Abstract
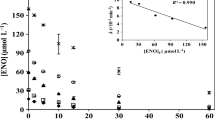
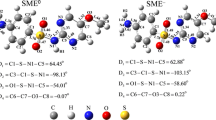
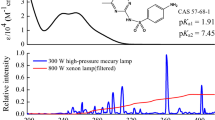
This study aimed at investigating the photochemical behavior of sulfa drugs containing five and six-membered heterocyclic substituents (sulfamethoxazole (SMX) and sulfadiazine (SDZ), respectively), in an aqueous medium. Despite their importance, studies devoted to the use of photochemical models to predict the environmental phototransformation of pollutants in surface waters, by combining laboratory results and natural aquatic systems parameters, are still scarce in the scientific literature. In this work, the second-order reaction rate constants of SDZ and SMX with hydroxyl radicals (●OH), singlet oxygen (1O2), and triplet excited states of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (3CDOM*) were experimentally determined at pH 7, using the competition kinetics approach. The results show that ●OH and 3CDOM* are the key species involved in sulfonamide degradation, with anionic SMX, most prevalent at pH 6–9, being degraded much slower than the anionic form of SDZ. Moreover, SDZ and SMX photodegradation in natural water samples (spring-fed natural pond, public supply reservoir, and sea water) was significantly enhanced relative to depletion in pure water. Finally, from mathematical simulations of the sunlight-driven sulfonamide degradation, half-life times were predicted for these drugs varying from less than 2 to about 90 days, depending on the water depth, concentration of key species (DOC, HCO3−, NO2−, CO32−) in natural aqueous systems, as well as on the particular heterocyclic substituent.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Arques A, Bianco Prevot A (2015) Soluble bio-based substances isolated from urban wastes: environmental applications. Springer International Publishing
Batista APS, Teixeira A, Cooper WJ, Cottrell BA (2016) Correlating the chemical and spectroscopic characteristics of natural organic matter with the photodegradation of sulfamerazine. Water Res 93:20–29
Bianco A, Fabbri D, Minella M, Brigante M, Mailhot G, Maurino V, Minero C, Vione D (2015) New insights into the environmental photochemistry of 5-chloro-2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenol (triclosan): reconsidering the importance of indirect photoreactions. Water Res 72:271–280
Bodrato M, Vione D (2014) APEX (aqueous photochemistry of environmentally occurring xenobiotics): a free software tool to predict the kinetics of photochemical processes in surface waters. Environ Sci-Proc Imp 16:732–740
Boreen AL, Arnold WA, McNeill K (2004) Photochemical fate of sulfa drugs in the aquatic environment: sulfa drugs containing five-membered heterocyclic groups. Environ Sci Technol 38:3933–3940
Boreen AL, Arnold WA, McNeill K (2005) Triplet-sensitized photodegradation of sulfa drugs containing six-membered heterocyclic groups: identification of an SO2 extrusion photoproduct. Environ Sci Technol 39:3630–3638
Carena L, Puscasu CG, Comis S, Sarakha M, Vione D (2019) Environmental photodegradation of emerging contaminants: a reexamination of the importance of triplet-sensitised processes, based on the use of 4-carboxybenzophenone as proxy for the chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Chemosphere 237:124476
De Laurentiis E, Prasse C, Ternes TA, Minella M, Maurino V, Minero C, Sarakha M, Brigante M, Vione D (2014) Assessing the photochemical transformation pathways of acetaminophen relevant to surface waters: transformation kinetics, intermediates, and modelling. Water Res 53:235–248
Fabbri D, Minella M, Maurino V, Minero C, Vione D (2015) A model assessment of the importance of direct photolysis in the photo-fate of cephalosporins in surface waters: possible formation of toxic intermediates. Chemosphere 134:452–458
Ge LK, Zhang P, Halsall C, Li YY, Chen CE, Li J, Sun HL, Yao ZW (2019) The importance of reactive oxygen species on the aqueous phototransformation of sulfonamide antibiotics: kinetics, pathways, and comparisons with direct photolysis. Water Res 149:243–250
Kolpin DW, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Thurman EM, Zaugg SD, Barber LB, Buxton HT (2002) Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in US streams, 1999-2000: a national reconnaissance. Environ Sci Technol 36:1202–1211
Lastre-Acosta AM, Barberato B, Parizi MPS, Teixeira A (2019) Direct and indirect photolysis of the antibiotic enoxacin: kinetics of oxidation by reactive photo-induced species and simulations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:4337–4347
Li YJ, Wei XX, Chen JW, Xie HB, Zhang YN (2015) Photodegradation mechanism of sulfonamides with excited triplet state dissolved organic matter: a case of sulfadiazine with 4-carboxybenzophenone as a proxy. J Hazard Mater 290:9–15
Marchetti G, Minella M, Maurino V, Minero C, Vione D (2013) Photochemical transformation of atrazine and formation of photointermediates under conditions relevant to sunlit surface waters: laboratory measures and modelling. Water Res 47:6211–6222
Minella M, Rapa L, Carena L, Pazzi M, Maurino V, Minero C, Brigante M, Vione D (2018) An experimental methodology to measure the reaction rate constants of processes sensitised by the triplet state of 4-carboxybenzophenone as a proxy of the triplet states of chromophoric dissolved organic matter, under steady-state irradiation conditions. Environ Sci Process Impacts 20:1007–1019
Montoneri E, Boffa V, Savarino P, Perrone D, Ghezzo M, Montoneri C, Mendichi R (2011) Acid soluble bio-organic substances isolated from urban bio-waste. Chemical composition and properties of products. Waste Manag 31:10–17
Oliveira C, Lima DLD, Silva CP, Calisto V, Otero M, Esteves VI (2019) Photodegradation of sulfamethoxazole in environmental samples: the role of pH, organic matter and salinity. Sci Total Environ 648:1403–1410
Parizi MPS, Acosta AML, Ishiki HM, Rossi RC, Mafra RC, Teixeira A (2019) Environmental photochemical fate and UVC degradation of sodium levothyroxine in aqueous medium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:4393–4403
Passananti M, Temussi F, Iesce MR, Previtera L, Mailhot G, Vione D, Brigante M (2014) Photoenhanced transformation of nicotine in aquatic environments: involvement of naturally occurring radical sources. Water Res 55:106–114
Perisa M, Babic S, Skoric I, Fromel T, Knepper TP (2013) Photodegradation of sulfonamides and their N (4)-acetylated metabolites in water by simulated sunlight irradiation: kinetics and identification of photoproducts. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8934–8946
Schwarzenbach RP (2003) Environmental organic chemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken
Shemer H, Sharpless CM, Elovitz MS, Linden KG (2006) Relative rate constants of contaminant candidate list pesticides with hydroxyl radicals. Environ Sci Technol 40:4460–4466
Silva MP, Mostafa S, McKay G, Rosario-Ortiz FL, Teixeira A (2015) Photochemical fate of amicarbazone in aqueous media: laboratory measurement and simulations. Environ Eng Sci 32:730–740
Trovo AG, Nogueira RFP, Aguera A, Sirtori C, Fernandez-Alba AR (2009) Photodegradation of sulfamethoxazole in various aqueous media: persistence, toxicity and photoproducts assessment. Chemosphere 77:1292–1298
Vione D (2020) A critical view of the application of the APEX software (aqueous photochemistry of environmentally-occurring xenobiotics) to predict photoreaction kinetics in surface freshwaters. Molecules 25:1–34
Vione D, Maddigapu PR, De Laurentiis E, Minella M, Pazzi M, Maurino V, Minero C, Kouras S, Richard C (2011) Modelling the photochemical fate of ibuprofen in surface waters. Water Res 45:6725–6736
Vione D, Fabbri D, Minella M, Canonica S (2018) Effects of the antioxidant moieties of dissolved organic matter on triplet-sensitized phototransformation processes: implications for the photochemical modeling of sulfadiazine. Water Res 128:38–48
Wenk J, von Gunten U, Canonica S (2011) Effect of dissolved organic matter on the transformation of contaminants induced by excited triplet states and the hydroxyl radical. Environ Sci Technol 45:1334–1340
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Prof. N. Y. M. Iha (Laboratory of Photochemistry and Energy Conversion, Institute of Chemistry, University of São Paulo, Brazil), for the disposal of the solar simulator, and to Prof. J. A. S. Tenório (Laboratory of Recycling, Waste Treatment and Extraction-LAREX, Department of Chemical Engineering, Escola Politécnica, University of São Paulo, Brazil) for the characterization of natural water samples.
Funding
This work was financially supported by São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) grant #2016/03695-8; Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior Brasil (CAPES) Finance Code 001 and post-doc grant #88887.340964/2019-00; and National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AMLA: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft, visualization
BSC: methodology, investigation
MPSP: conceptualization, methodology
CAON: resources, supervision, funding acquisition
ACSCT: conceptualization, validation, resources, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 22 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lastre-Acosta, A.M., Cristofoli, B.S., Parizi, M.P.S. et al. Photochemical persistence of sulfa drugs in aqueous medium: kinetic study and mathematical simulations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 23887–23895 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11715-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11715-x