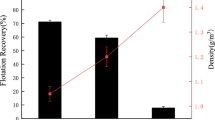
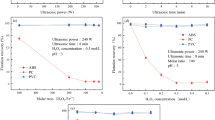
Abstract
This study reports the selective hydrophilization of the ABS/PC blend surface using the peroxide-sonochemical system and then its selective separation by froth flotation technique from other ABS-based plastics (ABS, ABS/PMMA) and PS/HIPS in electronic shredder residue (ESR). FT-IR and XPS measurements confirm that the hydrophilic moiety development on the ABS/PC surface led to increasing the wettability of ABS/PC and then decreased its floatability. The confocal scanning results also support the enhancement of microscale roughness of the treated ABS/PC surface. The enhanced surface roughness is attributed to the oxidative process which degrades hydrophobic moieties and promotes hydrophilic functional groups on the ABS/PC surface using commercial oxidant peroxide and ultrasound. This study also investigated removal of Br-containing compounds on the ABS/PC surface. The optimum conditions for selectively ABS/PC separation are peroxide concentration 2%, power cycle 70%, treatment time 5 min, temperature 50 °C, floating agent concentration 0.4 mg/L, flotation time 2 min, and airflow rate 0.5 L/min. ABS/PC was selectively separated from ESR styrene plastics with high recovery and purity of 98.9% and 99.8%, respectively. Hence, the developed novel surface treatments having removal of hazardous Br chemicals and none-formation of secondary pollutants should be applied for upgrading plastic recycling quality.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Altwaiq A m, Wolf M, van Eldik R (2003) Extraction of brominated flame retardants from polymeric waste material using different solents and supercritical carbon dioxide. Anal Chim Acta 491:111–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00785-2
Arends D, Schlummer M, Mäurer A, Markowski J, Wagenknecht U (2015) Characterisation and materials flow management for waste electrical and electronic equipment plastics from German dismantling centres. Waste Manag Res 33:775–784. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X15588585
Arnold JC, Watson T, Alston S, Carnie M, Glover C (2010) The use of FTIR mapping to assess phase distribution in mixed and recycled WEEE plastics. Polym Test 29:459–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2010.02.006
Beigbeder J, Perrin D, Mascaro JF, Lopez-Cuesta JM (2013) Study of the physico-chemical properties of recycled polymers from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) sorted by high resolution near infrared devices. Resour Conser Recycl 78:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2013.07.006
Chen D, Sharma SK, Mudhoo A (2011) Handbook on applications of ultrasound: sonochemistry for sustainability. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis
Fraunholcz N (2004) Separation of waste plastics by froth flotation-a review, part I. Miner Eng 17:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2003.10.028
Jang YC (2010) Waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) management in Korea: generation, collection, and recycling systems. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 12:283–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-010-0298-5
Jang YC, Lee S, Ko Y, Choi K (2014) Material recycling and flow of waste electrical and electronic equipment in Korea. Int J Appl Eng Res 9:25221–25230
Jung MR, Horgen FD, Orski S et al (2018) Validation of ATR FT-IR to identify polymers of plastic marine debris, including those ingested by marine organisms. Mar Pollut Bull 127:704–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.12.061
Khan MMK, Hilado CJ, Agarwal S, Gupta RK (2007) Flammability properties of virgin and recycled polycarbonate (PC) and Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) recovered from end-of-life electronics. J Polym Eniron 15:188–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-007-0059-2
Kobayashi Y, Hayashi M, Yoshino F, Tamura M, Yoshida A, Ibi H, Lee MCI, Ochiai K, Ogiso B (2014) Passive ultrasonic irrigation in the presence of a low concentration of hydrogen peroxide enhances hydroxyl radical generation and bactericidal effect against Enterococcus faecalis. J Oral Sci 56:35–39
Li J, Wu G, Xu Z (2015a) Tribo-charging properties of waste plastic granules in process of tribo-electrostatic separation. Waste Manag 35:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.10.001
Li P, Zong ZM, Li ZK, Wang YG, Liu FJ, Wei XY (2015b) Characterization of basic heteroatom-containing organic compounds in liquefaction residue from Shenmu-Fugu subbituminous coal by positive-ion electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Fuel Process Technol 132:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.12.026
Li J, Chen F, Yang L, Jiang L, Dan Y (2017) FTIR analysis on aging characteristics of ABS/PC blend under U-irradiation in air. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 184:361–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SAA.2017.04.075
Lim M, Son Y, Khim J (2014) The effects of hydrogen peroxide on the sonochemical degradation of phenol and bisphenol A. Ultrason Sonochem 21:1976–1981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.03.021
Mallampati SR, Lee BH, Mitoma Y, Simion C (2017) Selective sequential separation of ABS/HIPS and PC from automobile and electronic waste shredder residue by hybrid nano-Fe/Ca/CaO assisted ozonisation process. Waste Manag 60:428–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.01.003
Martinho G, Pires A, Saraia L, Ribeiro R (2012) Composition of plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) by direct sampling. Waste Manag 32:1213–1217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.02.010
McKeen L (2012) Styrenic plastics. In: The effect of sterilization on plastics and elastomers. pp. 85–132
Menad N, Guignot S, van Houwelingen JA (2013) New characterisation method of electrical and electronic equipment wastes (WEEE). Waste Manag 33:706–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.04.007
Michael N, Bhushan B (2007) Hierarchical roughness makes superhydrophobic states stable. Microelectron Eng 84:382–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2006.10.054
Naddeo, Rizzo L, Belgiorno (2011) Water, wastewater and soil treatment by advanced oxidation processes. LULU Press
Nagie TM (2007) Coherent synchronized oxidation reactions by hydrogen peroxide, 1st edn. Elseier, Boston
Nkwachukwu O, Chima C, Ikenna A, Albert L (2013) Focus on potential environmental issues on plastic world towards a sustainable plastic recycling in developing countries. Int J Ind Chem 4:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/2228-5547-4-34
Oepen S, Gottschalk A (2011) Styrene copolymers (ABS, ASA, SAN, MABS, and ABS blends)
Onwudili JA, Williams PT (2009) Degradation of brominated flame-retarded plastics (Br-ABS and Br-HIPS) in supercritical water. J Supercrit Fluids 49:356–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2009.03.006
Pascoe RD (2005) The use of selective depressants for the separation of ABS and HIPS by froth flotation. Miner Eng 18:233–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2004.07.006
Peng M, Kurokawa T, Gong JP, Osada Y, Zheng Q (2002) Effect of surface roughness of hydrophobic substrate on heterogeneous polymerization of hydrogels. J Phys Chem B 106:3073–3081. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp012521u
Reena G, Sangita, Verinder K (2011) FT-IR studies of e-plastic obtained from obsolete computers. J Chem Pharm Res 3:660–667
Schluep M, Streicher M, Morf L, Buser A (2009) Recycling of plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE)–tentative results of a Swiss study. Waste Manag 27:310–318. 19.10.2015
Shapiro M, Galperin (2005) Air classification of solid particles: a review. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 44:279–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2004.02.022
Stenall E, Tostar S, Boldizar A et al (2013) An analysis of the composition and metal contamination of plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE). Waste Manag 33:915–922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.12.022
Stubbings WA, Harrad S (2014) Extent and mechanisms of brominated flame retardant emissions from waste soft furnishings and fabrics: a critical review. Eniron Int 71:164–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enint.2014.06.007
Taurino R, Pozzi P, Zanasi T (2010) Facile characterization of polymer fractions from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) for mechanical recycling. Waste Manag 30:2601–2607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2010.07.014
Thanh Truc NT, Lee BK (2016) Sustainable and selective separation of PC and ABS from a WEEE plastic mixture using microwave and/or mild-heat treatment with froth flotation. Eniron Sci Technol 50:10580–10587. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02280
Thanh Truc NT, Lee B-KK (2017a) Selective separation of ABS/PC containing BFRs from ABSs mixture of WEEE by developing hydrophilicity with ZnO coating under microwave treatment. J Hazard Mater 329:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.01.027
Thanh Truc NT, Lee BK (2017b) Combining ZnO/microwave treatment for changing wettability of WEEE styrene plastics (ABS and HIPS) and their selective separation by froth flotation. Appl Surf Sci 420:746–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.04.075
Thanh Truc NT, Lee C-H, Lee B-K, Mallampati SR (2017a) Surface hydrophilization of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene by the mild heat treatment for its selective separation to recycling. Sep Purif Technol 173:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.09.042
Thanh Truc NT, Lee C-HH, Lee B-KK, Mallampati SR (2017b) Development of hydrophobicity and selective separation of hazardous chlorinated plastics by mild heat treatment after PAC coating and froth flotation. J Hazard Mater 321:193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.014
Torres-Palma RA, Serna-Galis EA (2018) Sonolysis. Ad Oxid Process Wastewater Treat Emerg Green Chem Technol 177–213
Wäger PA, Hischier R (2015) Life cycle assessment of post-consumer plastics production from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) treatment residues in a Central European plastics recycling plant. Sci Total Eniron 529:158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitoten.2015.05.043
Wäger P, Schluep M, Müller E, Gallen C-S (2010) RoHS substances in mixed plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipment. Empa 1–113. https://doi.org/10.1021/es202518n
Wang JC, Wang H (2017) Fenton treatment for flotation separation of polyinyl chloride from plastic mixtures. Sep Purif Technol 187:415–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.06.076
Wang H, Chen X l, Bai Y et al (2012) Application of dissolved air flotation on separation of waste plastics ABS and PS. Waste Manag 32:1297–1305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.03.021
Wang C q, Wang H, Wu B x, Liu Q (2014) Boiling treatment of ABS and PS plastics for flotation separation. Waste Manag 34:1206–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.02.005
Wang C q, Wang H, Fu J g, Liu Y n (2015a) Flotation separation of waste plastics for recycling-a review. Waste Manag 41:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.03.027
Wang J, Li Y, Song J, He M, Song J, Xia K (2015b) Recycling of acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) copolymers from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE), through using an epoxy-based chain extender. Polym Degrad Stab 112:167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.12.025
Yang X, Sun L, Xiang J, Hu S, Su S (2013) Pyrolysis and dehalogenation of plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE): a review. Waste Manag 33:462–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.07.025
Funding
This work was supported by the Korea Institute for Advanced of Technology (KIAT) grant funded by the Korea Government (MOTIE) (P0008421, 2020 The Company Development Program for Industry Specialist).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Nguyen Thi Thanh Truc analyzed and interpreted the main data and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. Prof. Hung Anh Le is responsible for data curation. Prof. Byeoung-Kyu Lee is a supervisor, taking responsibility for writing—review, and editing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication.
Not applicable
Additional information
Responsible Editor: VÃtor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 280 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thanh Truc, N., Le, H. & Lee, BK. Sono-oxidation treatment of hazardous ABS/PC surface for its selective separation from ESR styrene plastics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 24771–24784 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11796-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11796-8