Abstract
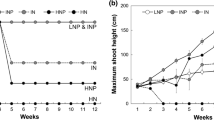
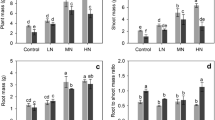
Pinus elliottii is an evergreen coniferous tree. It is considered a potential species for ecological restoration in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area (TGRA). To classify the effects of different degrees of flooding stress in winter on nutrient accumulation in Pinus elliottii after experiencing early drought stress in summer, simulated water treatments of deep submergence (DS) and moderate submergence (MS) were imposed after the summer drought period. The results indicated that the survival rate of seedlings was 95.3%, and the accumulation trend of the flooded plants was rapid at an average rate of 1.99 ± 0.33% in the early stage of flooding (stage I: 0–7 days), a rapid release rate in the second stage (stage II: 7–60 days), and an average rate of only 0.07 ± 0.04% in the later stage (stage III: 60–150 days). After 150 days of flooding, the leaves of Pinus elliottii released an average of 7.156 ± 0.4 g kg−1 of organic carbon, 8.839 ± 0.6 g kg−1 of nitrogen, 0.781 ± 0.1 g kg−1 of phosphorus, and 2.985 ± 0.3 g kg−1 of potassium of macroelement content, and an average of 0.201 ± 0.03 g kg−1 manganese, 0.147 ± 0.04 g kg−1 iron, 0.002 g kg−1 copper, and 0.023 g kg−1 of zinc of microelement contents. Our results also demonstrated that after 150 days of flooding, the C/N, N/P, and C/P ratios of the nutrient element content of Pinus elliottii in the water-level fluctuation zone of the TGRA were 0.810%, 11.32%, and 9.16%, respectively. The absorption and release of nutrients under water flooding are generally divided into three stages: first, the early storage stage (the first stage: 0 to 7 days, optional), then the rapid release (the second stage: 7 to 60 days), and the later stage slow release phase (third stage: 60 to 150 days). Water flooding reduced the contents of C, N, P, and K and affected the absorption of nutrient elements in the plant. At the same time, soluble Mn2 + and Fe2 + over absorbed during flooding could cause toxicity to leaf tissues. At the same time, Pinus elliottii selected to reduce Cu in leaves to ensure that the root has a strong redox capacity and improve nitrogen utilization, thereby preventing the long-term flooding of toxic cations and acid substances. Taken together, our results conclude that increased drought stress can reduce the ability of Pinus elliottii seedlings to withstand flooding stress; the seedlings of Pinus elliottii can maintain their growth by accumulating certain nutrient elements under submerged conditions, which implies that this species would be a suitable candidate for reforestation in the TGRA because of its tolerance to submergence.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Armstrong W, Justin SHFW, Beckett PM, Lythe S (1991) Root adaptation to soil waterlogging. Aquat Bot 39(1-2):57–73
Bhattacharjee S, Saha AK (2014) Plant water-stress response mechanisms[M]// Approaches to plant stress and their management. Springer India
Chen HS, Jin LG (2014) The effects of submergence on protective enzyme activities of Bermuda grass growth in water-level-fluctuation zone of reservoir. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Natural Science Edition 35(1):46–48
Chen H, Qualls RG, Blank RR (2005) Effect of soil flooding on photosynthesis, carbohydrate partitioning and nutrient uptake in the invasive exotic Lepidium latifolium. Aquat Bot 82(4):250–268
Delaune RD, Pezeshki SR, Lindau CW (1998) Influence of soil redox potential on nitrogen uptake and growth of wetland oak seedlings. J Plant Nutr 21(4):757–768
Ella ES, Kawano N, Ito O (2003) Importance of active oxygen scavenging system in the recovery of rice seedlings after submergence. Plant Sci Plant Science 165(1):85–93
Fan DY, Xiong GM, Zhang AY, Liu X, Xie ZQ, Li ZJ (2015) Effect of water-lever regulation on species selection for ecological restoration practice in the water-level fluctuation zone of Three Gorges Reservoir. Chin J Plant Ecol 39(4):416–432
Ford CR, Brooks JR (2002) Detecting forest stress and decline in response to increasing river flow in southwest Florida, USA. Forest ecology & management 160(1):45–64
Fuentes RG, Baltazar AM, Merca FE, Ismail AM (2010, 2010) Morphological and physiological responses of lowland purple nutsedge (Cyperus rotundus L.) to flooding. AoB Plants:plq010-plq010
Han WJ, Bai LL, Li CX (2016) Effects of flooding on photosynthesis, growth and nutrient content of Cynodon dactylon. Acta Pratacul Sin 25(5):49–59
Hisabae M, Sone S, Inoue M (2011) Breakdown and macroinvertebrate colonization of needle and leaf litter in conifer plantation streams in Shikoku, southwestern Japan. J For Res 16(2):108–115
Inman BNG (2004) Sugarcane water stress criteria for irrigation and drying off. Field Crop Res 89(1):107–122
Jackson MB, Colmer TD (2005) Response and Adaptation by Plants to Flooding Stress. Annals of Botany 96(4):501–505
Jacobson TKB, Bustamante MMDC, Kozovits AR (2011) Diversity of shrub tree layer, leaf litter decomposition and N release in a Brazilian Cerrado under N, P and N plus P additions. Environ Pollut 159(10):2236–2242
Kawano N, Ito O, Sakagami JI (2009) Morphological and physiological responses of rice seedlings to complete submergence (flash flooding). Ann Bot 103(2):161–169
Kogawara S, Yamanoshita T, Norisada M, Masaya M, Kojima K (2006) Photosynthesis and photoassimilate transport during root hypoxia in Melaleuca cajuputi, a flood-tolerant species, and in Eucalyptus camaldulensis, a moderately flood-tolerant species. Tree Physiol 26(11):1413–1423
Kozlowski TT (1997) Responses of woody plants to flooding[J]. Tree Physiol 1(7):129–163
Li XX, Li CX (2018) Carbohydrate consumption of Hemarthria altissima and Cynodon dactylon is affected by flooding and plant density. Pratacultural Sci 35(11):2593–2601
Li ZJ, Yu J, Fan DY, Xie ZQ, Xiong GM, Zhang XY (2011) Clonal integration enhances the ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species in root of Cynodon dactylon subjected to submergence. Acta Ecol Sin 31(17):4992–4999
Li XL, Luan CY, Yang J, Chen FJ (2012) Survival and recovery growth of riparian plant Distylium chinense seedlings to complete submergence in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Procedia Eng 28(8):85–94
Lin QL (2002) Growth characteristics analysis of Pinus taeda, Pinus ellliottii, Pinus massoniana [J]. J Fujian Coll Forest 22(002):133–136
Liu ZB, Cheng RM, Xiao WF, Guo QS, Wang XR, Feng XH (2013) Effects of submergence on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Rhizoma cyperi in hydro fluctuation belt of Three Gorges Reservoir area, Southwest China. Chin J Ecol 32(8):2015–2022
Liu Z, Cheng R, Xiao W, Guo QS (2014) Effect of off-season flooding on growth, photosynthesis, carbohydrate partitioning, and nutrient uptake in Distylium chinense. PLoS One 9(9):e107636
Liu Z, Cheng R, Xiao W, Guo QS (2015) Leaf gas exchange, chlorophyll fluorescence, non-structural carbohydrate content and growth responses of Distylium chinense, during complete submergence and subaerial re-emergence. Aquat Bot 124:70–77
Liu ZB, Cheng RM, Xiao WF, Guo QS (2016) Growth and physiological responses of Distylium chinense seedlings to autumn and winter flooding. J Lake Sci 28(2):405–413
Luo MJ, Cui LJ, Zhang SG, Huang YR, He WG (2012) Effects of flooding stress on water and mineral nutrients in Aegiceras corniculatum seedlings. J Fujian Coll Forest 32(4):336–340
Ma WC, Liu Y, Zhou C, Wang T, Wei H (2017) Effect of water-level change on nutritional characteristics of Taxodium distichum in the hydro-fluctuation belt of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Acta Ecol Sin 37(4):1128–1136
Mommer L, Lenssen JPM, Huber H, Visser EJW (2010) Ecophysiological determinants of plant performance under flooding: a comparative study of seven plant families. J Ecol 94(6):1117–1129
Mukassabi TA, Polwart A, Coleshaw T, Thomas PA (2012) How long can young Scots pine seedlings survive waterlogging. Trees: Struct Funct 26(5):1641–1649
New T, Xie Z (2008) Impacts of large dams on riparian vegetation: applying global experience to the case of China’s Three Gorges Dam. Biodivers Conserv 17(13):3149–3163
Nishiuchi S, Yamauchi T, Takahashi H, Hirokazu T, Lukasz K, Mikio N (2012) Mechanisms for coping with submergence and waterlogging in rice. Rice 5(1):1–14
Pan XX, Wan CY, Zhang ZY, Zhang ZY, Zheng ZW (2017) Protection and ecological restoration of water level fluctuation zone in the Three Gorges Reservoir. J Landsc Res 9(1):47–53
Panda D, Sharma SG, Sarkar RK (2008) Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, CO2, photosynthetic rate and regeneration capacity as a result of complete submergence and subsequent re-emergence in rice (Oryza sativa, L.). Aquat Bot 88(2):127–133
Pezeshki SR, Delaune RD (2012) Soil oxidation-reduction in wetlands and its impact on plant functioning. Biology 1(3):196–221
Pezeshki SR, Delaune RD, Anderson PH (1999) Effect of flooding on elemental uptake and biomass allocation in seedlings of three bottomland tree species. J Plant Nutr 22(9):14
Romero JL, Magalhaes PC, Alves JD, Duraes FOM, Vasconcellos CA (2003) Effect of calcium on some biophysical and morphological characteristics of maize plants BRS-4154 submitted to water logging. Revista Brasileira De Milho E Sorgo 2(3):21–33
Sarkar RK, Reddy JN, Sharma SG, Ismail AM (2006) Physiological basis of submergence tolerance in rice and implications for crop improvement. Curr Sci 91(10):899–906
Shabala S, Shabala L, Barcelo J, Poschenrieder C (2014) Membrane transporters mediating root signalling and adaptive responses to oxygen deprivation and soil flooding. Plant Cell Environ 37(10):2216–2233
Shi ZM, Tang JQ, Cheng RM, Luo D, Liu SR (2015) A review of nitrogen allocation in leaves and factors in its effects. Acta Ecol Sin 35(18):5909–5919
Smethurst CF, Garnett T, Shabala S (2005) Nutritional and chlorophyll fluorescence responses of lucerne (Medicago sativa) to waterlogging and subsequent recovery. Plant Soil 270(1):31–45
Tan S, Zhu M, Zhang Q (2010) Physiological responses of Bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon) to submergence. Acta Physiol Plant 32(1):133–140
Voesenek LACJ, Colmer TD, Pierik R, Millenaar FF, Peeters AJM (2006) How plants cope with complete submergence. New Phytol 170(2):213–226
Wang ZX, Wei H, Li CX, Lü Q, Zhou J, Gao W, Chen W (2012) Effects of soil moisture variations on photosynthetic characteristics of slash pine seedlings. Acta Botan Boreali-Occiden Sin 32(5):980–987
Wu JG, Huang JH, Han XG, Gao XM (2004) The Three Gorges Dam: an ecological perspective. Front Ecol Environ 2(5):241–248
Xiong HY, Yang J, An BG, Li YS (2013) Molecular mechanism of rice adaptation and improvement strategies to submergence stress. Journal of Wuhan University (Natural Science Edition) 1(59):017–023
Xu ZQ, Rao LY, Zhu JZ, Zhao Y (2015) Growth and photosynthesis characteristics of mulberry under flooding stress. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering 31(22):105–114
Yang F, Liu WW, Wang J, Liao L (2012) Riparian vegetation’s responses to the new hydrological regimes from the Three Gorges Project: clues to revegetation in reservoir water-level-fluctuation zone. Acta Ecol Sin 32(2):89–98
Yang Y J, Li CX, Zhang Y, Cui YF (2013) Effects of submergence and drought alternation on nutrient contents in the soil growing slash pine (Pinus elliottii) seedlings. 49(2): 61-71.
Ye Z (2011) Effects of submergence and drought alternation on photosynthesis and growth of Pinus elliottii seedlings. Scientia Silvae Sinicae
Zhang Y (2012) Physiological and ecological effects of flooding and drought stress on several suitable tree species in the water-level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Southwest University
Zhang Y, Li CX (2011) Effects of submergence and drought alternation on photosynthesis and growth of Pinus elliottii seedlings. Sci Silvae Sin 47(12):158–164
Zhang TP, Ren H, Peng SL, Yu ZY (1999) The ecological and biological characteristics of Pinus elliottii Engelm. Ecologic Sci 18(2):8–12
Zhang P, Tian X, He X, Fu QS, Li R, Ping J (2008) Effect of litter quality on its decomposition in broadleaf and coniferous forest. Eur J Soil Biol, 44(4): 0-399, 392.
Zheng SX, Shangguan Z (2007) Photosynthetic characteristics and their relationships with leaf nitrogen content and leaf mass per area in different plant functional types. Acta Ecol Sin 27(1):171–181
Zhou XH, Liu XQ (2005) The drought tolerance characteristics of the Main Afforestation Trees in northwest Hubei Province. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Nature Sciences Edition) 29(1):70–73
Zhou J, Wei H (2012) Effects of soil water regime on leaf photosynthetic characteristics of slash pine (Pinus elliottii Engelm) seedlings. Chin J Ecol 31(1):32–39
Zhu QH, Xia HX (2012) Effect of flooding stress on antioxidant enzyme system of Acorus tatarinowii Schott. J Hydroecol 33(4):138–141
Acknowledgments
The author Y.G. is thankful to the staff of Key Laboratory of Forest Ecology and Environment of the National Forestry and Grassland Administration, Research Institute of Forest Ecology, Environment and Protection, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program Projects (2017YFC0505304) and Special Funds for Basic Scientific Research Business of the Chinese Academy of Forestry Sciences (CAFYBB2017ZA002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.G. analyzed data and drafted the manuscript. Y.S. participated in collecting the experiment data. R.C. was involved in planning of study and designing of the work. W.X. was substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work. The remaining authors contributed to refining the ideas, carrying out additional analyses, and finalizing this paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Shen, Y., Cheng, R. et al. Effects of repetitive submergence on the accumulation and release of nutrient elements in Pinus elliottii seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 27420–27431 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12528-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12528-2