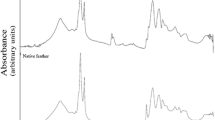
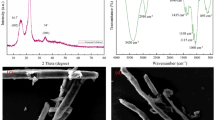
Abstract
Keratin/cellulose cryogels were successfully fabricated using chicken feathers (CF) and cardboard (C) from environmental waste for the first time, to be exploited in oil/solvent absorption. The keratin/cellulose-based composites were obtained by combining the dissolution of CF and C waste in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (Bmim−Cl+) ionic liquid green solvent via regeneration, simply by the freeze-drying method. The characterization analysis of the synthesized keratin/cellulose-based composites was performed using Fourier transform infrared spectrometry, X-ray diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy, and thermogravimetry. The as-prepared cryogel can absorb various oils and organic solvents. Moreover, its sorption capacity can reach up to 6.9–17.7 times the weight of the initial cryogel. This kind of CF/C cryogel revealed good and fast absorption efficiency. It could also be reused by simple absorption/distillation and absorption/desorption methods. Through the kinetic analysis, it was found that the pseudo-second-order model was more appropriate for the keratin/cellulose cryogel oil absorption process. Besides, owing to its low cost, good absorption capacity, and excellent reusability, this cryogel has potential for spill cleanup of oils and organic solvents.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Azmi NA, Idris A, Yusof NSM (2018) Ultrasonic technology for value added products from feather keratin. Ultrason Sonochem 47:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.04.016
Bagoole O, Rahman MM, Shah S et al (2018) Functionalized three-dimensional graphene sponges for highly efficient crude and diesel oil adsorption. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:23091–23105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2248-z
Ben Arfi R, Karoui S, Mougin K, Ghorbal A (2017) Adsorptive removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution by utilizing almond shell as bioadsorbent. Euro-Mediterranean J Environ Integr 2:20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-017-0032-y
Ben Arfi R, Karoui S, Mougin K, Ghorbal A (2019) Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-treated Phragmites australis powder as novel polymeric adsorbent for hazardous Eriochrome Black T removal from aqueous solutions. Polym Bull 76:5077–5102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2648-8
Cheng H, Gu B, Pennefather MP, Nguyen TX, Phan-Thien N, Duong HM (2017) Cotton aerogels and cotton-cellulose aerogels from environmental waste for oil spillage cleanup. Mater Des 130:452–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.05.082
Członka S, Sienkiewicz N, Strąkowska A, Strzelec K (2018) Keratin feathers as a filler for rigid polyurethane foams on the basis of soybean oil polyol. Polym Test 72:32–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2018.09.032
Danial WH, Abdul Majid Z, Mohd Muhid MN, Triwahyono S, Bakar MB, Ramli Z (2015) The reuse of wastepaper for the extraction of cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr Polym 118:165–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.10.072
De Silva R, Wang X, Byrne N (2016) Development of a novel cellulose/duck feather composite fibre regenerated in ionic liquid. Carbohydr Polym 153:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.090
Demirel Bayık G, Altın A (2017) Production of sorbent from paper industry solid waste for oil spill cleanup. Mar Pollut Bull 125:341–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.09.040
Fan P, Yuan Y, Ren J, Yuan B, He Q, Xia G, Chen F, Song R (2017) Facile and green fabrication of cellulosed based aerogels for lampblack filtration from waste newspaper. Carbohydr Polym 162:108–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.01.015
Feng J, Nguyen ST, Fan Z, Duong HM (2015) Advanced fabrication and oil absorption properties of super-hydrophobic recycled cellulose aerogels. Chem Eng J 270:168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.02.034
Flores-Hernández CG, Colin-Cruz A, Velasco-Santos C, Castaño VM, Almendarez-Camarillo A, Olivas-Armendariz I, Martínez-Hernández AL (2018) Chitosan–starch–keratin composites: improving thermo-mechanical and degradation properties through chemical modification. J Polym Environ 26:2182–2191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-1115-1
Ghosh A, Clerens S, Deb-Choudhury S, Dyer JM (2014) Thermal effects of ionic liquid dissolution on the structures and properties of regenerated wool keratin. Polym Degrad Stab 108:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.06.007
Hameed N, Guo Q (2009) Natural wool/cellulose acetate blends regenerated from the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Carbohydr Polym 78:999–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.07.033
Hameed N, Guo Q (2010) Blend films of natural wool and cellulose prepared from an ionic liquid. Cellulose 17:803–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9411-0
Han S, Sun Q, Zheng H, Li J, Jin C (2016) Green and facile fabrication of carbon aerogels from cellulose-based waste newspaper for solving organic pollution. Carbohydr Polym 136:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.024
Holkar CR, Jadhav AJ, Bhavsar PS, Kannan S, Pinjari DV, Pandit AB (2016) Acoustic cavitation assisted alkaline hydrolysis of wool based keratins to produce organic amendment fertilizers. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:2789–2796. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00298
Idris A, Vijayaraghavan R, Rana UA, Fredericks D, Patti AF, MacFarlane DR (2013) Dissolution of feather keratin in ionic liquids. Green Chem 15:525. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2gc36556a
Idris A, Vijayaraghavan R, Patti AF, Macfarlane DR (2014) Distillable protic ionic liquids for keratin dissolution and recovery. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:1888–1894. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc500229a
Ifelebuegu AO, Johnson A (2017) Nonconventional low-cost cellulose- and keratin-based biopolymeric sorbents for oil/water separation and spill cleanup: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 47:964–1001. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2017.1318620
Ifelebuegu AO, Anh Nguyen TV, Ukotije-Ikwut P, Momoh Z (2015) Liquid-phase sorption characteristics of human hair as a natural oil spill sorbent. J Environ Chem Eng 3:938–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.02.015
Jin C, Han S, Li J, Sun Q (2015) Fabrication of cellulose-based aerogels from waste newspaper without any pretreatment and their use for absorbents. Carbohydr Polym 123:150–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.01.056
Li B, Xu W, Kronlund D, Määttänen A, Liu J, Smått JH, Peltonen J, Willför S, Mu X, Xu C (2015) Cellulose nanocrystals prepared via formic acid hydrolysis followed by TEMPO-mediated oxidation. Carbohydr Polym 133:605–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.07.033
Liu R-L, Li X, Liu H et al (2016) Eco-friendly fabrication of sponge-like magnetically carbonaceous fiber aerogel for high-efficiency oil–water separation. RSC Adv 6:30301–30310. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA02794F
Ma B, Qiao X, Hou X, Yang Y (2016) Pure keratin membrane and fibers from chicken feather. Int J Biol Macromol 89:614–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.04.039
Ma B, Sun Q, Yang J, Wizi J, Hou X, Yang Y (2017) Degradation and regeneration of feather keratin in NMMO solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:17711–17718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9410-x
Maaloul N, Oulego P, Rendueles M, Ghorbal A, Díaz M (2019) Synthesis and characterization of eco-friendly cellulose beads for copper (II) removal from aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:23447–23463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3812-2
Nguyen ST, Feng J, Le NT et al (2013) Cellulose aerogel from paper waste for crude oil spill cleaning. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:18386–18391. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4032567
Oh SY, Yoo DI, Shin Y, Seo G (2005) FTIR analysis of cellulose treated with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide. Carbohydr Res 340:417–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2004.11.027
Paulauskiene T (2018) Ecologically friendly ways to clean up oil spills in harbor water areas: crude oil and diesel sorption behavior of natural sorbents. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:9981–9991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1316-8
Ramakrishnan N, Sharma S, Gupta A, Alashwal BY (2018) Keratin based bioplastic film from chicken feathers and its characterization. Int J Biol Macromol 111:352–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.037
Riaz MA, Hadi P, Abidi IH, Tyagi A, Ou X, Luo Z (2017) Recyclable 3D graphene aerogel with bimodal pore structure for ultrafast and selective oil sorption from water. RSC Adv 7:29722–29731. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra02886e
Sabir S (2015) Approach of cost-effective adsorbents for oil removal from oily water. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 45:1916–1945. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2014.1001143
Sadeghi S, Dadashian F, Eslahi N (2019) Recycling chicken feathers to produce adsorbent porous keratin-based sponge. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:1119–1128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1669-z
Shang W, Sheng Z, Shen Y, Ai B, Zheng L, Yang J, Xu Z (2016) Study on oil absorbency of succinic anhydride modified banana cellulose in ionic liquid. Carbohydr Polym 141:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.01.009
Song K, Xu H, Xu L, Xie K, Yang Y (2017) Cellulose nanocrystal-reinforced keratin bioadsorbent for effective removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 232:254–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.01.070
Su C, Yang H, Zhao H, Liu Y, Chen R (2017) Recyclable and biodegradable superhydrophobic and superoleophilic chitosan sponge for the effective removal of oily pollutants from water. Chem Eng J 330:423–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.157
Sun P, Liu ZT, Liu ZW (2009) Particles from bird feather: a novel application of an ionic liquid and waste resource. J Hazard Mater 170:786–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.034
Thai QB, Nguyen ST, Ho DK, Tran TD, Huynh DM, Do NHN, Luu TP, le PK, le DK, Phan-Thien N, Duong HM (2020) Cellulose-based aerogels from sugarcane bagasse for oil spill-cleaning and heat insulation applications. Carbohydr Polym 228:115365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115365
Tran CD, Mututuvari TM (2015) Cellulose, chitosan, and keratin composite materials. Controlled drug release. Langmuir 31:1516–1526. https://doi.org/10.1021/la5034367
Tran CD, Mututuvari TM (2016) Cellulose, chitosan and keratin composite materials: facile and recyclable synthesis, conformation and properties. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:1850–1861. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00084
Tran CD, Prosenc F, Franko M (2018) Facile synthesis, structure, biocompatibility and antimicrobial property of gold nanoparticle composites from cellulose and keratin. J Colloid Interface Sci 510:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.09.006
Wang YX, Cao XJ (2012) Extracting keratin from chicken feathers by using a hydrophobic ionic liquid. Process Biochem 47:896–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.02.013
Wang M, Zhao T, Wang G, Zhou J (2014) Blend films of human hair and cellulose prepared from an ionic liquid. Text Res J 84:1315–1324. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517514521123
Wang X, Xu S, Tan Y et al (2019) Remodeling of raw cotton fiber into flexible, squeezing-resistant macroporous cellulose aerogel with high oil retention capability for oil/water separation. Carbohydr Polym 5:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.03.097
Wattie B, Dumont M-J, Lefsrud M (2018a) Synthesis and properties modified feather keratin-based motor oil sorbing cryogels with high oil holding capacity. J Polym Environ 26:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0919-8
Wattie B, Dumont M-J, Lefsrud M (2018b) Synthesis and properties of feather keratin-based superabsorbent hydrogels. Waste Biomass Valoriz 9:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9773-0
Xia G, Wan J, Zhang J, Zhang X, Xu L, Wu J, He J, Zhang J (2016) Cellulose-based films prepared directly from waste newspapers via an ionic liquid. Carbohydr Polym 151:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.05.080
Zhou L-T, Yang G, Yang X-X, Cao ZJ, Zhou MH (2014) Preparation of regenerated keratin sponge from waste feathers by a simple method and its potential use for oil adsorption. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:5730–5736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2513-8
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Madame Rim Najjar for her help in editing, correcting, and proofreading the English of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research and the University of Gabes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.G. performed all the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. R.B.A. supervised the entire work and reviewed the paper. K.M. supervised the entire work and reviewed the paper. C.V. contributed in the Brunauer, Emmett, and Teller (BET) surface area measurements and analysis. L.M. contributed in the X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements. L.J. contributed in the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis. G.S. contributed in the TGA/DTG analysis. A.G. supervised the entire work and reviewed the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guiza, K., Ben Arfi, R., Mougin, K. et al. Development of novel and ecological keratin/cellulose-based composites for absorption of oils and organic solvents. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 46655–46668 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11260-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11260-7