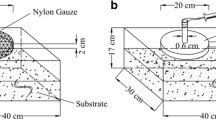
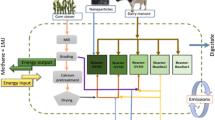
Abstract
Global environmental performances of anaerobic co-digestion and co-composting of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) contaminated corn were investigated by a life cycle assessment approach. Anaerobic co-digestion of pig slurry and corn with 25 μgkg-1 ww AFB1 concentration resulted able to generate 627 NLkgVS-1 of biogas with a reduction of the AFB1 concentration in the digestate of 44%. At AFB1 concentration of 100 μg kg-1 ww, the process resulted strongly inhibited with a biogas generation of 122 NLkgVS-1 and AFB1 concentration reduction in the digestate of 25%. Co-composting of 100 μg kg-1 dw AFB1 contaminated corn with other substrates as organic fraction of municipal waste, pig slurry, and other lignin-cellulosic residues showed a removal efficiency of AFB1 ranging from about 80 up to 95% depending on the different mixtures adopted. Environmental consequences associated to the removal of 1 mg of AFB1 in different scenarios investigated, including also the use on land of the digestate and of the compost, indicated that global warming was affected equally by co-digestion and co-composting, about 95 kgCO2eq. Co-digestion showed also the possibility of achieving avoided emissions of about − 0.007 kgNMVOCeq, − 2.5E-3 kgPeq, and − 30CTUe. Benefits concerning resource depletion resulted higher for co-composting due to the high amount of mineral fertilizer replaced. Contribution of AFB1 in the determination of human health (DALY) resulted lower than about 4% for co-digestion and practically negligible for co-composting.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adebayo AO, Jekayinfa SO, Linke B (2014) Effect of co-digestion on anaerobic digestion of pig slurry with maize cob at mesophilic temperature. J Nat Sci Res 4(22):66–73
Akoto EY, Klu YAK, Lamptey M, Asibuo JY, Davis J, Phillips R, Chen J (2017) Use of peanut meal as a model matrix to study the effect of composting on aflatoxin decontamination. World Mycotoxin J 10(2):131–141
ANPA (2001) Metodi di analisi del compost. ANPA Handbook Manuali e linee guida 2001/3, Roma, Italy
APHA, American Public Health Association, Water Environment Federation (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Washington, DC, USA
Bernstad A, la Cour Jansen J (2011) A life cycle approach to the management of household food waste – a Swedish full-scale case study. Waste Manag 31:1879–1896
Blengini GA (2008) Using LCA to evaluate impacts and resources conservation potential of composting: a case study of the Asti District in Italy. Resour Conserv Recycl 52:1373–1381
Børgesen CD, Djurhuus J, Kyllingsbaek A (2001) Estimating the effect of legislation on nitrogen leaching by up scaling field simulation. Ecol Model 136:31–48
Brogaard LK, Christensen TH (2016) Life cycle assessment of capital goods in waste management systems. Waste Manag 56:561–574
Cucina M, Tacconi C, Sordi S, Pezzolla D, Gigliotti G, Zadra C (2018) Valorization of a pharmaceutical organic sludge through different composting treatments. Waste Manag 74:203–212
Di Maria F, Micale C (2015) Life cycle analysis of incineration compared to anaerobic digestion followed by composting for managing organic waste: the influence of system components for an Italian district. Int J Life Cycle Assess 20:377e88
Di Maria F, Sisani F (2019) A sustainability assessment for use on land or wastewater treatment of the digestate from bio-waste. Waste Manag 87:741–750
Di Maria F, Sordi A, Cirulli G, Gigliotti G, Massaccesi L, Cucina M (2014) Cotreatment of fruit and vegetable waste in sludge digesters. An analysis of the relationship among bio-methane generation, process stability and digestate phytotoxicity. Waste Manag 34(9):1603–1608
Di Maria F, Micale C, Contini S, Morettini E (2016a) Impact of biological treatments of bio-waste for nutrients, energy and bio-methane recovery in a life cycle perspective. Waste Manag 52:86–95
Di Maria F, Segoloni E, Pezzolla D (2016b) Solid anaerobic digestion batch of bio-waste as pre-treatment for improving amendment quality: The effect of inoculum recirculation. Waste Manag 56:106–112
Di Maria F, Sisani F, Lasagni M, Borges MS, Gonzales TH (2018) Replacement of energy crops with bio-waste in an existing anaerobic digestion plant: an energetic and environmental analysis. Energy 152:202–213
EC (2010) European Commission – Joint Research Centre – Institute for Environment and Sustainability. 2010. International Reference Life Cycle Data System (ILCD) Handbook – general guide for life cycle assessment – detailed guidance. First edition EUR 24708 EN March 2010 Publications Office of the European Union Luxembourg, LU
EC (2012) European commission - joint research centre - institute for environment and sustainability: European reference life cycle database (ELCD). Available at: Version 3.2. https://eplca.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ELCD3/datasetDownload.xhtml. Accessed 29 October 2019
Ferrer I, Vazquez F, Font X (2010) Long term operation of a thermophilic anaerobic reactor: process stability and efficiency at decreasing sludge retention time. Bioresour Technol 101:297–280
Goedkoop M, Oele M, Leijting J, Ponsioen T, Meijer E (2016) Introduction to LCA with SimaPro. Report version 5.2. Available at: https://www.presustainability.com/download/SimaPro8IntroductionToLCA.pdf. Accessed 21 10 2019
Guendouz J, Buffiere P, Cacho J, Carrere M, Delgenes JP (2010) Dry anaerobic digestion in batch mode: design and operation of a laboratory-scale, completely mixed reactor. Waste Manag 30:1768–1771
Hansen S, Abrahamsen P, Petersen CT, Styczen M (2012) Daisy: model use, calibration, and validation. T Am Soc Agr Biol Eng 55(4):1315–1333
Humbert S, Rossi V, Margni M, Jolliet O, Loerincik Y (2009) Life cycle assessment of two baby food packaging alternatives: glass jars vs. plastic pots. Int J Life Cycle Assess 14:95–106
IARC (2018) IARC Monographs – 100F. Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/mono100F-23.pdf. Accessed 18.04.2020
ISO 14040 (2006) Environmental Management: Life Cycle Assessment. Principles and Guidelines. International Organization of Standardization, Geneva, p 2006
ISO 14044 (2018) Environmental management: life cycle assessment –requirements and guidelines. International Organization of Standardization, Geneva, p 2018
Jackson LW III, Pryor BM (2017) Degradation of aflatoxin B1 from naturally contaminated maize using the edible fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. AMB Express 7:110
Jolliet O, Pennington D, Amman C, Pelichet T, Margni M, Crettaz P (2005) Comparative assessment of the toxic impact of metals on humans within IMPACT 2002. In: Dubreuil A (ed) Life-cycle assessment of metals: issues and research directions. Society of Environmental Toxicology & Chemist
Klinglmair M, Lemming C, Jensen LS, Rechberger H, Astrup TF, Scheutz C (2015) Phosphorus in Denmark: National and regional anthropogenic flows. Resour Conserv Recycl 105:31–324
Marcato CE, Mohtar R, Revel JC, Pouech P, Hafidi M, Guiressem M (2009) Impact of anaerobic digestion on organic matter quality in pig slurry. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63:260–266
Massaccesi L, Sordi A, Micale C, Cucina M, Zadra C, Di Maria F, Gigliotti G (2013) Chemical characterization of percolate and digestate during the hybrid solid anaerobic digestion batch process. Process Biochem 48:1361–1367
Murthy GS, Townsend DE, Meerdink GL, Bargren GL, Tumbleson ME, Singh V (2005) Effect of Aflatoxin B1 on Dry-Grind Ethanol Process. Cereal Chem 82:302–304
Pezzolla D, Di Maria F, Zadra C, Massaccesi L, Sordi A, Gigliotti G (2017) Optimization of solid-state anaerobic digestion through the percolate recirculation. Biomass Bioenergy 96:112–118
Qian X, Shen G, Wang Z, Guo C, Liu Y, Lei Z, Zhang Z (2014) Co-composting of livestock manure with rice straw: characterization and establishment of maturity evaluation system. Waste Manag 34(2):530–535
Rehl T, Muller J (2011) Life cycle assessment of biogas digestate processing technologies. Resour Conserv Recycl 56:92–104
Ruiz D, San Miguel G, Corona B, Gaitero A, Domínguez A (2018) Environmental and economic analysis of power generation in a thermophilic biogas plant. Sci Total Environ 633:1418–1428
Salati S, D’Imporzano G, Panseri S, Pasquale E, Adani F (2014) Degradation of aflatoxin B1 during anaerobic digestion and its effect on process stability. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 94:19–23
Salehiyoun AR, Di Maria F, Sharifi M, Norouzi O, Zilouei H, Aghbashlo M (2020) Anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and slaughterhouse waste in existing wastewater digesters. Renew Energy 145:2503–2509
Scano EA, Asquer C, Pistis A, Ortu L, Demontis V, Cocco D (2014) Biogas from anaerobic digestion of fruit and vegetable waste: experimental results on pilot scale preliminary performance evaluation of full-scale power plant. Energy Convers Manag 77:22–30
Tacconi C, Cucina M, Pezzolla D, Zadra C, Gigliotti G (2018) Effect of the mycotoxin aflatoxin B1 on a semi-continuous anaerobic digestion process. Waste Manag 78:467–473
Tacconi C, Cucina M, Zadra C, Gigliotti G, Pezzolla D (2019) Plant nutrients recovery from aflatoxin B1 contaminated corn through co-composting. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103046
Thibodeau C, Frederic M, Glaus M (2014) Comparison of development scenarios of black water source-separation sanitation systems using life cycle assessment and environmental life cycle costing. Resour Conserv Recycl 92:38–54
Vazquez-Rowe I, Golkowska K, Lebuf V, Vaneeckhaute C, Michelis E, Meers E, Benetto E, Koster D (2015) Environmental assessment of digestate treatment technologies using LCA methodology. Waste Manag 43:442–459
Wan C, Zhou Q, Fu G, Li Y (2011) Semi-continuous anaerobic co-digestion of thickened waste activated sludge and fat, oil and grease. Waste Manag 31:1752–1758
Wang M, Zhou J, Yuan YX, Dai YM, Li D, Li ZD, Liu XF, Zhang XY, Yan ZY (2017) Methane production characteristics and microbial community dynamics of mono-digestion and co-digestion using corn stalk and pig manure. Bioresour Technol 42:4896,4901
Wernet G, Bauer C, Steubing B, Reinhard J, Moreno-Ruiz E, Weidema B (2016) The Ecoinvent database version 3 (part I): overview and methodology. Int J Life Cycle Assess 21:1218–1230
Xu C, Chen W, Hong J (2014) Life-cycle environmental and economic assessment of sewage sludge treatment in China. J Clean Prod 67:79–87
Yoshida H, Nielsen MP, Scheutz C, Jensen LS, Bruun S, Christensen TH (2016) Deriving long-term nitrogen emission factors from land application of treated organic waste. Environ Model Assess 21:111–124
Zhou S, Zhang J, Zou G, Riya S, Hosomi M (2015) Mass and energy balances of dry thermophilic anaerobic digestion treating swine manure mixed with rice straw. Biotechnol Res Int:895015, 11 pages. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/895015
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.D.M. initiated and designed the study and drafted the manuscripts. F.S. performed the numerical simulations. G.G. designed the experimental runs. D.P. elaborated the data from experimental runs. C.T. executed the experimental runs. M.C. performed the chemical analysis on the organic substrates. C.Z. performed the chemical analysis on gaseous substrates.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent to publish
Not applicable
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Loubet
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Maria, F., Sisani, F., Gigliotti, G. et al. Environmental consequences of the treatment of corn contaminated by aflatoxin B1 with co-digestion and co-composting in a life cycle perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 9267–9275 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11372-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11372-0