Abstract
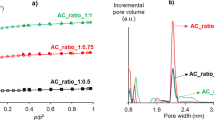
This study provides insight into the decolorization strategy for crude glycerol obtained from biodiesel production using waste cooking oil as raw material. A sequential procedure that includes physico-chemical treatment and adsorption using activated carbon from oil palm biomass was investigated. The results evidenced decolorization and enrichment of glycerol go hand in hand during the treatment, achieving >89% color removal and > 98% increase in glycerol content, turning the glycerol into a clear (colorless) solution. This is attributed to the complete removal of methanol, free fatty acids, and triglycerides, as well as 85% removal of water, and 93% removal of potassium. Properties of the resultant glycerol met the quality standard of BS 2621:1979. The economic aspects of the proposed methods are examined to fully construct a predesign budgetary estimation according to chemical engineering principles. The starting capital is proportionate to the number of physical assets to acquire where both entail a considerable cost at USD 13,200. Having the benefit of sizeable scale production, it reasonably reduces the operating cost per unit product. As productivity sets at 33 m3 per annum, the annual operating costs amount to USD 79,902 in glycerol decolorization. This is translatable to USD 5.38 per liter glycerol, which is ~69% lower compared to using commercial activated carbon.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (any additional raw data may be provided upon reasonable request).
References
Ahmad Farid MA, Hassan MA, Roslan AM, Samsudin MH, Mohamad ZJJ, Othman MR, Shirai Y (2020) Carbon monoxide reduction in the flue gas during biochar production from oil palm empty fruit bunch. J Clean Prod 258:120580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120580
Ahmad Farid MA, Hassan MA, Taufiq-Yap YH, Shirai Y, Hasan MY, Zakaria MR (2017a) Waterless purification using oil palm biomass-derived bioadsorbent improved the quality of biodiesel from waste cooking oil. J Clean Prod 165:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.136
Ahmad Farid MA, Hassan MA, Taufiq-Yap YH, Ibrahim ML, Othman MR, Ali AAM, Shirai Y (2017b) Production of methyl esters from waste cooking oil using a heterogeneous biomass-based catalyst. Renew Energy 114:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.07.064
Ardi MS, Aroua MK, Hashim NA (2015) Progress, prospect and challenges in glycerol purification process: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 42:1164–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.10.091
Atadashi IM (2014) Purification of crude biodiesel using dry washing and membrane technologies. Alexandria Eng J 54:1265–1272
Bahrin EK, Baharuddin AS, Ibrahim MF et al (2012) Physicochemical property changes and enzymatic hydrolysis enhancement of oil palm empty fruit bunches treated with superheated steam. BioResources 7:1784–1801. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.7.2.1784-1801
Bedolla PO, Feldbauer G, Wolloch M, Eder SJ, Dörr N, Mohn P, Redinger J, Vernes A (2014) Effects of van der Waals interactions in the adsorption of isooctane and ethanol on Fe(100) surfaces. J Phys Chem C 118:17608–17615. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp503829c
Chol CG, Dhabhai R, Dalai AK, Reaney M (2018) Purification of crude glycerol derived from biodiesel production process: experimental studies and techno-economic analyses. Fuel Process Technol 178:78–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.05.023
Dhabhai R, Ahmadifeijani E, Dalai AK, Reaney M (2016) Purification of crude glycerol using a sequential physico-chemical treatment, membrane filtration, and activated charcoal adsorption. Sep Purif Technol 168:101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.05.030
Faccini CS, Aranda S (2011) Dry washing in biodiesel purification: a comparative study of adsorbents. J Brazillian Chem Soc 22:558–563. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532011000300021
García JR, Sedran U, Zaini MAA, Zakaria ZA (2018) Preparation, characterization, and dye removal study of activated carbon prepared from palm kernel shell. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:5076–5085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8975-8
Gomes MG, Santos DQ, De Morais LC, Pasquini D (2015) Purification of biodiesel by dry washing, employing starch and cellulose as natural adsorbents. Fuel 155:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.04.012
Hor KY, Chee JMC, Chong MN, Jin B, Saint C, Poh PE, Aryal R (2016) Evaluation of physicochemical methods in enhancing the adsorption performance of natural zeolite as low-cost adsorbent of methylene blue dye from wastewater. J Clean Prod 118:197–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.056
Hunsom M, Saila P, Chaiyakam P, Kositnan W (2013) Comparison and combination of solvent extraction and adsorption for crude glycerol enrichment. Int J Renew Energy Res 3:364–371
Iakovleva E, Maydannik P, Ivanova TV, Sillanpää M, Tang WZ, Mäkilä E, Salonen J, Gubal A, Ganeev AA, Kamwilaisak K, Wang S (2016) Modified and unmodified low-cost iron-containing solid wastes as adsorbents for efficient removal of As(III) and As(V) from mine water. J Clean Prod 133:1095–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.147
Idris J, Shirai Y, Andou Y, Mohd Ali AA, Othman MR, Ibrahim I, Hassan MA (2015) Self-sustained carbonization of oil palm biomass produced an acceptable heating value charcoal with low gaseous emission. J Clean Prod 89:257–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.11.016
Isahak WNRW, Ismail M, Yarmo MA, Jahim JM, Salimon J (2010) Purification of crude glycerol from transesterification rbd palm oil over homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts for the biolubricant preparation. J Appl Sci 10:2590–2595. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2010.2590.2595
Jafri N, Wong WY, Doshi V, Yoon LW, Cheah KH (2018) A review on production and characterization of biochars for application in direct carbon fuel cells. Process Saf Environ Prot 118:152–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.06.036
Javani A, Hasheminejad M, Tahvildari K, Tabatabaei M (2012) High quality potassium phosphate production through step-by-step glycerol purification: a strategy to economize biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol 104:788–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.134
Kongjao S, Damronglerd S, Hunsom M (2010) Purification of crude glycerol derived from waste used-oil methyl ester plant. Korean J Chem Eng 27:944–949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0148-0
Manosak R, Limpattayanate S, Hunsom M (2011) Sequential-refining of crude glycerol derived from waste used-oil methyl ester plant via a combined process of chemical and adsorption. Fuel Process Technol 92:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2010.09.002
Mena-Cervantes VY, Hernández-Altamirano R, Tiscareño-Ferrer A (2020) Development of a green one-step neutralization process for valorization of crude glycerol obtained from biodiesel. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:28500–28509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07287-0
Peters MS, Timmerhaus KO, West RE (2003) Plant design and economics for chemical engineers, 4th Editio. McGraw-Hill Education, Singapore
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2010) Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. J Hazard Mater 177:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.047
Rodrigues A, Bordado JC, Dos Santos RG (2017) Upgrading the glycerol from biodiesel production as a source of energy carriers and chemicals - a technological review for three chemical pathways. Energies 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111817
Saifuddin N, Refal H, Kumaran P (2014) Rapid purification of glycerol by-product from biodiesel production through combined process of microwave assisted acidification and adsorption via chitosan immobilized with yeast. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 7:593–602. https://doi.org/10.19026/rjaset.7.295
Schaffner F, Pontalier PY, Sanchez V, Lutin F (2003) Bipolar electrodialysis for glycerin production from diester wastes. Filtr Sep 40:35–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0015-1882(03)00037-5
Su H, Wang X, Kim YG, Kim SB, Seo YG, Kim JS, Kim CJ (2014) Optimization of decoloring conditions of crude fatty acids recovered from crude glycerol by acid-activated clay using response surface method. Korean J Chem Eng 31:2070–2076. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0158-4
Sukiran MA, Abnisa F, Wan Daud WMA, Abu Bakar N, Loh SK (2017) A review of torrefaction of oil palm solid wastes for biofuel production. Energy Convers Manag 149:101–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.07.011
Sukiran MA, Loh SK, Abu Bakar N, Choo YM (2011) Production and characterization of bio-char from the pyrolysis of empty fruit bunches Mohamad Azri Sukiran , Loh Soh Kheang , Nasrin Abu Bakar and Choo Yuen May Engineering and Processing Division , Malaysian Palm Oil Board , No . 6 ,. Am J Appl Sci 8:984–988, Production and Characterization of Bio-Char from the Pyrolysis of Empty Fruit Bunches
Tan IAW, Ahmad AL, Hameed BH (2009) Adsorption isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and desorption studies of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol on oil palm empty fruit bunch-based activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 164:473–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.08.025
USP-grade (2013) United State Pharmacopeia (USP) Glycerol Specification. In: SRS Biodiesel. http://www.srsbiodiesel.com/technologies/glycerin-purification/glycerin-specifications/. Accessed 29 Nov 2020
Valdes H, Sanchez-Polo M, Rivera-Utrilla J, Zaror C a (2002) Effect of ozone treatment on surface properties of activated carbon. Langmuir 18:2111–2116. Doihttps://doi.org/10.1021/La010920a
Yong KC, Yunus W, Ooi TL et al (2001) Refining of crude glycerine recovered from glycerol residue by simple vacuum distillation. J Oil Palm Res 13:2001
Živković S, Veljković M (2018) Environmental impacts the of production and use of biodiesel. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0649-z
Funding
This study is funded by the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme – Malaysia’s Research Star Award (FRGS-MRSA) (Grant No: 5540052) by the Ministry of Education Malaysia (MOE) and the marching grant of the Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (SATREPS) by Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) (Vot No: 6300156).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Funding acquisition: M.A.H. Conception and design: M.A.H., A.M.R., H.A., and Y.S. Data analysis and interpretation: M.A.A.F., M.N.F.N., and M.R.O. Drafting and revising the article: M.A.A.F., M.A.H, and A.M.R. Supervision: M.A.H.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
This manuscript has not been submitted to, nor is under review at, another journal, or other publishing venue.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad Farid, M.A., Hassan, M.A., Roslan, A.M. et al. Improving the decolorization of glycerol by adsorption using activated carbon derived from oil palm biomass. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 27976–27987 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12585-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12585-7