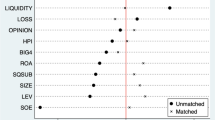
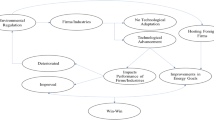
Abstract
Pollution control policies have achieved remarkable results in China. However, industrial firms still lack enthusiasm for technological innovation to reduce pollution and endogenous motivation for controlling pollution, which pose severe obstacles to industrial pollution control. The top-runner scheme can stimulate the pollution control behaviors of firms to a certain extent. Therefore, the top-runner scheme is combined with economic incentive policies to design an appropriate incentive scheme in this paper, theoretical research is conducted on the selection standards and incentive methods, and four industries mainly responsible for pollution in a developed province of China are investigated as case studies. The results show that (1) the selection standard that stipulates the rewarded quotas instead of the discharge amount achieved higher emission reduction efficiency; (2) tax cuts are the best incentive for top-runners, and (3) the top-runner incentive scheme achieves a greater reduction effect in high-pollution industries than low-pollution industries. Value-added tax exemption for the top-runner, as determined by the rewarded quotas, contributes to increasing the enthusiasm from firms to participate in and improve pollution control measures.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Allcott H, Knittel C, Taubinsky D (2015) Tagging and targeting of energy efficiency subsidies. Am Econ Rev 105:187–191. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.p20151008
Arguedas C, van Soest DP (2009) On reducing the windfall profits in environmental subsidy programs. J Environ Econ Manag 58:192–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2009.04.002
Bahadur N, Bhargava N (2019) Novel pilot scale photocatalytic treatment of textile & dyeing industry wastewater to achieve process water quality and enabling zero liquid discharge. J Water Process Eng 32:100934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100934
Brown R, Webber C, Koomey JG (2002) Status and future directions of the Energy Star program. Energy 27:505–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-5442(02)00004-X
Busch P, Jörgens H (2005) The international sources of policy convergence: explaining the spread of environmental policy innovations. J Eur Public Policy 12:860–884. https://doi.org/10.1080/13501760500161514
Changotra R, Rajput H, Guin JP, Khader SA, Dhir A (2020) Techno-economical evaluation of coupling ionizing radiation and biological treatment process for the remediation of real pharmaceutical wastewater. J Clean Prod 242:118544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118544
Clark M (2005) Corporate environmental behavior research: informing environmental policy. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 16:422–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2004.04.006
Du W, Li M (2020) Assessing the impact of environmental regulation on pollution abatement and collaborative emissions reduction: micro-evidence from Chinese industrial enterprises. Environ Impact Assess Rev 82:106382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2020.106382
Hirose K, Matsumura T (2020) A comparison between emission intensity and emission cap regulations. Energy Policy 137:111115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111115
Huang B, Mauerhofer V, Geng Y (2016) Analysis of existing building energy saving policies in Japan and China. J Clean Prod 112:1510–1518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.07.041
Huang S, Fan Z, Wang N (2020) Green subsidy modes and pricing strategy in a capital-constrained supply chain. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 136:101885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2020.101885
Inoue N, Matsumoto S (2019) An examination of losses in energy savings after the Japanese Top Runner Program? Energy Policy 124:312–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.09.040
Kimura O (2013) The role of standards: the Japanese Top Runner Programme for end-use efficiency [WWW Document]. Energy Technol Innov Learn Hist Successes Fail. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139150880.023
Knill C, Heichel S, Arndt D (2012) Really a front-runner, really a straggler? Of environmental leaders and laggards in the European Union and beyond — a quantitative policy perspective. Energy Policy 48:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.04.043
Lee W, Yik F (2002) Regulatory and voluntary approaches for enhancing energy efficiencies of buildings in Hong Kong. Appl Energy 71:251–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-2619(02)00014-4
Lee W, Yik F (2004) Regulatory and voluntary approaches for enhancing building energy efficiency. Prog Energy Combust Sci 30:477–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2004.03.002
Li H, Carrión-Flores CE (2017) An analysis of the ENERGY STAR® program in Alachua County. Florida Ecol Econ 131:98–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2016.08.014
Li N, Zhang X, Shi M, Hewings GJD (2019) Does China’s air pollution abatement policy matter? An assessment of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on a multi-regional CGE model. Energy Policy 127:213–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.12.019
Nie P, Wang C, Chen Y (2018) Top runner program in China: a theoretical analysis for potential subsidies. Energy Strategy Rev 21:157–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2018.06.006
Nie P, Yang Y, Chen Y, Wang Z (2016) How to subsidize energy efficiency under duopoly efficiently? Appl. Energy 175:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.04.105
Porter ME (1991) America’s green strategy. Sci Am 264(4):193–246
Porter ME, van der Linde C (1995) Toward a new conception of the environment-competitiveness relationship. J Econ Perspect 9:97–118. https://doi.org/10.1257/jep.9.4.97
Portney PR, Dower RC (1990) Public policies for environmental protection.
Rode J, Gómez-Baggethun E, Krause T (2015) Motivation crowding by economic incentives in conservation policy: a review of the empirical evidence. Ecol Econ 117:270–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2014.11.019
Siderius PJS, Nakagami H (2013) A MEPS is a MEPS is a MEPS: comparing Ecodesign and Top Runner schemes for setting product efficiency standards. Energy Effic 6:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-012-9166-6
Vazquez-Brust DA, Liston-Heyes C, Plaza-Úbeda JA, Burgos-Jiménez J (2010) Stakeholders pressures and strategic prioritisation: an empirical analysis of environmental responses in Argentinean firms. J Bus Ethics 91:171–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-010-0612-0
Wang K-L, Pang S-Q, Ding L-L, Miao Z (2020) Combining the biennial Malmquist - Luenberger index and panel quantile regression to analyze the green total factor productivity of the industrial sector in China. Sci Total Environ 739:140280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140280
Wei X, Peng J (2014) An empirical study on impacts of environmental regulation on environmental information disclosure of listed companies of China: based on researches on listed companies in nonferrous metal industry. Can Soc Sci 10:113–123. https://doi.org/10.3968/4329
Wu H, Guo H, Zhang B, Bu M (2017) Westward movement of new polluting firms in China: pollution reduction mandates and location choice. J Comp Econ 45:119–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jce.2016.01.001
Xepapadeas A, de Zeeuw A (1999) Environmental policy and competitiveness: the Porter hypothesis and the composition of capital. J Environ Econ Manag 37:165–182. https://doi.org/10.1006/jeem.1998.1061
Xia F, Xu J (2020) Green total factor productivity: A re-examination of quality of growth for provinces in China. China Econ Rev 62:101454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2020.101454
Xie F, Zhang B (2020) Impact of China’s outward foreign direct investment on green total factor productivity in “Belt and Road” participating countries: a perspective of institutional distance. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10849-2
Ya V, Martin N, Choo K-H, Chou Y-H, Lee S-J, Le NC, Li C-W (2019) High-pressure electrocoagulation system with periodic air replenishment for efficient dye wastewater treatment: reaction dynamics and cost evaluation. J Clean Prod 213:1127–1134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.249
Yang J, Guo H, Liu B, Shi R, Zhang B, Ye W (2018) Environmental regulation and the pollution haven hypothesis: do environmental regulation measures matter? J Clean Prod 202:993–1000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.144
Yi Y, Li J (2018) The effect of governmental policies of carbon taxes and energy-saving subsidies on enterprise decisions in a two-echelon supply chain. J Clean Prod 181:675–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.188
Funding
This research is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the Research Funds of Renmin University of China. Project No. 17XNB025.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Xiangbo Xu and Dunhu Chang; methodology: Dunhu Chang and Donghui Gao; formal analysis and investigation: Dunhu Chang, Donghui Gao, and Ying Ju; writing—original draft preparation: Dunhu Chang and Donghui Gao; writing—review and editing: Xiangbo Xu; funding acquisition: Dunhu Chang; resources: Dondhui Gao, Xiaoyue Shen, and Xin Wang; supervision: Xiangbo Xu.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Baojing Gu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, D., Gao, D., Xu, X. et al. Top-runner incentive scheme in China: a theoretical and empirical study for industrial pollution control. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 29344–29356 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12561-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12561-1