Abstract
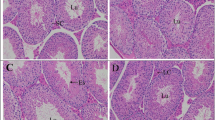
Nicotine is an active pharmacological ingredient in cigarette smoke, which may negatively influence the male reproductive system and fertility. This study aims to investigate the effect of fractionated low-dose radiation (fractionated-LDR) and/or ellagic acid (EA) on nicotine-induced hormonal changes and testicular toxicity in rats. Nicotine was administrated orally (1 mg/kg) for 30 days, afterward, rats were treated with LDR (2 × 0.25 Gy/1-week interval), EA (10 mg/kg, 14 consecutive days p.o.), or a combination of both fractionated-LDR and EA. Rats were sacrificed 24 h after the last dose of treatment, then testes were dissected for histopathology examination, along with some biochemical parameters in serum and testicular tissue were evaluated. Nicotine-induced oxidative stress was evidenced by an increase in testicular thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and a decrease in reduced glutathione (GSH) content. Additionally, the activities of testicular androgenic enzymes were decreased, and the activity of serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was significantly increased. The hormonal changes were verified by a noticeable reduction in follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and testosterone serum levels. Histological evaluation revealed that the testicular seminiferous tubules structure was distorted. On the contrary, fractionated-LDR plus EA attenuated the negative changes caused by nicotine observed through biochemical and histological findings. Accordingly, the exposure to fractionated-LDR combined with EA may be a promising candidate for treating hormonal changes and testicular toxicity caused by nicotine.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aitken RJ, Baker MA (2006) Oxidative stress, sperm survival and fertility control. Mol Cell Endocrinol 250:66–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2005.12.026
Akkoyun HT, Karadeniz A (2016) Investigation of the protective effect of ellagic acid for preventing kidney injury in rats exposed to nicotine during the fetal period. Biotech Histochem 91:108–115. https://doi.org/10.3109/10520295.2015.1078910
Appasamy M, Muttukrishna S, Pizzey A, Ozturk O, Groome N, Serhal P, Jauniaux E (2007) Relationship between male reproductive hormones, sperm DNA damage and markers of oxidative stress in infertility. Reprod BioMed Online 14:159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1472-6483(10)60783-3
Aydos K, Guven MC, Can B, Ergun A (2001) Nicotine toxicity to the ultra-structure of the testis in rats. BJU Int 88:622–626. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-4096.2001.02384.x
Bancroft JD, Stevens A (1996) Theory and practice of histological techniques, 4th edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York, p 766
Bandyopadhyay G, Sinha S, Chattopadhyay BD, Chakraborty A (2008) Protective role of cucumin against nicotine induced genotoxicity on rat liver under restricted dietary protein. Eur J Pharmacol 588:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.04.023
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Bilinska B, Hejmej A, Kotula-Balak M (2018) Preparation of testicular samples for histology and immunohistochemistry. Methods Mol Biol 1748:17–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7698-0_3
Bisht S, Faiq M, Tolahunase M, Dada R (2017) Oxidative stress and male infertility. Nat Rev Urol 14:470–485. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2017.69
Bose M, Debnath D, Chen Y, Bose HS (2007) Folding, activity and import of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein into mitochondria changed by nicotine exposure. J Mol Endocrinol 39:67–79
Celik G, Semiz A, Karakurt S, Arslan S, Adali O, Sen A (2013) A comparative study for the evaluation of two doses of ellagic acid on hepatic drug metabolizing and antioxidant enzymes in the rat. Biomed Res Int 2013:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/358945
Çeribaşı AO, Sakin F, Türk G, Sönmez M, Ateşşahin A (2012) Impact of ellagic acid on adriamycin-induced testicular histopathological lesions, apoptosis, lipid peroxidation and sperm damages. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:717–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2011.01.006
Chen P, Chen F, Zhou B (2018) Antioxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of ellagic acid in liver and brain of rats treated by D-galactose. Sci Rep 8:1465. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19732-0
Chen SL, Cai L, Meng QY, Xu S, Wan H, Liu SZ (2000) Low-dose whole-body irradiation (LD-WBI) changes protein expression of mouse thymocytes: effect of a LD-WBI-enhanced protein RIP10 on cell proliferation and spontaneous or radiation-induced thymocyte apoptosis. Toxicol Sci 55:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/55.1.97
Darbandi S, Darbandi M (2016) Lifestyle modifications on further reproductive problems. Cresco J Reprod Sci 1:1–2
Devipriya N, Srinivasan M, Sudheer AR, Menon VP (2007) Effect of ellagic acid, a natural polyphenol, on alcohol-induced prooxidant and antioxidant imbalance: a drug dose dependent study. Singap Med J 48:311–318
El-Ghazaly M, Kenawy S, Khayyal MT, Roushdy H, Saleh S (1985) Effect of exposure to radiation on the inflammatory process and its influence by diclofenac. Br J Pharmacol 85:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08829.x
El-Ghazaly MA, Fadel NA, Abdel-Naby DH, Abd El-Rehim HA, Zaki HF, Sanaa A, Kenawy SA (2020) Amelioration of adjuvant-induced arthritis by exposure to low dose gamma radiation and resveratrol administration in rats. Int J Radiat Biol 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/09553002.2020.1748911
El-Ghazaly MA, Sadik NA, Rashed ER, Abd-El-Fattah AA (2015) Neuroprotective effect of EGb761® and low-dose whole-body γ-irradiation in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Toxicol Ind Health 31:1128–1143. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233713487251
Feinendegen LE (2005) Evidence for beneficial low level radiation effects and radiation hormesis. Br J Rad 78:3–7. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/63353075
Funabashi T, Sano A, Mitsushima D, Kimura F (2005) Nicotine inhibits pulsatile luteinizing hormone secretion in human males but not in human females, and tolerance to this nicotine effect is lost within one week of quitting smoking. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(3):908–913. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2005-0041
García-Niño WR, Zazueta C (2015) Ellagic acid: pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms involved in liver protection. Pharmacol Res 97:84–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2015.04.008
Georgy GS, Maher OW (2017) Ellagic acid and rosmarinic acid attenuate doxorubicin-induced testicular injury in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 31:9. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.21937
Girish C, Shweta O, Raj V, Balakrishnan S, Varghese RG (2014) Ellagic acid modulates sodium valproate induced reproductive toxicity in male Wistar rats. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 58:416–422
Hayes WJ (1982) Pesticides studied in man. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, London pp 86–91
Ina Y, Tanooka H, Yamada T, Sakai K (2005) Suppression of thymic lymphoma induction by life-long low-dose-rate irradiation accompanied by immune activation in C57BL/6 mice. Radiat Res 163:153–158. https://doi.org/10.1667/rr3289
Izquierdo-Vega JA, Madrigal-Santillán EO, Chavez-Pagola JT, Valadez-Vega CM, Sánchez-Gutiérrez M (2019) The activity of ellagic acid in male reproduction: a mini-review. Int J Med Rev 6:135–139. https://doi.org/10.30491/ijmr.2019.101966
Jana K, Samanta PK, De DK (2010) Nicotine diminishes testicular gametogenesis, steroidogenesis, and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein expression in adult albino rats: possible influence on pituitary gonadotropins and alteration of testicular antioxidant status. Toxicol Sci 116:647–659. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfq149
Jarabak J, Adams JA, Williams-Ashman HG, Talalay P (1962) Purification of a 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase of human placenta and studies on its transhydrogenase function. J Biol Chem 237:345–357
Kannan MM, Quine SD (2011) Ellagic acid ameliorates isoproterenol induced oxidative stress: evidence from electrocardiological, biochemical and histological study. Eur J Pharmacol 659:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.02.037
Kasson BG, Hsueh AJ (1985) Nicotinic cholinergic agonists inhibit androgen biosynthesis by cultured rat testicular cells. Endocrinology 117:1874–1880. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-117-5-1874
Kaur P, Bansal MP (2004) Influence of selenium induced oxidative stress on spermatogenesis and lactate dehydrogenase-X in mice testis. Asian J Androl 6:227–232
Kavitharaj NK, Vijayammal PL (1999) Nicotine administration induced changes in the gonadal functions in male rats. Pharmacol 58:2–7. https://doi.org/10.1159/000028262
Kaya N, Ozan G, Dabak DO, Gur S, Ozan IE (2017) Antioxidant effects of ellagic acid on testicular tissue of rats exposed to tobacco smoke metabolite-acetic acid. J Turgut Ozal Med Cent 24:381–386. https://doi.org/10.5455/jtomc.2017.05.068
Kojima S, Ishida H, Takahashi M, Yamaoka K (2002) Elevation of glutathione induced by low-dose gamma rays and its involvement in increased natural killer activity. Radiat Res 157:275–280. https://doi.org/10.1667/0033-7587(2002)157[0275:eogibl]2.0.co;2
Kojima S, Matsuki O, Nomura T, Kubodera A, Honda Y, Honda S, Tanooka H, Wakasugi H, Yamaoka K (1998a) Induction of mRNAs for glutathione synthesis-related proteins in mouse liver by low doses of γ-rays. Biochem Biophys Acta 1381:312–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-4165(98)00043-9
Kojima S, Matsuki O, Nomura T, Shimura N, Kubodera A, Yamaoka K, Tanooka H, Wakasugi H, Honda Y, Honda S, Sasaki T (1998b) Localization of glutathione and induction of glutathione synthesis-related proteins in mouse brain by low doses of γ rays. Brain Res 808:262–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(98)00832-4
Kolawole T, Adienbo O, Dapper V (2019) Ameliorative effects of hydromethanolic extract of citrullus lanatus (watermelon) rind on semen parameters, reproductive hormones, and testicular oxidative status following nicotine administration in male wistar rats. Niger J Physiol Sci 34:83–90
Lee EK, Kim JA, Kim JS, Park SJ, Heo K, Yang KM, Son TG (2013) Activation of de novo GSH synthesis pathway in mouse spleen after long term low-dose γ-ray irradiation. Free Radic Res 47:89–94. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2012.747678
Li W, Wang G, Cui J, Xue L, Cai L (2004) Low-dose radiation (LDR) induces hematopoietic hormesis: LDR-induced mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells into peripheral blood circulation. Exp Hematol 32:1088–1096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2004.07.015
Liebmann A, Hindemith M, Jahns J, Madaj-Sterba P, Weisheit S, Kamprad F, Hildebrandt G (2004) Low-dose X-irradiation of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Efficacy of different fractionation schedules. Strahlenther Onkol 180:165–172
Liu G, Gong P, Zhao H, Wang Z, Gong S, Cai L (2006) Effect of low-level radiation on the death of male germ cells. Radiat Res 165:379–389. https://doi.org/10.1667/rr3528.1
Liu SZ (2010) Biological effects of low level exposures to ionizing radiation: theory and practice. Hum Exp Toxicol 29:275–281. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327109363967
Luckey TD (1982) Physiological benefits from low levels of ionizing radiation. Health Phys 43:771–789. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004032-198212000-00001
Madole MB, Dilip B, Mamatha MT, Ankur P (2016) Study of serum lactate dehydrogenase and lipid profile in patients with chronic cough. Int J Clin Biochem Res 3:409–412
Mohamed DA, Abdelrahman SA (2019) The possible protective role of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) on testicular and epididymal structure and sperm parameters in nicotine-treated adult rats (a histological and biochemical study). Cell Tissue Res 375:543–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2909-8
Mosbah R, Yousef MI, Mantovani A (2015) Nicotine-induced reproductive toxicity, oxidative damage, histological changes and haematotoxicity in male rats: the protective effects of green tea extract. Exp Toxicol Pathol 67:253–259
Nowosielska EM, Cheda A, Wrembel-Wargocka J, Janiak MK (2009) Immunological mechanism of the low-dose radiation induced suppression of cancer metastases in a mouse model. Dose-Response 8:209–226. https://doi.org/10.2203/dose-response.09-016.Nowosielska
Okamoto M, Kita T, Okuda H, Tanaka T, Nakashima T (1994) Effects of aging on acute toxicity of nicotine in rats. Pharmacol Toxicol 75:1–6
Olivieri G, Bodycote J, Wolff S (1984) Adaptive response of human lymphocytes to low concentrations of radioactive thymidine. Science 223:594–597. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.6695170
Oyeyipo IP, Raji Y, Bolarinwa AF (2013) Nicotine alters male reproductive hormones in male albino rats: the role of cessation. J Hum Reprod Sci 6:40–44. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-1208.112380
Oyeyipo IP, Raji Y, Bolarinwa AF (2014) Antioxidant profile changes in reproductive tissues of rats treated with nicotine. J Hum Reprod Sci 7:41–46. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-1208.130823
Oyeyipo IP, Raji Y, Emikpe BO, Bolarinwa AF (2010) Effects of oral administration of nicotine on organ weight, serum testosterone level and testicular pathology in adult male rats. Niger J Physiol Sci 25:81–86
Oyeyipo IP, Raji Y, Emikpe BO, Bolarinwa AF (2011) Effects of nicotine on sperm characteristics and fertility profile in adult male rats: a possible role of cessation. J Reprod Infertil 12:201–207
Rajpurkar A, Dhabuwala CB, Jiang Y, Li H (2000) Chronic cigarette smoking induces an oxidant antioxidant imbalance in the testis. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 19:369–373
Ramlau-Hansen CH, Thulstrup AM, Aggerholm AS, Jensen MS, Toft G, Bonde JP (2007) Is smoking a risk factor for decreased semen quality? A cross-sectional analysis. Hum Reprod 22:188–196. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/del364
Ray D, Majumder S (2018) The protective effects of chlorophytum borivilianum on nicotine-induced reproductive toxicity, oxidative damage, histological changes and haematotoxicity in male rats. JIPBS 5:76–81
Reddy A, Sood A, Rust PF, Busby JE, Varn E, Mathur RS, Mathur S (1995) The effect of nicotine on in-vitro sperm motion characteristics. J Assist Reprod Genet 12:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02211802
Sarasin A, Schlumpf M, Muller M, Fleischmann I, Lauber ME, Lichtensteiger W (2003) Adrenal-mediated rather than direct effects of nicotine as a basis of altered sex steroid synthesis in fetal and neonatal rat. Reprod Toxicol 17:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0890-6238(02)00119-3
Seema P, Swathy SS, Indira M (2007) Protective effect of selenium on nicotine-induced testicular toxicity in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 120:212–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-007-8021-7
Segarra AC, Strand FL (1989) Prenatal administration of nicotine alters subsequent sexual behaviour and testosterone levels of male rats. Brain Res 480:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(89)91577-1
Spiers JG, Chen HJ, Sernia C, Lavidis NA (2015) Activation of the hypothalamic pituitary-adrenal stress axis induces cellular oxidative stress. Front Neurosci 8:456. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2014.00456
Sudheer AR, Muthukumaran S, Devipriya N, Devraj H, Menon VP (2008) Influence of ferulic acid on nicotine induced lipid peroxidation, DNA damage and inflammation in experimental rats as compared to N-acetylcysteine. Toxicology 243:317–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2007.10.016
Talalay P (1962) Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. In: Colowick SP, Kaplan NO (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 5. Academic Press, New York, pp 512–516
Tuglu D, Yuvanc E, Yilmaz E, Gencay IY, Atasoy P, Kisa U, Batislam E (2015) The antioxidant effect of dexmedetomidine on testicular ischemia-reperfusion injury. Acta Cir Bras 30:414–421. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-865020150060000007
Türk G, Ateşşahin A, Sönmez M, Çeribaşı AO, Yüce A (2008) Improvement of cisplatin-induced injuries to sperm quality, the oxidant-antioxidant system, and the histologic structure of the rat testis by ellagic acid. Fertil Steril 89:1474–1481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.04.059
Türk G, Çeribaşi AO, Sahna E, Ateşşahin A (2011) Lycopene and ellagic acid prevent testicular apoptosis induced by cisplatin. Phytomedicine 18:356–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2010.07.008
Türk G, Çeribaşi AO, Sakin F, Sönmez M, Ateşşahin A (2010) Antiperoxidative and anti-apoptotic effects of lycopene and ellagic acid on cyclophosphamide-induced testicular lipid peroxidation and apoptosis. Reprod Fertil Dev 22:587–596. https://doi.org/10.1071/RD09078
Tweed JO, Hsia SH, Lutfy K, Friedman TC (2012) The endocrine effects of nicotine and cigarette smoke. Trends Endocrinol Metab 23:334–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2012.03.006
Uchiyama M, Mihara M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 86:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(78)90342-1
Ukwenya VO, Olawuyi TS, Adam AM, Ukwenya MU (2020) Hormonal changes and redox imbalance in nicotine-induced testicular toxicity: the mitigating influence of D-ribose L-cysteine JOBAZ 81:48.https://doi.org/10.1186/s41936-020-00173-z
Umesalma S, Sudhandiran G (2011) Ellagic acid prevents rat colon carcinogenesis induced by 1, 2 dimethyl hydrazine through inhibition of AKT-phosphoinositide- 3 kinase pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 660:249–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.03.036
Wetscher GJ, Bagchi D, Perdikis G, Bagchi M, Redmond EJ, Hinder PR, Glaser K, Hinder RA (1995) In vitro free radical production in rat oesophageal mucosa induced by nicotine. Dig Dis Sci 40:853–858. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02064991
Yamamoto Y, Isoyama E, Sofikitis N, Miyagawa I (1998) Effects of smoking on testicular function and fertilizing potential in rats. Urol Res 26:45–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002400050022
Yamaoka K, Edamatsu R, Mori A (1991) Increased SOD activities and decreased lipid peroxide levels induced by low dose X irradiation in rat organs. Free Radic Biol Med 11:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/0891-5849(91)90127-O
Yang G, Li W, Jiang H, Liang X, Zhao Y, Yu D, Zhou L, Wang G, Tian H, Han F, Cai L, Cui J (2016) Low-dose radiation may be a novel approach to enhance the effectiveness of cancer therapeutics. Int J Cancer 139:2157–2168. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30235
Yildiz D, Liu YS, Ercal N, Armstrong DW (1999) Comparison of pure nicotine and smokeless tobacco extract induced toxicities and oxidative stress. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 37:434–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002449900537
Yoshimoto M, Kataoka T, Toyota T, Taguchi T, Yamaoka K (2012) Inhibitory effects of prior low dose X-irradiation on cold-induced brain injury in mouse. Inflammation 35:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-011-9293-9
Zhao H, Xu S, Wang Z, Li Y, Guo W, Lin C, Gong S, Li C, Wang G, Cai L (2010) Repetitive exposures to low-dose X-rays attenuate testicular apoptotic cell death in streptozotocin-induced diabetes rats. Toxicol Lett 192:356–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.11.011
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Ahmed H. Osman, Professors of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University, for his professional assistance in carrying out the histological examinations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Aliaa H. Ashoub, Doaa H. Abdel-Naby, Marwa M. Safar, Mona A. El-Ghazaly, and Sanaa A. Kenawy. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Aliaa H. Ashoub and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript to be submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All experiments were performed following the guidelines set by the Environment-European Commission (EEC) (revised directive 86/609/EEC), and an ethical approval (Permit no: PT 1175) was granted from the Ethical Committee for Animal Experimentation, Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo University.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 502 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashoub, A.H., Abdel-Naby, D.H., Safar, M.M. et al. Ameliorative effect of fractionated low-dose gamma radiation in combination with ellagic acid on nicotine-induced hormonal changes and testicular toxicity in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 23287–23300 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12334-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12334-2