976–1983. Great Lakes Section. Ontario Ministry of the Environment, Ontario
Read EK, Ivancic M, Hanson P, Cade-Menun BJ, McMahon KD (2014) Phosphorus speciation in a eutrophic lake by 31P NMR spectroscopy. Water Res 62:229–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.06.005
Saiardi A (2012) How inositol pyrophosphates control cellular phosphate homeostasis? vol 52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbior.2012.03.002
Schindler DW, Carpenter SR, Chapra SC, Hecky RE, Orihel DM (2016) Reducing phosphorus to curb lake eutrophication is a success. Environ Sci Technol 50:8923–8929. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02204
Sundareshwar PV, Morris JT, Pellechia PJ, Cohen HJ, Porter DE, Jones BC (2001) Occurrence and ecological implications of pyrophosphate in estuaries. Limnol Oceanogr 46:1570–1577. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2001.46.6.1570
Turner BL, Cheesman AW, Godage HY, Riley AM, Potter BVL (2012) Determination of neo- and D-chiro-inositol hexakisphosphate in soils by solution 31P NMR spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 46:4994–5002. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204446z
Van Moorleghem C, De Schutter N, Smolders E, Merckx R (2013) The bioavailability of colloidal and dissolved organic phosphorus to the alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata in relation to analytical phosphorus measurements. Hydrobiologia 709:41–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1442-8
Wenqiang Z, Baoqing S, Hong Z, Wenzhong T (2015) Characteristics of phosphorus compounds and their effects in sediments of an Eutrophic Chaohu Lake, China. CLEAN Soil Air Water 43:544–550. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201300254
Westheimer FH (1987) Why nature chose phosphates. Science 235:1173–1178. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2434996
Within Reach: 2015 Toronto and Region Remedial Action Plan (2015). Toronto, Ontario, https://torontorap.ca/app/uploads/2019/12/2015-RAP-Progress-Report.pdf
Worsfold PJ, Monbet P, Tappin AD, Fitzsimons MF, Stiles DA, McKelvie ID (2008) Characterisation and quantification of organic phosphorus and organic nitrogen components in aquatic systems: a review. Anal Chim Acta 624:37–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2008.06.016
Xie F, Li L, Song K, Li G, Wu F, Giesy JP (2019) Characterization of phosphorus forms in a Eutrophic Lake, China. Sci Total Environ 659:1437–1447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.466
Zhang YM, Chen J, Gao YX, Wang LM, Yang F (2014) Characteristics of organic phosphorus in a shallow lake Gehu investigated by sequential fractionation and 31P-NMR. Tech Adv Mater Res 955–959:3529–3539. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.955-959.3529
Zhang C, Feng W, Chen H, Zhu Y, Wu F, Giesy JP, He Z, Wang H, Sun F (2019) Characterization and sources of dissolved and particulate phosphorus in 10 freshwater lakes with different trophic statuses in China by solution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Ecol Res 34:106–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1703.1006
Zhao J, Liu X (2013) Organic and inorganic phosphorus uptake by bacteria in a plug-flow microcosm. Front Environ Sci Eng 7:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-013-0494-3
Zhu Y, Wu F, He Z, Guo J, Qu X, Xie F, Giesy JP, Liao H, Guo F (2013) Characterization of organic phosphorus in lake sediments by sequential fractionation and enzymatic hydrolysis. Environ Sci Technol 47:7679–7687. https://doi.org/10.1021/es305277g
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Andrew Laursen (Ryerson University) for helpful recommendations in manuscript preparation. Stefanie Maedler (MECP) is thanked for manuscript suggestions. Hany Eskander, Shelly Chan, Andrew Senyi, Carlos Jurado, Sajid Feeroze, and Mark Duric (MECP) are thanked for the analysis of additional parameters by accredited methods.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Vlastimil Packa: resources, investigation, formal analysis, visualization, writing–original draft. Todd Howell: conceptualization, resources, writing–review and editing. Vadim Bostan: conceptualization, supervision, resources, writing–review and editing. Vasile Furdui: conceptualization, supervision, visualization, writing–review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Thomas Hein
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
Additional information about analytical methods of Pi, TP, and sulfate, MDLs for species, schematic of the 2D-IC configuration and Pi loss (%) in samples spiked 48 h after collection are available at https://doi.... (DOCX 382 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Packa, V., Howell, T., Bostan, V. et al. Phosphorus-based metabolic pathway tracers in surface waters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 29498–29508 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12697-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12697-0