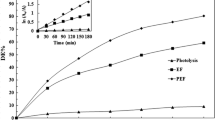
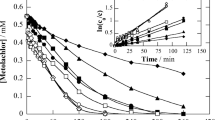
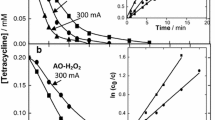
Abstract
One of the main challenges of electrochemical Fenton-based processes is the treatment of organic pollutants at near-neutral pH. As a potential approach to this problem, this work addresses the use of a low content of soluble chelated metal catalyst, formed between Fe(III) and ethylenediamine-N,N'-disuccinic (EDDS) acid (1:1), to degrade the herbicide triclopyr in 0.050 M Na2SO4 solutions at pH 7.0 by photoelectro-Fenton with UVA light or sunlight (PEF and SPEF, respectively). Comparison with electro-Fenton treatments revealed the crucial role of the photo-Fenton-like reaction, since this promoted the production of soluble Fe(II) that enhanced the pesticide removal. Hydroxyl radicals formed at the anode surface and in the bulk were the main oxidants. A boron-doped diamond (BDD) anode yielded a greater mineralization than an IrO2-based one, at the expense of reduced cost-effectiveness. The effect of catalyst concentration and current density on the performance of PEF with BDD was examined. The PEF trials in 0.25 mM Na2SO4 + 0.35 mM NaCl medium showed a large influence of generated active chlorine as oxidant, being IrO2 more suitable than RuO2 and BDD. In SPEF with BDD, the higher light intensity from solar photons accelerated the removal of the catalyst and triclopyr, with small effect on mineralization. A plausible route for the herbicide degradation by Fe(III)–EDDS-catalyzed PEF and SPEF is finally proposed based on detected byproducts: three heteroaromatic and four linear N-aliphatic compounds, formamide, and tartronic and oxamic acids.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
APHA, AWWA, WEF (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. Method Number 4500-Cl Chlorine (residual)–G. DPD Colorimetric Method. American Public Health Association, Washington D.C., pp 4–67 and 4–68
Battaglin WA, Rice KC, Focazio MJ, Salmons S, Barry RX (2009) The occurrence of glyphosate, atrazine, and other pesticides in vernal pools and adjacent streams in Washington, DC, Maryland, Iowa, and Wyoming, 2005-2006. Environ Monit Assess 155:281–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0435-y
Brillas E (2014) A review on the degradation of organic pollutants in waters by UV photoelectro-Fenton and solar photoelectro-Fenton. J Braz Chem Soc 25:393–417. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20130257
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review. Appl Catal B Environ 166–167:603–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.11.016
Clarizia L, Russo D, Di Somma I, Marotta R, Andreozzi R (2017) Homogeneous photo-Fenton processes at near neutral pH: a review. Appl Catal B Environ 209:358–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.03.011
Clematis D, Cerisola G, Panizza M (2017) Electrochemical oxidation of a synthetic dye using a BDD anode with a solid polymer electrolyte. Electrochem Commun 75:21–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2016.12.008
Edginton AN, Stephenson GR, Sheridan PM, Thompson DG, Boermans HJ (2003) Effect of pH and release on two life stages of four anuran amphibians. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2673–2678. https://doi.org/10.1897/02-484
El-Ghenymy A, Rodríguez RM, Brillas E, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2014) Electro-Fenton degradation of the antibiotic sulfanilamide with Pt/carbon-felt and BDD/carbon-felt cells. Kinetics, reaction intermediates, and toxicity assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8368–8378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2773-3
El-Ghenymy A, Centellas F, Rodríguez RM, Cabot PL, Garrido JA, Sirés I, Brillas E (2015) Comparative use of anodic oxidation, electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton with Pt or boron-doped diamond anode to decolorize and mineralize Malachite Green oxalate dye. Electrochim Acta 182:247–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.09.078
Galia A, Lanzalaco S, Sabatino MA, Dispenza C, Scialdone O, Sirés I (2016) Crosslinking of poly(vinylpyrrolidone) activated by electrogenerated hydroxyl radicals: a first step towards a simple and cheap synthetic route of nanogel vectors. Electrochem Commun 62:64–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2015.12.005
Ganiyu SO, Zhou M, Martínez-Huitle CA (2018) Heterogeneous electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton processes: a critical review of fundamental principles and application for water/wastewater treatment. Appl Catal B Environ 235:103–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.04.044
Ganzenko O, Oturan N, Sirés I, Huguenot D, van Hullebusch ED, Esposito G, Oturan MA (2018) Fast and complete removal of the 5-fluorouracil drug from water by electro-Fenton oxidation. Environ Chem Lett 16:281–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0659-6
Jaber S, Leremboure M, Thery V, Delort A-M, Mailhot G (2020) Mechanism of photochemical degradation of Fe(III)-EDDS complex. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 399:112646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112646
Janíková-Bandžuchová L, Šelešovská R, Schwarzová-Pecková K, Chýlková J (2015) Sensitive voltammetric method for rapid determination of pyridine herbicide triclopyr on bare boron-doped diamond electrode. Electrochim Acta 154:421–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.12.064
Lanzalaco S, Sirés I, Sabatino MA, Dispenza C, Scialdone O, Galia A (2017) Synthesis of polymer nanogels by electro-Fenton process: investigation of the effect of main operation parameters. Electrochim Acta 246:812–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.06.097
Lanzalaco S, Sirés I, Galia A, Sabatino MA, Dispenza C, Scialdone O (2018) Facile crosslinking of poly(vinylpyrrolidone) by electro-oxidation with IrO2-based anode under potentiostatic conditions. J Appl Electrochem 48:1343–1352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1237-8
Lei W, Tang X, Zhou X (2018) Transport of 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol (a main pesticide degradation product) in purple soil: experimental and modeling. Appl Geochem 88:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.07.010
Li W, Mao J, Dai X, Zhao X, Qiao C, Zhang X, Pu E (2018) Residue determination of triclopyr and aminopyralid in pastures and soil by gas chromatography-electron capture detector: dissipation pattern under open field conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 155:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.035
Maddila S, Rana S, Pagadala R, Maddila SN, Vasam C, Jonnalagadda SB (2015) Ozone-driven photocatalyzed degradation and mineralization of pesticide triclopyr by Au/TiO2. J Environ Sci Health B 50:571–583. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2015.1028835
Martínez-Huitle CA, Panizza M (2018) Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for wastewater treatment. Curr Opin Electrochem 11:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2018.07.010
Martínez-Huitle CA, Rodrigo MA, Sirés I, Scialdone O (2015) Single and coupled electrochemical processes and reactors for the abatement of organic water pollutants: a critical review. Chem Rev 115:13362–13407. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00361
Miralles-Cuevas S, Oller I, Ruíz-Delgado A, Cabrera-Reina A, Cornejo-Ponce L, Malato S (2019) EDDS as complexing agent for enhancing solar advanced oxidation processes in natural water: effect of iron species and different oxidants. J Hazard Mater 372:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.03.018
Moreira FC, Boaventura RAR, Brillas E, Vilar VJP (2015) Degradation of trimethoprim antibiotic by UVA photoelectro-Fenton process mediated by Fe(III)–carboxylate complexes. Appl Catal B Environ 162:34–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.06.008
Pérez T, Sirés I, Brillas E, Nava JL (2017) Solar photoelectro-Fenton flow plant modeling for the degradation of the antibiotic erythromycin in sulfate medium. Electrochim Acta 228:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.01.047
Pérez-Lucas G, Aliste M, Vela N, Garrido I, Fenoll J, Navarro S (2020) Decline of fluroxypyr and triclopyr residues from pure, drinking and leaching water by photo-assisted peroxonation. Process Saf Environ Prot 137:358–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.02.039
Qamar M, Muneer M, Bahnemann D (2006) Heterogeneous photocatalysed degradation of two selected pesticide derivatives, triclopyr and aminozid in aqueous suspensions of titanium dioxide. J Environ Manag 80:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.09.002
Ridruejo C, Centellas F, Cabot PL, Sirés I, Brillas E (2018) Electrochemical Fenton-based treatment of tetracaine in synthetic and urban wastewater using active and non-active anodes. Water Res 128:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.10.048
Rippy MA, Deletic A, Black J, Aryal R, Lampard JL, Tang JYM, McCarthy D, Kolotelo P, Sidhu J, Gernjak W (2017) Pesticide occurrence and spatio-temporal variability in urban run-off across Australia. Water Res 115:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.03.010
Roth H, Gendel Y, Buzatu P, David O, Wessling M (2016) Tubular carbon nanotube-based gas diffusion electrode removes persistent organic pollutants by a cyclic adsorption – electro-Fenton process. J Hazard Mater 307:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.12.066
Senseman SA (2007) Herbicide Handbook, 9th edn. Weed Society of America, Champaign
Solís RR, Rivas FJ, Gimeno O, Pérez-Bote JL (2016) Photocatalytic ozonation of clopyralid, picloram and triclopyr. Kinetics, toxicity and influence of operational parameters. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4542
Steter JR, Brillas E, Sirés I (2016) On the selection of the anode material for the electrochemical removal of methylparaben from different aqueous media. Electrochim Acta 222:1464–1474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.11.125
Thiam A, Sirés I, Brillas E (2015) Treatment of a mixture of food color additives (E122, E124 and E129) in different water matrices by UVA and solar photoelectro-Fenton. Water Res 81:178–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.05.057
Vasudevan S, Oturan MA (2014) Electrochemistry as cause and cure in water pollution. An overview. Environ Chem Lett 12:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0434-2
Woodburn KB, Batzer FR, White FH, Schultz MR (1993) The aqueous photolysis of triclopyr. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620120107
Yadav S, Kumar N, Kumari V, Mittal A, Sharma S (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of triclopyr, a persistent pesticide by ZnO/SnO2 nano-composites. Mater Today: Proc 19:642–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.07.746
Yahya MS, Oturan N, El Kacemi K, El Karbane M, Aravindakumar CT, Oturan MA (2014) Oxidative degradation study on antimicrobial agent ciprofloxacin by electro-Fenton process: kinetics and oxidation products. Chemosphere 117:447–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.08.016
Yang W, Zhou M, Oturan N, Li Y, Oturan MA (2019) Electrocatalytic destruction of pharmaceutical imatinib by electro-Fenton process with graphene-based cathode. Electrochim Acta 305:285–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.03.067
Ye Z, Brillas E, Centellas F, Cabot PL, Sirés I (2019a) Electro-Fenton process at mild pH using Fe(III)–EDDS as soluble catalyst and carbon felt as cathode. Appl Catal B Environ 257:117907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117907
Ye Z, Guelfi DRV, Álvarez G, Alcaide F, Brillas E, Sirés I (2019b) Enhanced electrocatalytic production of H2O2 at Co-based air-diffusion cathodes for the photoelectro-Fenton treatment of bronopol. Appl Catal B Environ 247:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.01.029
Ye Z, Sirés I, Zhang H, Huang Y-H (2019c) Mineralization of pentachlorophenol by ferrioxalate-assisted solar photo-Fenton process at mild pH. Chemosphere 217:475–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.221
Ye Z, Brillas E, Centellas F, Cabot PL, Sirés I (2020a) Expanding the application of photoelectro-Fenton treatment to urban wastewater using the Fe(III)–EDDS complex. Water Res 169:115219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115219
Ye Z, Padilla JA, Xuriguera E, Beltran JL, Alcaide F, Brillas E, Sirés I (2020b) A highly stable metal−organic framework-engineered FeS2/C nanocatalyst for heterogeneous electro-Fenton treatment: validation in wastewater at mild pH. Environ Sci Technol 54:4664–4674. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b07604
Zhang Y, Klamerth N, Ashagre Messele S, Chelme-Ayala P, Gamal El-Din M (2016) Kinetics study on the degradation of a model naphthenic acid by ethylenediamine-N,N’-disuccinic acid-modified Fenton process. J Hazard Mater 318:371–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.06.063
Funding
The authors thank the financial support from projects CTQ2016-78616-R (AEI/FEDER, EU), PID2019-109291RB-I00 (AEI, Spain), CNPq – 439344/2018-2 (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, Brazil), and FAPESP project 2014/50945-4 (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Brazil), as well as the PhD scholarships awarded to I.C. Da Costa Soares (CNPq 200009/2018-4, Brazil), Z. Ye (State Scholarship Fund, CSC, China), and R. Oriol (MINECO, Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Z.H. Ye and I. Sirés. Formal analysis and investigation: I.C. Da Costa Soares, Z.H. Ye, and R. Oriol. Funding acquisition: I. Sirés, P.L. Cabot, and C.A. Martínez-Huitle. Methodology: Z.H. Ye and I. Sirés. Resources: I. Sirés and E. Brillas. Supervision: I. Sirés and C.A. Martínez-Huitle. Writing—original draft preparation: I. Sirés and E. Brillas. Writing review and editing: all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Da Costa Soares, I.C., Oriol, R., Ye, Z. et al. Photoelectro-Fenton treatment of pesticide triclopyr at neutral pH using Fe(III)–EDDS under UVA light or sunlight. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 23833–23848 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11421-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11421-8