Abstract
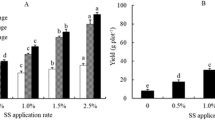
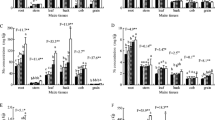
High-yielding and sustainable production of rice in salt-affected mudflat is restricted by high soil salinity. Although sewage sludge can be used for mudflat amendment especially soil salt reduction, the possibility of potential heavy metal contamination in sludge-amended mudflat especially under paddy cultivation remains unclear, which hinders the further utilization of sewage sludge. In this study, a field experiment was conducted in a newly reclaimed mudflat to assess the sustained effects of one-time sludge input with different addition rates (0, 30, 60, 120, and 180 t ha−1) on soil salinity, rice yield, and potential metal contamination under paddy cultivation. The results indicated that sewage sludge addition (SSA) significantly decreased soil salinity and increased soil fertility. The increasing SSA rates and amending years led to the gradual increase of rice yield in salt-affected mudflat. The maximum increases in rice yield were 125.1%, 124.7%, and 127.9% in 2016, 2017, and 2018, and the average annual increase in rice yield in sludge-treated mudflat was 1.7%. Sludge addition increased metals accumulation in mudflat soil and metals uptake by rice tissues except Cr, Cu, and Pb in rice grain. The maximum increments in metal concentrations in soil and rice plant all occurred at 180 t ha−1 sludge addition rate. However, the metal concentrations in rice grain were below the safety limits even in the treatment with the highest sludge addition rate. Metal concentrations in sludge-treated soil and rice plant showed downward trend during the 3-year trial, and the decreases in total amount of soil metals were mainly concentrated in the first amending year, accounting for more than 50%. In summary, one-time sludge input achieved sustained mudflat amendment and efficient rice production. In addition, controlling the total amount of sludge input realized safe utilization of sewage sludge in salt-affected mudflat under paddy cultivation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarenga P, Mourinha C, Farto M, Santos T, Palma P, Sengo J, Morais MC, Cunha-Queda C (2015) Sewage sludge, compost and other representative organic wastes as agricultural soil amendments: Benefits versus limiting factors. Waste Manag 40:44–52
Alvarenga P, Farto M, Mourinha C, Palma P (2016) Beneficial use of dewatered and composted sewage sludge as soil amendments: Behaviour of metals in soils and their uptake by plants. Waste Biomass Valori 7:1189–1201
Antoniadis V, Alloway BJ (2002) The role of dissolved organic carbon in the mobility of Cd, Ni and Zn in sewage sludge-amended soils. Environmental Pollution 117:515–521
Arancon NQ, Edwards CA, Bierman P, Welch C, Metzger JD (2004) Influences of vermicomposts on field strawberries: 1. effects on growth and yields. Bioresource Technol 93:145–153
Bai YC, Zuo WG, Zhao HT, Mei LJ, Gu CH, Guan YX, Wang XK, Gu MJ, Zang CY, Shan YH, Feng K (2016) Distribution of heavy metals in maize and mudflat saline soil amended by sewage sludge. J Soil Sediment 17:1565–1578
Bai YC, Yan YY, Zuo WG, Gu CH, Xue WJ, Mei LJ, Shan YH, Feng K (2017a) Coastal mudflat saline soil amendment by dairy manure and green manuring. Int J Agron 2017:4635964
Bai YC, Zuo WG, Yan YY, Gu CH, Guan YX, Mei LJ, Xue WJ, Shan YH, Feng K (2017b) Sewage sludge amendment combined with green manuring to a coastal mudflat salt-soil in eastern China: effects on soil physicochemical properties and maize yield. Int J Agron 2017:8526598
Bai YC, Yan YY, Zuo WG, Gu CH, Guan YX, Wang XK, Zhao HT, Shan YH, Shao HB, Feng K (2018) Distribution of cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc in mudflat salt-soils amended with sewage sludge. Land Degrad Dev 29:1120–1129
Bao S (2000) Soil and agro-chemistry analysis, 3rd edn. China agriculstural press, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Celik I, Ortas I, Kilic S (2004) Effects of compost, mycorrhiza, manure and fertilizer on some physical properties of a Chromoxerert soil. Soil Till Res 78:59–67
Chen H, Yan SH, Ye ZL, Meng HJ, Zhu YG (2012) Utilization of urban sewage sludge: Chinese perspectives. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 19:1454–1463
Chenu C, Le Bissonnais Y, Arrouays D (2000) Organic matter influence on clay wettability and soil aggregate stability. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:1479–1486
Cheshire MV, Sparling GP, Mundie CM (1983) Effect of periodate treatment of soil on carbohydrate constituents and soil aggregation. J Soil Sci 34:105–112
Clemente R, Escolar A, Bernal MP (2006) Heavy metals fractionation and organic matter mineralisation in contaminated calcareous soil amended with organic materials. Bioresour Technol 97:1894–1901
Cook BD (1992) Dissolved organic carbon in old field soils: compositional changes during the biodegration of soil organic matter. Soil Biol Biochem 24:595–600
Donner E, Ryan CG, Howard DL, Zarcinas B, Scheckel KG, McGrath SP, de Jonge MD, Paterson D, Naidu R, Lombi E (2012) A multi-technique investigation of copper and zinc distribution, speciation and potential bioavailability in biosolids. Environ Pollut 166:57–64
Feng XH, Banin A (1999) Long-term transformation and redistribution of potentially toxic heavy metals in arid-zone soils: II. Incubation at the field capacity moisture content. Water Air Soil Poll 114:221–250
García-Orenes F, Guerrero C, Mataix-Solera J, Navarro-Pedreño J, Gómez I, Mataix-Beneyto J (2005) Factors controlling the aggregate stability and bulk density in two different degraded soils amended with biosolids. Soil Till Res 82:65–76
Gregorich EG, Liang BC, Ellert BH (1996) Fertilization effects on soil organic matter turnover and corn residue C storage. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:472–476
Grosbellet C, Vidal-Beaudet L, Caubel V, Charpentier S (2011) Improvement of soil structure formation by degradation of coarse organic matter. Geoderma 162:27–38
Gu CH, Bai YC (2018) Heavy metal leaching and plant uptake in mudflat soils amended with sewage sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:31031–31039
Gu CH, Bai YC, Tao TY, Chen GH, Shan YH (2013) Effect of sewage sludge amendment on heavy metal uptake and yield of ryegrass seedling in a mudflat soil. J Environ Qual 42:421–428
Guo K, Liu X (2014) Dynamics of meltwater quality and quantity during saline ice melting and its effects on the infiltration and desalinization of coastal saline soils. Agr Water Manage 139:1–6
Han FX, Banin A (1997) Long-term transformations and redistribution of potentially toxic heavy metals in arid-zone soils incubated: I. Under saturated conditions. Water Air Soil Poll 95:399–423
He MC, Yang JR, Cha Y (2000) Distribution, removal and chemical forms of heavy metals in polluted rice seed. Toxicol Environ Chem 76:137–145
Hernández T, Moreno JI, Costa F (1991) Influence of sewage sludge application on crop yields and heavy metal availability. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 37:201–210
Hu YJ, Qian HJ, Cao WW, Xing ZP, Zhang HC, Dai QG, Huo ZY, Xu K, Wei HY, Guo BW (2016) Effect of different mechanical transplantation methods and density on yield and its components of different panicle-typed rice. Chin J Rice Sci 30:493–506 (in Chinese)
Jamali MK, Kazi TG, Arain MB, Afridi HI, Memon AR, Jalbani N, Shah A (2008) Use of sewage sludge after liming as fertilizer for maize growth. Pedosphere 18:203–213
Jastrow JD (1996) Soil aggregate formation and the accrual of particulate and mineral-associated organic matter. Soil Biol Biochem 28:665–676
Ju CX, Chen YJ, Zhao BH, Liu LJ, Wang ZQ, Yang JC (2018) Effect of site-specific nitrogen management on grain yield and quality of japonica rice varieties differed in response to nitrogen. Chin J Rice Sci 32:237–246 (in Chinese)
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (1999) Biogeochemistry of trace elements. Polish Scientific Publishing, Warsaw (in Polish)
Kashem MA, Singh BR (2001) Metal availability in contaminated soils: I. Effects of flooding and organic matter on changes in Eh, pH and solubility of Cd, Ni and Zn. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 61:247–255
Kelessidis A, Stasinakis AS (2012) Comparative study of the methods used for treatment and final disposal of sewage sludge in European countries. Waste Manag 32:1186–1195
Kizilkaya R, Hepsen Turkay FS, Turkmen C, Durmus M (2012) Vermicompost effects on wheat yield and nutrient contents in soil and plant. Arch Agron Soil Sci 58:S175–S179
Lamy I (1993) Soil cadmium mobility as a consequence of sewage sludge disposal. J Environ Qual 22:731–737
Lax A, García-Orenes F (1993) Carbohydrates ofmunicipal solid wastes as aggregation factor of soils. Soil Technol 6:157–162
Li Q, Guo XY, Xu XH, Zuo YB, Wei DP, Ma YB (2012) Phytoavailability of copper, zinc and cadmium in sewage sludge-amended calcareous soils. Pedosphere 22:254–262
López-Rayo S, Laursen KH, Lekfeldt JDS, Grazie FD, Magid J (2016) Long-term amendment of urban and animal wastes equivalent to more than 100 years of application had minimal effect on plant uptake of potentially toxic elements. Agr Ecosyst Environ 231:44–53
McBride MB (2003) Toxic metals in sewage sludge-amended soils: has promotion of beneficial use discounted the risks? Adv Environ Res 8:5–19
Moreno JL, García C, Hernández T, Ayuso M (1997) Application of composted sewage sludges contaminated with heavy metals to an agricultural soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 43:565–573
Nabulo G, Black CR, Young SD (2011) Trace metal uptake by tropical vegetables grown on soil amended with urban sewage sludge. Environ Pollut 159:368–376
Ngole VM (2010) Variations in sludge effects on selected properties of four soil types and vegetable yield. Afr J Pharm Pharmaco 5:3279–3290
Obon T, Crannill BS (1996) Green and animal manure-derived dissolved organic matter effects on phosphorus sorption. J Environ Qual 25:1137–1143
Poschenrieder C, Bech J, Llugany M, Pace A, Fenés E, Barceló J (2001) Copper in plant species in a copper gradient in Catalonia (North East Spain) and their potential for phytoremediation. Plant Soil 230:247–256
Pritchard DL, Penney N, McLaughlin MJ, Rigby H, Schwarz K (2010) Land application of sewage sludge (biosolids) in Australia: Risks to the environment and food crops. Water Sci Technol 62:48–57
Rawls WJ, Pachepsky YA, Ritchie JC, Sobecki TM, Bloodworth H (2003) Effect of soil organic carbon on soil water retention. Geoderma 116:61–76
Rigby H, Clarke BO, Pritchard DL, Meehan B, Beshah F, Smith SR, Porter NA (2016) A critical review of nitrogen mineralization in biosolids-amended soil, the associated fertilizer value for crop production and potential for emissions to the environment. Sci Total Environ 541:1310–1338
Singh RP, Agrawal M (2007) Effects of sewage sludge amendment on heavy metal accumulation and consequent responses of Beta vulgaris plants. Chemosphere 67:2229–2240
Singh RP, Agrawal M (2009) Use of sewage sludge as fertiliser supplement for Abelmoschus esculentus plants: Physiological, biochemical and growth responses. Int J Environ Waste Manage 3:91–106
Sinha S, Pandey K, Gupta AK, Bhatt K (2005) Accumulation of metals in vegetables and crops grown in the area irrigated with river water. B Environ Contam Tox 74:210–218
Tisdall JM, Oades JM (1982) Organic matter and water-stable aggregates in soils. J Soil Sci 33:141–163
Verlicchi P, Zambello E (2015) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in untreated and treated sewage sludge: Occurrence and environmental risk in the case of application on soil—a critical review. Sci Total Environ 538:750–767
Walker DJ, Clemente R, Roig A, Bernal MP (2003) The effects of soil amendments on heavy metal bioavailability in two contaminated Mediterranean soils. Environ Pollut 122:303–312
Wang F, Wall G (2010) Mudflat development in Jiangsu Province, China: practices and experiences. Ocean Coast Manage 53:691–699
Yao GH, Wu DT, Hu YY, Liu D, Yao F, Ye XZ, Ye ZQ (2016) Effects of organic fertilizers On transformation and migration of soil heavy metals under flooded condition. Acta Agr Zhejiangensis 28:127–133 (in Chinese)
Zhao HT, Li TP, Zhang Y, Hu J, Bai YC, Shan YH, Ke F (2017) Effects of vermicompost amendment as a basal fertilizer on soil properties and cucumber yield and quality under continuous cropping conditions in a greenhouse. J Soil Sediment 17:2718–2730
Zheng SA, Zhang MK (2011) Effect of moisture regime on the redistribution of heavy metals in paddy soil. J Environ Sci 23:434–443
Zuo WG, Gu CH, Zhang WJ, Xu KD, Wang Y, Bai YC, Shan YH, Dai QG (2018) Sewage sludge amendment improved soil properties and sweet sorghum yield and quality in a newly reclaimed mudflat land. Sci Total Environ 654:541–549
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872179 and 41828701), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (310432103), Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province (20161148), and Important Research and Development of Jiangsu Province (BE2018330).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors participated sufficiently in the work. Design and Formulation of overarching research goals and aims were completed by YHS, YCB, and QGD. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by WGZ, ML, ZHT, CD, and ML. The first draft of the manuscript was written by WGZ and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Revision was completed by CHG. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, W., Bai, Y., Lv, M. et al. Sustained effects of one-time sewage sludge addition on rice yield and heavy metals accumulation in salt-affected mudflat soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 7476–7490 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11115-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11115-1