Abstract
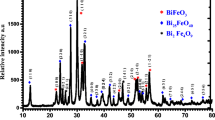
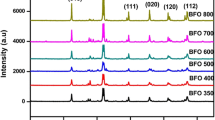
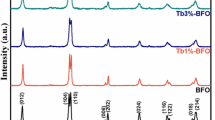
Narrow band gap of ferrites makes it a good photocatalyst, and it plays very prominent role in the level of degradation of organic dyes by photocatalysis. In the current study, bismuth ferrite (BFO) nanoparticles were synthesized by auto-combustion technique. The synthesized BFO particles have the average crystallite size of 33 nm and band gap energy of 1.9 eV. As revealed by microscopic images, uniform, distinct, and hexahedral shaped BFO nanoparticles of 42.7 nm are formed. The BFO nanoparticles exhibited visible and solar light-mediated photocatalytic activity in degrading Acid Yellow-17. The optimum pH and catalyst loading were found to be pH 5 and 0.2 g/L respectively. Around complete degradation under solar and 95% degradation under visible light could be achieved within 135 min of irradiation. Around 85% and 83% chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal could also be achieved under solar and visible light respectively. The degradation followed first-order kinetics in terms of COD removal. The BFO nanoparticles are promising as solar light active catalysts for wastewater treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Achenbach GD, James WJ, Gerson R (1967) Preparation of single-phase polycrystalline BiFeO3. J Am Ceram Soc 50:437–437. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1967.tb15153.x
Akpan UG, Hameed BH (2009) Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2-based photocatalysts: a review. J Hazard Mater 170:520–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.039
APHA (2011) Method 5220 C. standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Aruna ST, Mukasyan AS (2008) Combustion synthesis and nanomaterials. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 12:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2008.12.002
Assi N, Aberoomand Azar P, Saber Tehrani M, Waqif Husain S, Darwish M, Pourmand S (2017) Synthesis of ZnO-nanoparticles by microwave assisted sol-gel method and its role in photocatalytic degradation of food dye Tartrazine (Acid Yellow 23). Int J Nano Dimens 8:241–249
Behnajady M, Modirshahla N, Hamzavi R (2006) Kinetic study on photocatalytic degradation of C.I. Acid Yellow 23 by ZnO photocatalyst. J Hazard Mater 133:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.10.022
Campos LM, Tontcheva A, Günes S et al (2005) Extended photocurrent spectrum of a low band gap polymer in a bulk heterojunction solar cell. Chem Mater 17(16):4031–4033
Dalrymple OK, Stefanakos E, Trotz MA, Goswami DY (2010) A review of the mechanisms and modeling of photocatalytic disinfection. Appl Catal B Environ 98:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.05.001
Elhalil A, Elmoubarki R, Sadiq M et al (2017) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of caffeine as a model pharmaceutical pollutant by Ag-ZnO-Al2O3 nanocomposite. Desalin Water Treat 94:254–262. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.21587
Favier L, Harja M, Simion AI et al (2016) Advanced oxidation process for the removal of chlorinated phenols in aqueous suspensions. J Environ Prot Ecol 17(3):1132–1141
Gabbasova ZV, Kuz’min MD, Zvezdin AK et al (1991) Bi1-xRxFeO3 (R=rare earth): a family of novel magnetoelectrics. Phys Lett A 158:491–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-9601(91)90467-M
Ganapathi P (2015) Study of structural and magnetic properties of some hexaferrite material. 2014
Gao F, Chen XY, Yin KB, Dong S, Ren ZF, Yuan F, Yu T, Zou ZG, Liu JM (2007) Visible-light photocatalytic properties of weak magnetic BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Adv Mater 19:2889–2892. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200602377
Gao T, Chen Z, Huang Q et al (2015) A review : preparation of bismuth ferrite nanoparticles and its applications in visible-light induced photocatalyses. Rev Adv Mater Sci 40:97–109
Gümüş D, Akbal F (2011) Photocatalytic degradation of textile dye and wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut 216:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0520-z
Habibi MH, Vosooghian H (2005) Photocatalytic degradation of some organic sulfides as environmental pollutants using titanium dioxide suspension. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 174:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2005.02.012
Huda A, Ichwani R, Handoko CT et al (2019) Comparative photocatalytic performances towards Acid Yellow 17 (AY17) and direct blue 71 (DB71) degradation using Sn3O4 flower-like structure. In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series
Kalikeri S, Shetty Kodialbail V (2018) Solar light-driven photocatalysis using mixed-phase bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3/Bi25FeO40) nanoparticles for remediation of dye-contaminated water: kinetics and comparison with artificial UV and visible light-mediated photocatalysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:13881–13893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1291-0
Kalikeri S, Kamath N, Gadgil DJ, Shetty Kodialbail V (2018) Visible light-induced photocatalytic degradation of Reactive Blue-19 over highly efficient polyaniline-TiO2 nanocomposite: a comparative study with solar and UV photocatalysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:3731–3744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0663-1
Ke H, Wang W, Wang Y, Xu J, Jia D, Lu Z, Zhou Y (2011) Factors controlling pure-phase multiferroic BiFeO3 powders synthesized by chemical co-precipitation. J Alloys Compd 509:2192–2197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.09.213
Khanna A, Shetty KV (2013) Solar photocatalysis for treatment of Acid Yellow-17 (AY-17) dye contaminated water using Ag@TiO2 core-shell structured nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:5692–5707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1582-4
Khanna A, Shetty KV (2014a) Solar light-driven photocatalytic degradation of Anthraquinone dye-contaminated water by engineered Ag@TiO 2 core–shell nanoparticles. Desalin Water Treat 54:744–757. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.888681
Khanna A, Shetty VK (2014b) Solar light induced photocatalytic degradation of reactive blue 220 (RB-220) dye with highly efficient Ag@TiO2 core-shell nanoparticles: a comparison with UV photocatalysis. Sol Energy 99:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2013.10.032
Khezrianjoo S, Revanasiddappa HD (2013) Photocatalytic degradation of Acid Yellow 36 using zinc oxide photocatalyst in aqueous media. J Catal 2013:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/582058
Kim JK, Kim SS, Kim W-J, Bhalla AS (2007) Substitution effects on the ferroelectric properties of BiFeO3 thin films prepared by chemical solution deposition. J Appl Phys 101:14108
Li S, Lin YH, Zhang BP, Li JF, Nan CW (2009) BiFeO3/TiO2 core-shell structured nanocomposites as visible-active photocatalysts and their optical response mechanism. J Appl Phys 105:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3091286
Li S, Zhang J, Kibria MG, Mi Z, Chaker M, Ma D, Nechache R, Rosei F (2013) Remarkably enhanced photocatalytic activity of laser ablated Au nanoparticle decorated BiFeO3 nanowires under visible-light. Chem Commun 49:5856. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc40363g
Linsebigler AL, Lu G, Yates JT (1995) Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem Rev 95(3):735–758. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00035a013
Liu CC, Hsieh YH, Lai PF et al (2006) Photodegradation treatment of azo dye wastewater by UV/TiO2 process. Dyes Pigments 68:191–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2004.12.002
Matthews RW (1986) Photo-oxidation of organic material in aqueous suspensions of titanium dioxide. Water Res 20:569–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(86)90020-5
Mighat N, Khoshmanesh B (2019) Removal of Acid Yellow-36 Dye from textile industries waste water using photocatalytic process (UV/TiO2). Anthropog Pollut J 3:10–17. https://doi.org/10.22034/AP.2019.668485
Muthuvel I, Krishnakumar B, Swaminathan M (2012) Novel Fe encapsulated montmorillonite K10 clay for photo-Fenton mineralization of Acid Yellow 17. Indian Journal of Chemistry - Section A Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical and Analytical Chemistry 51A(06):800–806
Nair VR, Shetty Kodialbail V (2020) Floating bed reactor for visible light induced photocatalytic degradation of Acid Yellow 17 using polyaniline-TiO2 nanocomposites immobilized on polystyrene cubes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:14441–14453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07959-2
Neppolian B (2002) Solar/UV-induced photocatalytic degradation of three commercial textile dyes. J Hazard Mater 89:303–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(01)00329-6
Ounnar A, Favier L, Bouzaza A, Bentahar F, Trari M (2016) Kinetic study of spiramycin removal from aqueous solution using heterogeneous photocatalysis. Kinet Catal 57:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0023158416020087
Reyren N, Thiel S, Caviglia AD et al (2007) Superconducting interfaces between insulating oxides. Science (80- ) 317:1196–1199. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1146006
Sakthivel S, Kisch H (2003) Photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical properties of nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide. ChemPhysChem 4:487–490. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.200200554
San N, Hatipoǧlu A, Koçtürk G et al (2001) Prediction of primary intermediates and the photodegradation kinetics of 3-aminophenol in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 139:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(01)00368-9
Saquib M, Muneer M (2002) Semiconductor mediated photocatalysed degradation of an anthraquinone dye, Remazol Brilliant Blue R under sunlight and artificial light source. Dye Pigment 53:237–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7208(02)00024-4
Sevimli MF, Kinaci C (2002) Decolorization of textile wastewater by ozonation and Fenton’s process. Water Sci Technol 45:279–286
Sharma SK, Bhunia H, Bajpai PK (2012) Photocatalytic decolorization kinetics and mineralization of reactive black 5 aqueous solution by UV/TiO2 nanoparticles. Clean Soil Air Water 40:1290–1296. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201100557
Silva CG, Faria JL (2009) Effect of key operational parameters on the photocatalytic oxidation of phenol by nanocrystalline sol–gel TiO2 under UV irradiation. J Mol Catal A Chem 305:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2008.12.015
Simões AZ, Stojanovic BD, Ramirez MA, Cavalheiro AA, Longo E, Varela JA (2008) Lanthanum-doped Bi4Ti3O12 prepared by the soft chemical method: Rietveld analysis and piezoelectric properties. Ceram Int 34(2):257–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2006.09.019
Szafraniak I, Połomska M, Hilczer B, Pietraszko A, Kępiński L (2007) Characterization of BiFeO3 nanopowder obtained by mechanochemical synthesis. J Eur Ceram Soc 27:4399–4402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2007.02.163
Wang J, Neaton JB, Zheng H et al (2003) Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures. Science (80- ) 299:1719–1722. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1080615
Wu C-Y, Lee Y-L, Lo Y-S, Lin CJ, Wu CH (2013) Thickness-dependent photocatalytic performance of nanocrystalline TiO2 thin films prepared by sol–gel spin coating. Appl Surf Sci 280:737–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.05.053
Xie H, Wang K, Jiang Y, Zhao Y, Wang X (2014) An improved co-precipitation method to synthesize three bismuth ferrites. Synth React Inorg Met Org Nano-Met Chem 44:1363–1367. https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2013.801859
Zalesskiǐ AV, Frolov AA, Khimich TA, Bush AA (2003) Composition-induced transition of spin-modulated structure into a uniform antiferromagnetic state in a B1-xLaxFeO3 system studied using 57Fe NMR. Phys Solid State 45(1):141–145. https://doi.org/10.1134/1.1537425
Zhang L, Zhang X, Zou Y, Xu YH, Pan CL, Hu JS, Hou CM (2015) Hydrothermal synthesis, influencing factors and excellent photocatalytic performance of novel nanoparticle-assembled Bi25FeO40 tetrahedrons. CrystEngComm. 17:6527–6537. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ce00743g
Zhang L, Zou Y, Song J, Pan CL, Sheng SD, Hou CM (2016) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Bi25FeO40-Bi2WO6 heterostructures based on the rational design of the heterojunction interface. RSC Adv 6(31):26038–26044. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra00334f
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express sincere thanks to Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR), Bangalore, for providing the facility for TEM analysis.
Funding
The research work is funded by National Institute of Technology Karnataka, Surathkal, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization of the research (Vidya Shetty K, Shankramma K); design and development of methodology (Vidya Shetty K, Shankramma K); conducting experiments and original manuscript preparation (Shankramma K); formal analysis of the data (Vidya Shetty K, Shankramma K); review, revision, and editing the manuscript (Vidya Shetty K); supervision of the research work (Vidya Shetty K); and project administration (Vidya Shetty K).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalikeri, S., Shetty Kodialbail, V. Auto-combustion synthesis of narrow band-gap bismuth ferrite nanoparticles for solar photocatalysis to remediate azo dye containing water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 12144–12152 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10879-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10879-w