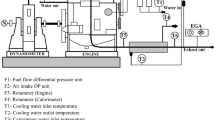
Abstract
Deterioration of air quality through the combustion of hydrocarbon fuels has been one of the global transboundary problems put before the research community since last five decades. According to the updated statistics, 79% of energy needs in India are met by fossil fuel combustion which results in the emission of toxic pollutants like carbon monoxide, oxides of nitrogen, and unburned hydrocarbons. Air quality has seriously been affected in many parts of India, and statistically, 13 out of 15 most polluted cities in the world lie in India. Magnetic field-assisted combustion has been proven as a reliable technology in internal combustion engines for enhancing the combustion of fuels and reduction of harmful emissions that are the byproducts of incomplete combustion of fuels. In the present work, the magnetic field-assisted combustion of a liquid-phase and a gas-phase fuel (gasoline and LPG) has been studied in a multicylinder automobile engine replicating on road driving conditions in a laboratory focusing on the levels of emissions in comparison with normal combustion of both the fuels. The experimental study concludes that the applied magnetic field positively influences combustion, resulting in reduced level of emission of toxic components irrespective of the phase of hydrocarbon fuels. It is also observed that the percentage reduction in emissions increases with increase in intensity of magnetization. The maximum reduction obtained for CO and UBHC emissions through this technique is 20.58% and 14.47%, respectively. The effectiveness of MFAC in countering air pollution from vehicular exhaust is also studied with respect to fuel phase and mode of operation. The effectiveness of MFAC is observed to be more in high-speed operation of the engine and decreases in the order CO > UBHC > NO. The obtained emission results have a cumulative significance as 45% of total air pollution in India is caused by combustion of hydrocarbons in automotive engines.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdel-Rehim A, Attia A (2014) Does magnetic fuel treatment affect engine's performance?. SAE Technical Paper 2014-01-1398. https://doi.org/10.4271/2014-01-1398
Azem A, Riahi B, Balali-Mood M (2016) Effects of air pollution on human health and practical measures for prevention in Iran. J Res Med Sci 21:65. https://doi.org/10.4103/1735-1995.189646
Brown M, Chen (2002) Developments in the processing and properties of NdFeB type permanent magnets. J Magn Magn Mater 248:432–440
Chi X, Li Y, Er D-q, Han X-h, Duan X-l, Sun J-b, Cui C-x (2018) Study of structure and magnetic properties of SmCo10 alloy prepared by different methods. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2018:1–10
Cong X (2018) Air pollution from industrial waste gas emissions is associated with cancer incidences in Shanghai, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:13067–13078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1538-9
Faris A, Saadi K, Jamal N, Isse R, Abed M, Fouad Z, Kazim A, Reheem N, Chaloob A, Mohammed H, Jasim H, Sadeq J, Salim A, Abas A (2012) Effect of magnetic field on fuel consumption and exhaust emissions in two-stroke engine. Energy Procedia 18:327–338
Folinsbee LJ (1992) Human health effects of air pollution. Environ Health Perspect 100:45–56
Ghosh JKC, Heck JE, Cockburn M, Su J, Jerrett M, Ritz B (2013) Prenatal exposure to traffic-related air pollution and risk of early childhood cancers. Am J Epidemiol 178(8):1233–1239. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwt129
Gillion P, Blanchard J, Gilard V (2010) Magnetic field influence on co-flow laminar diffusion flames. Russ J Phys Chem 4:279–285
Gong X, Lin Y, Zhan FB (2018) Industrial air pollution and low birth weight: a case-control study in Texas, USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:30375–30389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2941-y
Govindasamy P, Dhandapani S (2007) Performance and emission achievements by magnetic energizer with a single cylinder two stroke catalytic coated spark ignition engine. J Sci Ind Res 66:457–463
Greenstone M, Harish S, Pande R, Sudarshan A (2017) The solvable challenge of air pollution in India. India Policy Forum, 11-12 July 2017
Gu H, Yan W, Elahi E, Cao Y (2020) Air pollution risks human mental health: an implication of two-stages least squares estimation of interaction effects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:2036–2043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06612-x
Haavisto, Touminen, Santa-Nokki, Kankaanpa, Paju M, Ruuskanen (2014) Magnetic behavior of sintered NdFeB magnets on long term time scale. Adv Mater Sci Eng 760584:1–7
Kampa M, Castanas E (2007) Human health effects of air pollution. Environ Pollut 151:362–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.06.012
Kline SJ, McClintock FA (1953) Analysis of uncertainty in single-sample experiments. Mech Eng 75:3–9
Kristiantoro, Idayanti, Sudrajat, Septiani, Dedi (2016) Application of bonded NdFeB magnet for C-band circulator component. J Phys Conf Ser 776:012030
Künzli N, Jerrett M, Mack WJ, Beckerman B, Labree L, Gilliland F (2005) Ambient air pollution and atherosclerosis in Los Angeles. Environ Health Perspect 113:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.7523
Kurniawan, Purba, Setiadi, Simbolon, Warman, Sebayang (2017) Effect of Fe-Mn addition on microstructure and magnetic properties of NdFeB magnetic powders. J Phys Conf Ser 985:012044
Mattiuzzi C, Lippi G (2020) Gender-based fatal effects of ambient air pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:11458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07983-2
Morozov Y, Kuznetsov M (1999) Effect of magnetic fields on combustion electromotive force. Combust Explos Shock Waves 35:18–22
Muljadi R, Sardjono P, Setiyabudidaya D, Gulo F (2019) Mechanical, magnetic properties and corrosion resistance of hybrid bonded magnet NdFeB- BaFe12O19. IOP Conf. Series. J Phys Conf Ser 1191:012048. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1191/1/012048
Nayak V, Rashmi S, Chitragar P, Padmanabha M (2016) Combustion characteristics and cyclic variation of a LPG fuelled MPFI four cylinder gasoline engine. Energy Procedia 90:270–280
Olmo NR, Hila IP, Santos UDP, Alberto L, Pereira A (2011) A review of low-level air pollution and adverse effects on human health : implications for epidemiological studies and public policy. Clinics 66:681–690. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1807-59322011000400025
Oommen LP, Kumar GN (2020a) Experimental studies on the impact of part-cooled high-pressure loop EGR on the combustion and emission characteristics of liquefied petroleum gas. J Therm Anal Calorim 141:2265–2275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09762-0
Oommen LP, Kumar GN (2020b) Experimental studies on the influence of axial and radial fields of sintered neo-delta magnets in reforming the energy utilization combustion and emission properties of a hydrocarbon fuel. Energy Sources Part A Recover Util Environ Effects 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1767729
Oommen LP, Kumar GN (2020c) Experimental analysis of synergetic effect of part cooled EGR on magnetic field assisted combustion of liquefied petroleum gas. Arab J Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04696-z
Oommen LP, Kumar GN (2019) A study on the effect of magnetic field on the properties and combustion of hydrocarbon fuels. Int J Mech Prod Eng Res Dev 9(3):89–98
Regens J (2007) Ambient air pollution and daily pediatric hospitalizations for asthma (5 pp). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 14:19–23. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2006.08.333
Regis da Costa e Oliveira J, Base LH, Maia LCP et al (2020) Geometric indexes of heart rate variability in healthy individuals exposed to long-term air pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:4170–4177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06965-3
Sahoo R, Jain A (2019) Experimental analysis of nanofuel additives with magnetic fuel conditioning for diesel engine performance and emissions. Fuel 236:365–372
Ueno S, Harada K (1987) Combustion process under strong DC magnetic fields. IEEE Trans Magn 23:2752–2754
Xu J, Geng W, Geng X, Cui LJ, Ding T, Xiao C, Zhang J, Tang J, Zhai J (2020) Study on the association between ambient air pollution and daily cardiovascular death in Hefei, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:547–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06867-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Libin P Oommen conceived, planned, and carried out the experimental work. Kumar G N contributed to the analysis and interpretation of results and drafting of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oommen, L.P., Narayanappa, K.G. Assimilative capacity approach for air pollution control in automotive engines through magnetic field-assisted combustion of hydrocarbons. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 63661–63671 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11923-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11923-5