Abstract
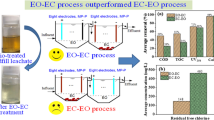
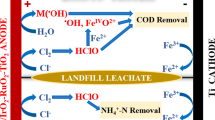
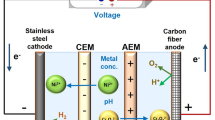
An attempt has been made to improve the treatment efficiency of mature landfill leachate prior to the existing biological treatment. In this study, electrochemical oxidation (EO) was applied as a pre-treatment to remove organic contaminants and was simultaneously combined with electrodialysis (ED) to remove ionic constituents, such as ammonium and phosphate. A laboratory-scale electrochemical reactor was designed by utilizing a carbon graphite anode and a stainless steel cathode and separated by an anion exchange membrane (AEM) and cation exchange membrane (CEM), creating a three-compartment reactor. The oxidation of the organic pollutant would occur in the anodic compartment, while the targeted ammonium and phosphate ions would be migrated and accumulated in the central compartment. The treatment process was performed in a batch recirculation time of 12 h at a constant supplied current of 0.25 A and evaluated by means of the initial leachate pH (i.e., original pH value of 7.85; adjusted pH value of 5.50 and 8.50) and three different initial chloride concentrations. The higher the chloride concentration in the leachate, the higher the removal efficiency, except for total phosphate. The highest chemical oxidation demand (COD) removal was 86.2% (0.88 g W−1 h−1), at an initial leachate pH value of 7.85 with the addition of 2 g L−1 of NaCl. Furthermore, under the same conditions, the ammonium, total phosphate, and chloride removals were 85% (0.44 g W−1 h−1), 89% (0.08 g W−1 h−1), and 83% (0.69 g W−1 h−1), respectively. Also, the concentrated ionic compounds in the central compartment can lower the energy consumption and can possibly be further treated or managed.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. Data sharing is not applicable to this article since no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Abbas AA, Jingsong G, Ping LZ, Ya PY, Al-Rekabi WS (2009) Review on landfill leachate treatments. Am J Appl Sci 6(4):672–684 https://thescipub.com/pdf/ajassp.2009.672.684.pdf
Agustina F, Bagastyo AY, Nurhayati E (2019) Electro-oxidation of landfill leachate using boron-doped diamond: role of current density, pH and ions. Water Sci Technol 79:921–928. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2019.040
Anglada Á, Urtiaga A, Ortiz I (2009a) Contributions of electrochemical oxidation to waste-water treatment: fundamentals and review of applications. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:1747–1755. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2214
Anglada Á, Urtiaga A, Ortiz I (2009b) Pilot scale performance of the electro-oxidation of landfill leachate at boron-doped diamond anodes. Environ Sci Technol 43:2035–2040. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802748c
Anglada Á, Urtiaga A, Ortiz I, Mantzavinos D, Diamadopoulos E (2011) Boron-doped diamond anodic treatment of landfill leachate: evaluation of operating variables and formation of oxidation by-products. Water Res 45:828–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.09.017
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington D.C
Ardakani MB, Ebadi T, Hosseini SMM (2016) The effects of using reprocessable material on the durability and mechanical properties of landfill leachate collection HDPE pipes. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 19:1166–1176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-016-0502-3
Asaithambi P, Govindarajan R, Yesuf MB, Alemayehu E (2020) Removal of color, COD and determination of power consumption from landfill leachate using an electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Sep Purif Technol 233:115935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115935
Aslanzadeh S, Rajendran K, Taherzadeh MJ (2014) A comparative study between single- and two-stage anaerobic digestion processes: effects of organic loading rate and hydraulic retention time. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 95:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.06.008
Atkins P, Paula JD (2006) Physical chemistry. W.H. Freeman and Company, New York
Bagastyo AY, Batstone DJ, Rabaey K, Radjenovic J (2013) Electrochemical oxidation of electrodialysed reverse osmosis concentrate on Ti/Pt–IrO2, Ti/SnO2–Sb and boron-doped diamond electrodes. Water Res 47:242–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.10.001
Bashir MJK, Isa MH, Kutty SRM, Awang ZB, Aziz HA, Mohajeri S, Farooqi IH (2009) Landfill leachate treatment by electrochemical oxidation. Waste Manag 29:2534–2541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2009.05.004
Bashir MJK, Aziz HA, Aziz SQ, Abu ASS (2013) An overview of electro-oxidation processes performance in stabilized landfill leachate treatment. Desalination Water Treat 51:2170–2184. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.734698
Berkessa YW, Mereta ST, Feyisa FF (2019) Simultaneous removal of nitrate and phosphate from wastewater using solid waste from factory. Appl Water Sci 9:28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0906-z
Bunce NJ, Bejan D (2011) Mechanism of electrochemical oxidation of ammonia. Electrochim Acta 56:8085–8093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.07.078
Cabeza A, Urtiaga A, Rivero MJ, Ortiz I (2007) Ammonium removal from landfill leachate by anodic oxidation. J Hazard Mater 144:715–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.106
Cañizares P, Díaz M, Domínguez JA, Lobato J, Rodrigo MA (2005) Electrochemical treatment of diluted cyanide aqueous wastes. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 80:565–573. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.1228
Chiang LC, Chang JE, Wen TC (1995) Indirect oxidation effect in electrochemical oxidation treatment of landfill leachate. Water Res 29:671–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)00146-X
Chu Y, Zhu M, Liu C (2015) Electrochemical treatment of biotreated landfill leachate using a porous carbon nanotube-containing cathode: performance, toxicity reduction, and biodegradability enhancement. Environ Eng Sci 32:445–450. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2014.0433
Del Moro G, Prieto-Rodríguez L, De Sanctis M, Di Iaconi C, Malato S, Mascolo G (2016) Landfill leachate treatment: comparison of standalone electrochemical degradation and combined with a novel biofilter. Chem Eng J 288:87–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.11.069
Deng Y, Feng C, Chen N, Hu W, Kuang P, Liu H, Hu Z, Li R (2018) Research on the treatment of biologically treated landfill leachate by joint electrochemical system. Waste Manag 82:177–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.10.028
de Oliveira MS, da Silva LF, Barbosa AD, Romualdo LL, Sadoyama G, Andrade LS (2019) Landfill leachate treatment by combining coagulation and advanced electrochemical oxidation techniques. ChemElectroChem 10:1002–1433. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201801677
Ding J, Wei L, Huang H, Zhao Q, Hou W, Kabutey FT, Yuan Y, Dionysiou DD (2018) Tertiary treatment of landfill leachate by an integrated electro-oxidation/electro-coagulation/electro-reduction process: performance and mechanism. J Hazard Mater 351:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.02.038
Engelke JL, Strain HH (1954) Electrical mobility of phosphate ions in paper electrochromatography. Anal Chem 26:1872–1874. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60096a004
Fernandes A, Catalão E, Ciríaco L, Pacheco MJ, Lopes A (2013) Electrochemical treatment of leachates from sanitary landfills. J Electrochem Sci Eng 3:125–135. https://doi.org/10.5599/jese.2013.0034
Fernandes A, Pacheco MJ, Ciríaco L, Lopes A (2015) Review on the electrochemical processes for the treatment of sanitary landfill leachates: present and future. Appl Catal B Environ 176–177:183–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.03.052
Freire DDC, Sant’Anna GL (1998) A proposed method modification for the determination of COD in saline waters. Environ Technol 19:1243–1247. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593331908616784
Huang C, Xu T, Zhang Y, Xue Y, Chen G (2007) Application of electrodialysis to the production of organic acids: state-of-the-art and recent developments. J Membr Sci 288:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2006.11.026
Ilhan F, Kabuk HA, Kurt U, Avsar Y, Sari H, Gonullu MT (2014) Evaluation of treatment and recovery of leachate by bipolar membrane electrodialysis process. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 75:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2013.11.005
Ilhan F, Yazici Guvenc S, Avsar Y, Kurt U, Gonullu MT (2016) Optimization of treatment leachates from young, middle-aged and elderly landfills with bipolar membrane electrodialysis. Environ Technol 38:2733–2742. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1276221
Kapałka A, Joss L, Anglada Á, Comninellis C, Udert KM (2010) Direct and mediated electrochemical oxidation of ammonia on boron-doped diamond electrode. Electrochem Commun 12:1714–1717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2010.10.004
Kasih KN, Siburian K (2018) Technology-based concept development and EKONID workshop in Indonesia 2018 –waste management in Tasikmalaya. German-Indonesian Chamber of Industry and Commerce (EKONID), on site study report. EKONID, BlackForest Solutions GmbH, pp 1-43
Kawai M, Purwanti IF, Nagao N, Hermana J, Toda T (2009) Chemical characteristics of leachate at the Benowo landfill in Surabaya Indonesia. Turning Waste Into Ideas: Proceedings ISWA/APESB World Congress, Lisbon, Portugal
Kawai M, Purwanti IF, Nagao N, Slamet A, Hermana J, Toda T (2012) Seasonal variation in chemical properties and degradability by anaerobic digestion of landfill leachate at Benowo in Surabaya, Indonesia. J Environ Manag 110:267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.06.022
Kim KW, Kim YJ, Kim IT, Park GI, Lee EH (2005) The electrolytic decomposition mechanism of ammonia to nitrogen at an IrO2 anode. Electrochim Acta 50:4356–4364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.01.046
Kim KW, Kim YJ, Kim IT, Park GI, Lee EH (2006) Electrochemical conversion characteristics of ammonia to nitrogen. Water Res 40:1431–1441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.01.042
Kjeldsen P, Barlaz MA, Rooker AP, Baun A, Ledin A, Christensen TH (2002) Present and long-term composition of msw landfill leachate: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 32:297–336. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380290813462
Kurniawan TA, Lo WH, Chan GYS (2006) Physico-chemical treatments for removal of recalcitrant contaminants from landfill leachate. J Hazard Mater 129:80–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.08.010
Kurniawan TA, Lo W (2009) Removal of refractory compounds from stabilized landfill leachate using an integrated H2O2 oxidation and granular activated carbon (GAC) adsorption treatment. Water Res 43:4079–4091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.060
Lee S, Hur J (2016) Heterogeneous adsorption behavior of landfill leachate on granular activated carbon revealed by fluorescence excitation emission matrix (EEM)-parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC). Chemosphere 149:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.01.081
Li M, Feng C, Zhang Z, Sugiura N (2009) Efficient electrochemical reduction of nitrate to nitrogen using Ti/IrO2–Pt anode and different cathodes. Electrochim Acta 54:4600–4606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.03.064
Li W, Zhou Q, Hua T (2010) Removal of organic matter from landfill leachate by advanced oxidation processes: a review. Int J Chem Eng 2010:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/270532
Lin SH, Chang CC (2000) Treatment of landfill leachate by combined electro-Fenton oxidation and sequencing batch reactor method. Water Res 34:4243–4249. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00185-8
Liu C, Wu T, Hsu P, Xie J, Zhao J, Liu K, Sun J, Xu J, Tang J, Ye Z, Lin D, Ciu Y (2019) Direct/alternating current electrochemical method for removing and recovering heavy metal from water using graphene oxide electrode. ACS Nano 13(6):6431–6437. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b09301
Liu Y, Kwag JH, Kim JH, Ra C (2011) Recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus by struvite crystallization from swine wastewater. Desalination 277(1–3):364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.04.056
Lopez A, Pagano M, Volpe A, Claudio Di Pinto A (2004) Fenton’s pre-treatment of mature landfill leachate. Chemosphere 54:1005–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.09.015
Mackay MW, Fitzgerald KA, Jackson D (1996) The solubility of calcium and phosphate in two specialty amino acid solutions. J Parenter Enter Nutr 20:63–66. https://doi.org/10.1177/014860719602000163
Martínez-Huitle CA, Brillas E (2009) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: a general review. Appl Catal B Environ 87:105–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.09.017
Mor S, Ravindra K, Dahiya RP, Chandra A (2006) Leachate characterization and assessment of groundwater pollution near municipal solid waste landfill site. Environ Monit Assess 118:435–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-1505-7
Mussa ZH, Othman MR, Abdullah MP (2015) Electrochemical oxidation of landfill leachate: investigation of operational parameters and kinetics using graphite-PVC composite electrode as anode. J Braz Chem Soc 26:939–948. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20150055
Niu A, Ren YW, Yang L, Xie SL, Jia PP, Zhang JH, Wang X, Li J, Pei DS (2016) Toxicological characterization of a novel wastewater treatment process using EDTA-Na2Zn as draw solution (DS) for the efficient treatment of MBR-treated landfill leachate. Chemosphere 155:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.045
Noerfitriyani E, Hartono DM, Moersidik SS, Gusniani I (2017) Leachate characterization and performance evaluation of leachate treatment plant in Cipayung landfill, Indonesia. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 106:012086. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/106/1/012086
Nurhayati E, Bagastyo AY, Hartatik DD, Direstiyani LC (2020) The enhancement of biodegradability index of mature landfill leachate by electrochemical oxidation process using boron-doped diamond and dimensionally stable anode. Res Chem Intermed 46:4811–4822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-020-04242-4
Oktiawan W, Priyambada IB, Ardhianto R (2020) Treatment of leachate using electrocoagulation technology; study case in Jatibarang landfill-Semarang city. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 448:012056. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/448/1/012056
Panizza M, Delucchi M, Sirés I (2010) Electrochemical process for the treatment of landfill leachate. J Appl Electrochem 40:1721–1727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-010-0109-7
Pérez G, Saiz J, Ibañez R, Urtiaga AM, Ortiz I (2012) Assessment of the formation of inorganic oxidation by-products during the electrocatalytic treatment of ammonium from landfill leachates. Water Res 46:2579–2590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.02.015
Qiang Z, Adams CD (2004) Determination of monochloramine formation rate constants with stopped-flow spectrophotometry. Environ Sci Technol 38:1435–1444. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0347484
Renou S, Givaudan JG, Poulain S, Dirassouyan F, Moulin P (2008) Landfill leachate treatment: review and opportunity. J Hazard Mater 150:468–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.077
Sawaittayothin V, Polprasert C (2007) Nitrogen mass balance and microbial analysis of constructed wetlands treating municipal landfill leachate. Bioresour Technol 98:565–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.02.002
Schoeman JJ (2008) Evaluation of electrodialysis for the treatment of a hazardous leachate. Desalination 224:178–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.02.090
Schoeman JJ, Steyn A, Makgae M (2005) Evaluation of electrodialysis for the treatment of an industrial solid waste leachate. Desalination 186:273–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.04.061
Tatsi AA, Zouboulis AI, Matis KA, Samaras P (2003) Coagulation–flocculation pretreatment of sanitary landfill leachates. Chemosphere 53:737–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00513-7
Turro E, Giannis A, Cossu R, Gidarakos E, Mantzavinos D, Katsaounis A (2011) Electrochemical oxidation of stabilized landfill leachate on DSA electrodes. J Hazard Mater 190:460–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.03.085
Vanlangendonck Y, Corbisier D, Van Lierde A (2005) Influence of operating conditions on the ammonia electro-oxidation rate in wastewaters from power plants (ELONITA™ technique). Water Res 39:3028–3034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.05.013
Vlyssides A, Karlis P, Loizidou M, Zorpas A, Arapoglou D (2001) Treatment of leachate from a domestic solid waste sanitary landfill by an electrolysis system. Environ Technol 22:1467–1476. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593332208618184
Wang G, Zhang L, Zhang J (2012) A review of electrode materials for electrochemical supercapacitors. Chem Soc Rev 41:797–828. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CS15060J
Wu L, Zhang L, Shi X, Liu T, Peng Y, Zhang J (2015) Analysis of the impact of reflux ratio on coupled partial nitrification–anammox for co-treatment of mature landfill leachate and domestic wastewater. Bioresour Technol 198:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.072
Xaypanya P, Takemura J, Chiemchaisri C, Seingheng H, Tanchuling M (2018) Characterization of landfill leachates and sediments in major cities of indochina peninsular countries—heavy metal partitioning in municipal solid waste leachate. Environments 5:65. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5060065
Yao J, Mei Y, Xia G, Lu Y, Xu D, Sun N, Wang J, Chen J (2019) Process optimization of electrochemical oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen for actual dyeing wastewater treatment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162931
Yu D, Cui J, Li X, Zhang H, Pei Y (2020) Electrochemical treatment of organic pollutants in landfill leachate using a three-dimensional electrode system. Chemosphere 243:125438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125438
Acknowledgments
The authors would also like to acknowledge Prof. I.G. Wenten for his support regarding the utilization of ion exchange membranes.
Funding
This study was funded by Kurita Water and Environment Foundation (KWEF) under the KARG Research Grant Scheme and the Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember (ITS) under Laboratory Research Grant Agreement No. 855/PKS/ITS/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study conceptualization, research methodology design, and funding acquisition were performed by Arseto Yekti Bagastyo. The experiment, material preparation, and data collection were performed by Putu Putri Indira Sari. All authors contributed to the data analysis and visualization. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Arseto Yekti Bagastyo, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagastyo, A.Y., Sari, P.P.I. & Direstiyani, L.C. Effect of chloride ions on the simultaneous electrodialysis and electrochemical oxidation of mature landfill leachate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 63646–63660 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11519-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11519-z