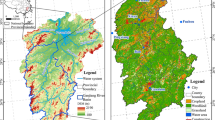
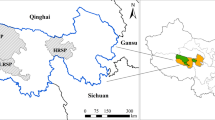
Abstract
Water shortage is one of the main hinder drivers of sustainable development in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, and ecological restoration is one of the main means to effectively curb ecological degradation. Addressing ecological degradation in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region has been a major concern of the Chinese government, and this has led to a focus on intensified ecological restoration efforts in this area. However, the effect of these restoration actions is not clear. To understand how ecological restoration is impacting ecological quality in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, we used geographical information system technology, such as the vegetation index-biomass method and cumulative net primary production (NPP) method, to assess the change in ecosystem quality. We carried out the pixel binary model and Pearson’s correlation coefficient analyses to understand the driving forces behind the change. Results showed that from 2000 to 2010, the quality of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei ecosystem has been improving, that natural vegetation is slowly re-establishing, and that there has been a slow increase toward climax communities. The change in ecosystem quality is positively correlated with the Sanbei shelterbelt and Beijing–Tianjin Sandstorm control project and negatively correlated with socioeconomic and agricultural factors.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Álvarez X, Valero E, Santos RMB, Varandas SGP, Sanches Fernandes LF, Pacheco FAL (2017) Anthropogenic nutrients and eutrophication in multiple land use watersheds: best management practices and policies for the protection of water resources. Land Use Policy 69:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.08.028
Bell G, Gonzalez A (2011) Adaptation and evolutionary rescue in metapopulations experiencing environmental deterioration. Science 332:1327–1330. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1203105
Cai B, Li W, Dhakal S, Wang J (2018) Source data supported high resolution carbon emissions inventory for urban areas of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region: spatial patterns, decomposition and policy implications. J Environ Manag 206:786–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.11.038
Cao S, Shang D, Yue H, Ma H (2017) A win-win strategy for ecological restoration and biodiversity conservation in Southern China. Environ Res Lett 12. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa650c
Cao S, Zhang J, Chen L, Zhao T (2016) Ecosystem water imbalances created during ecological restoration by afforestation in China, and lessons for other developing countries. J Environ Manag 183:843–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.07.096
Carpenter SR, DeFries R, Dietz T, Mooney HA, Polasky S, Reid WV, Scholes RJ (2006) Millennium ecosystem assessment: research needs. Science 314:257–258. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1131946
Chen Z, Jiang W, Wang W, Deng Y, He B, Jia K (2017) The impact of precipitation deficit and urbanization on variations in water storage in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Remote Sens 10:4. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010004
Gao Y, Jia Y, Yu G, He N, Zhang L, Zhu B, Wang Y (2019a) Anthropogenic reactive nitrogen deposition and associated nutrient limitation effect on gross primary productivity in inland water of China. J Clean Prod 208:530–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.137
Gao Y, Zhong B, Yue H, Wu B, Cao S (2011) A degradation threshold for irreversible loss of soil productivity: a long-term case study in China. J Appl Ecol 48:1145–1154. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2664.2011.02011.x
Gao Y et al (2019b) Human activities aggravate nitrogen-deposition pollution to inland water over China. Natl Sci Rev 7:430–440. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwz073
Ge J et al (2018) Modeling alpine grassland cover based on MODIS data and support vector machine regression in the headwater region of the Huanghe River, China. Remote Sens Environ 218:162–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.09.019
Gopar LF, Velázquez A (2016) Componentes del paisaje como predictores de cubiertas de vegetación: estudio de caso del estado de Michoacán, México. Investigaciones Geográficas, Boletín del Instituto de Geografía 2016:75–88. https://doi.org/10.14350/rig.46688
Gou J et al (2020) Sensitivity analysis-based automatic parameter calibration of the VIC model for streamflow simulations over China. Water Resour Res 56:e2019WR025968. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019WR025968
Hamamouche MF, Kuper M, Riaux J, Leduc C (2017) Conjunctive use of surface and ground water resources in a community-managed irrigation system — the case of the Sidi Okba palm grove in the Algerian Sahara. Agric Water Manag 193:116–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2017.08.005
Jana P, Dasgupta S, Todaria NP (2017) Impact and ecosystem service of forest and sacred grove as saviour of water quantity and quality in Garhwal Himalaya, India. Environ Monit Assess 189:477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6173-2
Jia P, Zhuang D, Wang Y (2017) Impacts of temperature and precipitation on the spatiotemporal distribution of water resources in Chinese mega cities: the case of Beijing. J Water Clim Chang 8:593–612. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2017.038
Juntti M, Lundy L (2017) A mixed methods approach to urban ecosystem services: experienced environmental quality and its role in ecosystem assessment within an inner-city estate. Landsc Urban Plan 161:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2017.01.002
Kinzig AP, Perrings C, Chapin FS, Polasky S, Smith VK, Tilman D, Turner BL (2012) Response—ecosystem services: free lunch no more. Science 335:656. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.335.6069.656-b
Kong D, Wu J, Borthwick A, Duan Q, Zhang X (2016) Environmental impact assessments of the Xiaolangdi Reservoir on the most hyperconcentrated laden river, Yellow River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7975-4
Lillesund VF, Hagen D, Michelsen O, Foldvik A, Barton DN (2017) Comparing land use impacts using ecosystem quality, biogenic carbon emissions, and restoration costs in a case study of hydropower plants in Norway. Int J Life Cycle Assess 22:1384–1396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-017-1263-5
Liu X, Jiang W, Li J, Wang W (2017) Evaluation of the vegetation coverage resilience in areas damaged by the Wenchuan earthquake based on MODIS-EVI data. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 17:259. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17020259
Lu C, Zhao T, Shi X, Cao S (2018) Ecological restoration by afforestation may increase ground water depth and create potentially large ecological and water opportunity costs in arid and semiarid China. J Clean Prod 176:1213–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.03.046
Miao C, Duan Q, Sun Q, Lei X, Li H (2019) Non-uniform changes in different categories of precipitation intensity across China and the associated large-scale circulations. Environ Res Lett 14:025004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aaf306
Miao C, Kong D, Wu J, Duan Q (2016) Functional degradation of the water–sediment regulation scheme in the lower Yellow River: spatial and temporal analyses. Sci Total Environ 551-552:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.006
Peng J, Liu Y, Liu Z, Yang Y (2017) Mapping spatial non-stationarity of human-natural factors associated with agricultural landscape multifunctionality in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 246:221–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2017.06.007
Petus C et al (2018) Defining wet season water quality target concentrations for ecosystem conservation using empirical light attenuation models: a case study in the Great Barrier Reef (Australia). J Environ Manag 213:451–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.02.028
Qi X, Fu Y, Wang RY, Ng CN, Dang H, He Y (2018) Improving the sustainability of agricultural land use: an integrated framework for the conflict between food security and environmental deterioration. Appl Geogr 90:214–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2017.12.009
Sun Q, Miao C, AghaKouchak A, Duan Q (2016) Century-scale causal relationships between global dry/wet conditions and the state of the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Geophys Res Lett 43:6528–6537. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL069628
Wang Z-J, Jiao J-Y, Su Y, Chen Y (2014) The efficiency of large-scale afforestation with fish-scale pits for revegetation and soil erosion control in the steppe zone on the hill-gully Loess Plateau. CATENA 115:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.11.012
Wu J, Miao C, Zhang X, Yang T, Duan Q (2017) Detecting the quantitative hydrological response to changes in climate and human activities. Sci Total Environ 586:328–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.010
Xiao Q, Tao J, Xiao Y, Qian F (2017) Monitoring vegetation cover in Chongqing between 2001 and 2010 using remote sensing data. Environ Monit Assess 189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6210-1
Xiao Q, Xiao Y, Liu Y, Tao J (2020a) Driving forest succession in karst areas of Chongqing municipality over the past decade. For Ecosyst 7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40663-020-0213-z
Xiao Q, Xiao Y, Luo Y, Song C, Bi J (2019) Effects of afforestation on water resource variations in the Inner Mongolian Plateau. PeerJ 7. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7525
Xiao Y, Xiao Q, Sun X (2020b) Ecological risks arising from the impact of large-scale afforestation on the regional water supply balance in Southwest China. Sci Rep 10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61108-w
Xie Z, Gao Y, Li C, Zhou J, Zhang T (2017) Spatial heterogeneity of typical ecosystem services and their relationships in different ecological–functional zones in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China. Sustainability 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010006
Yu W, Zhou W (2018) Spatial pattern of urban change in two Chinese megaregions: contrasting responses to national policy and economic mode. Sci Total Environ 634:1362–1371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.039
Zhang D, Huang Q, He C, Wu J (2017) Impacts of urban expansion on ecosystem services in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, China: a scenario analysis based on the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Resour Conserv Recycl 125:115–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.06.003
Zheng H, Cao S (2015) Threats to China’s biodiversity by contradictions policy. AMBIO 44:23–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-014-0526-7
Zheng H, Miao C, Wu J, Lei X, Liao W, Li H (2019) Temporal and spatial variations in water discharge and sediment load on the Loess Plateau, China: a high-density study. Sci Total Environ 666:875–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.246
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Becky Stewart for his help in writing this paper as well as the journal editors and anonymous reviewers for their comments on an earlier version of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFC0503004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KP X and YY Ch collected and analyzed the data and were major contributors in writing the manuscript. JJ W, RF G, and XH W made substantial contributions to the conception and design, the interpretation of data, and writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Agreement.
Consent for publication
Agreement.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, K., Chi, Y., Wang, J. et al. Analysis of the spatial characteristics and driving forces determining ecosystem quality of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 12555–12565 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11146-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11146-8