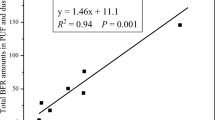
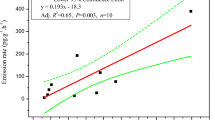
Abstract
It remains unclear whether internal or external sources play the more significant role in flame retardant (FR) contamination of surface dust from personal computers (PCs), which may lead to bias on dermal exposure assessment of FRs. In the present study, the occurrence and profiles of several brominated and phosphate FRs were measured in the interior dust, and the upper surface (keyboard) and bottom surface (bottom cover) wipes of PCs. BDE 209 (639 ng/g), decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE, 885 ng/g), and triphenyl phosphate (TPHP, 1880 ng/g) were the most abundant chemicals in interior PC dust, while tris(2-chloroisopropyl) phosphate (TCIPP), TPHP, and DBDPE were dominant on both surfaces of PCs. No significant correlation between interior dust and both PC surfaces was observed for concentrations of most FRs except BDE 183. Different sources of FRs for interior and surface dust of PCs were further revealed by principal component analysis (PCA). FRs from external sources, rather than emission from inner PC components, are likely the main contributor for FR profiles on PC surfaces. Exposure assessment results demonstrated a minor contribution from PC dermal contact, compared with hand-to-mouth uptake, to total exposure. The applicability of surface wipes to assess dermal exposure to FR-treated products needs to be further investigated.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi G, Buser AM, Soehl A, Murray MW, Diamond ML (2015) Stocks and flows of PBDEs in products from use to waste in the U.S. and Canada from 1970 to 2020. Environ Sci Technol 49:1521–1528. https://doi.org/10.1021/es504007v
Abbasi G, Saini A, Goosey E, Diamond ML (2016) Product screening for sources of halogenated flame retardants in Canadian house and office dust. Sci Total Environ 545-546:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.028
Abou-Elwafa Abdallah M, Harrad S (2018) Dermal contact with furniture fabrics is a significant pathway of human exposure to brominated flame retardants. Environ Int 118:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.05.027
Abou-Elwafa Abdallah M, Harrad S, Covaci A (2008) Hexabromocyclododecanes and tetrabromobisphenol-A in indoor air and dust in Birmingham, U.K.: Implications for human exposure. Environ Sci Technol 42:6855–6861. https://doi.org/10.1021/es801110a
Abou-Elwafa Abdallah M, Pawar G, Harrad S (2015) Effect of bromine substitution on human dermal absorption of polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Environ Sci Technol 49:10976–10983. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b03904
Abou-Elwafa Abdallah M, Pawar G, Harrad S (2016) Human dermal absorption of chlorinated organophosphate flame retardants; implications for human exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 291:28–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2015.12.004
Alaee M, Arias P, Sjödin A, Bergman Å (2003) An overview of commercially used brominated flame retardants, their applications, their use patterns in different countries/regions and possible modes of release. Environ Int 29:683–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00121-1
Ali N, Ali L, Mehdi T, Dirtu AC, Al-Shammari F, Neels H, Covaci A (2013) Levels and profiles of organochlorines and flame retardants in car and house dust from Kuwait and Pakistan: Implication for human exposure via dust ingestion. Environ Int 55:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.02.001
Blum A, Behl M, Birnbaum LS, Diamond ML, Phillips A, Singla V, Sipes NS, Stapleton HM, Venier M (2019) Organophosphate ester flame retardants: are they a regrettable substitution for polybrominated diphenyl ethers? Environ Sci Technol Lett 6:638–649. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.9b00582
Chen SJ, Ma YJ, Wang J, Tian M, Luo XJ, Chen D, Mai BX (2010) Measurement and human exposure assessment of brominated flame retardants in household products from South China. J Hazard Mater 176:979–984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.138
Covaci A, Harrad S, Abou-Elwafa Abdallah M, Ali N, Law RJ, Herzke D, de Wit CA (2011) Novel brominated flame retardants: a review of their analysis, environmental fate and behaviour. Environ Int 37:532–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2010.11.007
de Wit CA (2002) An overview of brominated flame retardants in the environment. Chemosphere 46:583–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0045-6535(01)00225-9
Ding J, Deng T, Xu M, Wang S, Yang F (2018) Residuals of organophosphate esters in foodstuffs and implication for human exposure. Environ Pollut 233:986–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.092
Dirtu AC, Covaci A (2010) Estimation of daily intake of organohalogenated contaminants from food consumption and indoor dust ingestion in Romania. Environ Sci Technol 44:6297–6304. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101233z
Gallen C, Banks A, Brandsma S, Baduel C, Thai P, Eagleshama G, Heffernan A, Leonards P, Bainton P, Mueller JF (2014) Towards development of a rapid and effective non-destructive testing strategy to identify brominated flame retardants in the plastics of consumer products. Sci Total Environ 491-492:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.074
Hahladakis JN, Velis CA, Weber R, Iacovidou E, Purnell P (2018) An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J Hazard Mater 344:179–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.10.014
Hazrati S, Harrad S (2006) Causes of variability in concentrations of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in indoor air. Environ Sci Technol 40:7584–7589. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0617082
He CT, Zheng J, Qiao L, Chen SJ, Yang JZ, Yuan JG, Yang ZY, Mai BX (2015) Occurrence of organophosphorus flame retardants in indoor dust in multiple microenvironments of southern China and implications for human exposure. Chemosphere 133:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.043
Kajiwara N, Noma Y, Takigami H (2011) Brominated and organophosphate flame retardants in selected consumer products on the Japanese market in 2008. J Hazard Mater 192:1250–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.06.043
Kemmlein S, Hahn O, Jann O (2003) Emissions of organophosphate and brominated flame retardants from selected consumer products and building materials. Atmos Environ 37:5485–5493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2003.09.025
Liu X, Yu G, Cao Z, Wang B, Huang J, Deng S, Wang Y (2017) Occurrence of organophosphorus flame retardants on skin wipes: insight into human exposure from dermal absorption. Environ Int 98:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.10.021
Liu X, Cao Z, Yu G, Wu M, Li X, Zhang Y, Wang B, Huang J (2018) Estimation of exposure to organic flame retardants via hand wipe, surface wipe, and dust: comparability of different assessment strategies. Environ Sci Technol 52:9946–9953. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b02723
Lowell Center for Sustainable Production (LCSP) (2005) Decabromodiphenylether: an investigation of non-halogen substitutes in electronic enclosure and textileapplications. UMass Lowell website. https://www.uml.edu/Research/Lowell-Center/Publications/AlternativesAssessment.aspx. Accessed 26 December 2019
MIIT (Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, China) (2016) The restriction of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (in Chinese). http://www.miit.gov.cn/n1146285/n1146352/n3054355/n3057254/n3057260/c4608532/content.html. Accessed June 2020
Rauert C, Harrad S (2015) Mass transfer of PBDEs from plastic TV casing to indoor dust via three migration pathways - a test chamber investigation. Sci Total Environ 536:568–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.07.050
Rauert C, Harrad S, Suzuki G, Takigami H, Uchida N, Takata K (2014a) Test chamber and forensic microscopy investigation of the transfer of brominated flame retardants into indoor dust via abrasion of source materials. Sci Total Environ 493:639–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.029
Rauert C, Lazarov B, Harrad S, Covaci A, Stranger M (2014b) A review of chamber experiments for determining specific emission rates and investigating migration pathways of flame retardants. Atmos Environ 82:44–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.10.003
Spengler JD, Sexton K (1983) Indoor air pollution: a public health perspective. Science 221:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.6857273
Stapleton HM, Kelly SM, Allen JG, McClean MD, Webster TF (2008) Measurement of polybrominated diphenyl ethers on hand wipes: estimating exposure from hand-to-mouth contact. Environ Sci Technol 42:3329–3334. https://doi.org/10.1021/es7029625
Stapleton HM, Klosterhaus S, Eagle S, Fuh J, Meeker JD, Blum A, Webster TF (2009) Detection of organophosphate flame retardants in furniture foam and U.S. house dust. Environ Sci Technol 43:7490–7495. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9014019
Sverko E, Tomy GT, Reiner EJ, Li Y, McCarry BE, Arnot JA, Law RJ, Hites RA (2011) Dechlorane plus and related compounds in the environment: a review. Environ Sci Technol 45:5088–5098. https://doi.org/10.1021/Es2003028
Tay JH, Sellström U, Papadopoulou E, Padilla-Sánchez JA, Haug LS, de Wit CA (2018) Assessment of dermal exposure to halogenated flame retardants: comparison using direct measurements from hand wipes with an indirect estimation from settled dust concentrations. Environ Int 115:285–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.03.038
UNEP (2009) Report of the Conference of the Parties to the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants on the work of its fourth meeting (UNEP/POPS/COP.4/38). http://chm.pops.int/TheConvention/ConferenceoftheParties/ReportsandDecisions/tabid/208/Default.aspx. Accessed June 2020
UNEP (2017a) Report of the Conference of the Parties to the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants on the work of its eighth meeting (UNEP/POPS/COP.8/32). http://chm.pops.int/TheConvention/ConferenceoftheParties/ReportsandDecisions/tabid/208/Default.aspx. Accessed June 2020
UNEP. (2017b) Guidance for the inventory of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) listed under the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants. http://chm.pops.int/Implementation/NationalImplementationPlans/GuidanceArchive/GuidancefortheinventoryofPBDEs/tabid/3171/Default.aspx. Accessed June 2020
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) (2018) Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs): Texts and Annexes Revised in 2017. http://chm.pops.int/TheConvention/Overview/TextoftheConvention/tabid/2232/Default.aspx. Accessed December 2019
USEPA (1989) Report to Congress on indoor air quality: Volume 2. EPA/400/1-89/001C. Washington, DC.
USEPA (2014) An alternatives assessment for the flame retardant decabromodiphenyl ether (DecaBDE). https://www.epa.gov/assessing-and-managing-chemicals-under-tsca/alternatives-assessment-flame-retardant. Accessed December 2019
van der Veen I, de Boer J (2012) Phosphorus flame retardants: properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 88:1119–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.067
Webster TF, Harrad S, Millette JR, David Holbrook R, Davis JM, Stapleton HM, Allen JG, McClean MD, Ibarra C, Abou-Elwafa Abdallah M, Covaci A (2009) Identifying transfer mechanisms and surces of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 209) in indoor environments using environmental forensic microscopy. Environ Sci Technol 43(9):3067–3072. https://doi.org/10.1021/es803139w
Wei GL, Li DQ, Zhuo MN, Liao YS, Xie ZY, Guo TL, Li JJ, Zhang SY, Liang ZQ (2015) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers: sources, occurrence, toxicity and human exposure. Environ Pollut 196:29–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.09.012
WHO (1998) Environmental Health Criteria 209. International Program on Chemical Safety. World Health Organization, Geneva
Xian QM, Siddique S, Li T, Feng YL, Takser L, Zhu JP (2011) Sources and environmental behavior of dechlorane plus - a review. Environ Int 37:1273–1284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2011.04.016
Xu F, Giovanoulis G, van Waes S, Padilla-Sanchez JA, Papadopoulou E, Magner J, Haug LS, Neels H, Covaci A (2016) Comprehensive study of human external exposure to organophosphate flame retardants via air, dust, and hand wipes: The importance of sampling and assessment strategy. Environ Sci Technol 50:7752–7760. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00246
Yang C, Harris SA, Jantunen LM, Siddique S, Kubwabo C, Tsirlin D, Latifovic L, Fraser B, St-Jean M, De La Campa R, You H, Kulka R, Diamond ML (2019) Are cell phones an indicator of personal exposure to organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers? Environ Int 122:104–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.10.021
Yang C, Harris SA, Jantunen LM, Kvasnicka J, Nguyen LV, Diamond ML (2020a) Phthalates: relationships between air, dust, electronic devices, and hands with implications for exposure. Environ Sci Technol 54:8186–8197. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00229
Yang C, Jílková SR, Melymuk L, Harris SA, Jantunen LM, Pertili J, Winn L, Diamond ML (2020b) Are we exposed to halogenated flame retardants from both primary and secondary sources? Environ Sci Technol Lett 7:585–593. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.0c00268
Zheng XB, Wu JP, Luo XJ, Zeng YH, She YZ, Mai BX (2012) Halogenated flame retardants in home-produced eggs from an electronic waste recycling region in South China: levels, composition profiles, and human dietary exposure assessment. Environ Int 45:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2012.04.006
Zheng XB, Qiao L, Covaci A, Sun RX, Guo HY, Zheng J, Luo XJ, Xie QL, Mai BX (2017a) Brominated and phosphate flame retardants (FRs) in indoor dust from different microenvironments: implications for human exposure via dust ingestion and dermal contact. Chemosphere 184:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.167
Zheng XB, Sun RX, Qiao L, Guo HY, Zheng J, Mai BX (2017b) Flame retardants on the surface of phones and personal computers. Sci Total Environ 609:541–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.202
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Guangzhou Science and Technology Program (No. 201707020033), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.41573088), Guangdong Foundation for Program of Science and Technology Research (Nos. 2017B030314057 and 2017BT01Z134), Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (QYZDJ-SSW-DQC018), and Post-doctoral Research Funding of Huangpu District and Guangzhou Development District, Guangzhou City (PM-zx799-202003-107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 97 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Ru, S., Zheng, X. et al. Brominated and phosphate flame retardants from interior and surface dust of personal computers: insights into sources for human dermal exposure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 12566–12575 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11132-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11132-0