Abstract
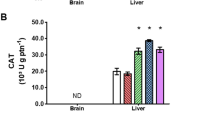
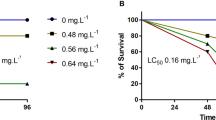
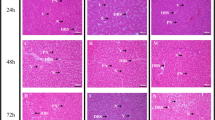
The present study investigated the ecotoxicity of raw mining effluent from the largest molybdenum (Mo) open-pit mine in the Qinling mountains, China, and the treated effluent with neutralization and coagulation/adsorption processes, using zebrafish (Danio rerio). The results showed the following: (1) the mining effluent is acid mine drainage (AMD) and is highly toxic to zebrafish with a 96-h median lethal concentration (LC50) of 3.80% (volume percentage) of the raw effluent; (2) sublethal concentrations of the raw effluent (1/50, 1/10, and 1/2 96-h LC50) induced oxidative stress and osmoregulatory impairment, as reflected by the alterations in activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase and contents of malondialdehyde, and inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase activity in gills and muscle after 28 days of sub-chronic exposure when compared with the unexposed group; and (3) the treatment of the raw effluent with neutralizer (NaOH) and adsorbent activated carbon reduced the acute lethal effect of raw effluent. The used endpoints including acute lethal and biochemical parameters related to oxidative stress and osmoregulatory impairment in zebrafish are cost-effective for toxicity assessment of AMD like the studied Mo mining effluent. Mining effluent management strategies extended by these results, i.e., the restriction of discharging raw and diluted effluent to adjacent waterways and the introduction of bio-monitoring system across all mining drainages in this area, were also proposed and discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated during this study are included in this published article.
References
Akcil A, Koldas S (2006) Acid mine drainage (AMD): causes, treatment and case studies. J Clean Prod 14:1139–1145
Ali I (2010) The quest for active carbon adsorbent substitutes: inexpensive adsorbents for toxic metal ions removal from wastewater. Sep Purif Rev 39:95–171
AQSIQ (General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China) (2008) Testing methods for industrial wastewater-fish acute toxicity (GB/T 21814-2008)
Atli G, Canli M (2010) Response of antioxidant system of freshwater fish Oreochromis niloticus to acute and chronic metal (Cd, Cu, Cr, Zn, Fe) exposures. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1884–1889
Atli G, Canli M (2011) Essential metal (Cu, Zn) exposures alter the activity of ATPases in gill, kidney and muscle of tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Ecotoxicology 20:1861–1869
Brandão Pereira TC, dos Santos KB, Lautert-Dutra W, de Souza Teodoro L, de Almeida VO, Weiler J, Homrich Schneider IA, Reis Bogo M (2020) Acid mine drainage (AMD) treatment by neutralization: evaluation of physical-chemical performance and ecotoxicological effects on zebrafish (Danio rerio) development. Chemosphere 253:126665
Chamorro S, Barata C, Piña B, Casado M, Schwarz A, Sáez K, Vidal G (2018) Toxicological analysis of acid mine drainage by water quality and land use bioassays. Mine Water Environ 37:88–97
da Silva AOF, Martinez CBR (2014) Acute effects of cadmium on osmoregulation of the freshwater teleost Prochilodus lineatus: enzymes activity and plasma ions. Aquat Toxicol 156:161–168
Das D, Moniruzzaman M, Sarbajna A, Chakraborty SB (2017) Effect of heavy metals on tissue-specific antioxidant response in Indian major carps. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:18010–18024
Diaz-de-Alba M, Raya AC, Granado-Castro MD, Ramírez MO, El Mai B, García FC, Troyano-Montoro M, Espada-Bellido E, Santiago RT, Galindo-Riaño MD (2017) Biomarker responses of Cu-induced toxicity in European seabass Dicentrarchus labrax: assessing oxidative stress and histopathological alterations. Mar Pollut Bull 124:336–348
Feng XB, Dai QQ, Qiu GL, Li GH, He L, Wang DY (2006) Gold mining related mercury contamination in Tongguan, Shaanxi Province, Pr China. Appl Geochem 21:1955–1968
Fu FL, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag 92:407–418
Gao YF, Xu YN, Zhang JH (2018) Evaluation of Cd pollution of a molybdenum ore area in Dongchuan River basin of the Qinling Mountain. Geol Bull China 37:2241–2250 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Genchi G, Sinicropi MS, Lauria G, Carocci A, Catalano A (2020) The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:3782
Gioda CR, Lissner LA, Pretto A, da Rocha JBT, Schetinger MRC, Neto JR, Morsch VM, Loro VL (2007) Exposure to sublethal concentrations of Zn(II) and Cu(II) changes biochemical parameters in Leporinus obtusidens. Chemosphere 69:170–175
Gitari WM (2014) Attenuation of metal species in acidic solutions using bentonite clay: implications for acid mine drainage remediation. Toxicol Environ Chem 96:201–217
Glatstein DA, Francisca FM (2015) Influence of pH and ionic strength on Cd, Cu and Pb removal from water by adsorption in Na-bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 118:61–67
Goldani E, Moro CC, Maia SM (2013) A study employing different clays for Fe and Mn removal in the treatment of acid mine drainage. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1401–1412
Gopi N, Vijayakumar S, Thaya R, Govindarajan M, Alharbi NS, Kadaikunnan S, Khaled JM, Al-Anbr MN, Vaseeharan B (2019) Chronic exposure of Oreochromis niloticus to sub-lethal copper concentrations: effects on growth, antioxidant, non-enzymatic antioxidant, oxidative stress and non-specific immune responses. J Trace Elem Med Biol 55:170–179
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sediment to logical approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hogsden KL, Harding JS (2012) Anthropogenic and natural sources of acidity and metals and their influence on the structure of stream food webs. Environ Pollut 162:466–474
Holland A, Duivenvoorden LJ, Kinnear SHW (2014) Humic acid decreases acute toxicity and ventilation frequency in eastern rainbowfish (Melanotaenia splendida splendida) exposed to acid mine drainage. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 110:16–20
Iakovleva E, Sillanpää M (2013) The use of low-cost adsorbents for wastewater purification in mining industries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:7878–7899
Jennings SR, Neuman DR, Blicker PS (2008) Acid mine drainage and effects on fish health and ecology: a review. Reclamation Research Group Publication, Bozeman, MT
Jiri Z, Tazvivinga A, Greenfield R, van Vuren JHJ (2018) Oxidative stress biomarkers in Oreochromis niloticus as early warning signals in assessing pollution from acid mine drainage and diffuse sources of pollutants in a subtropical river. Water SA 44:318–327
Kefeni KK, Msagati TAM, Mamba BB (2017) Acid mine drainage: prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: a review. J Clean Prod 151:475–493
Kimmel WG, Argent DG (2019) Impacts of point-source Net Alkaline Mine Drainage (NAMD) on stream macroinvertebrate communities. J Environ Manag 250:109484
Lei M, Du XL, Zhang F (1994) The comprehensive utilization of water resource in Jinduicheng molybdenum corporation. China Molybd Ind 18:8–10 (in Chinese)
Leitemperger J, Menezes C, Santi A, Murussi C, Lópes T, Costa M, Nogueira LS, Loro VL (2016) Early biochemical biomarkers for zinc in silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) after acute exposure. Fish Physiol Biochem 42:1005–1014
Li CY, Wang FY, Hao XL, Ding X, Zhang H, Ling MX, Zhou JB, Li YL, Fan WM, Sun WD (2012) Formation of the world’s largest molybdenum metallogenic belt: a plate-tectonic perspective on the Qinling molybdenum deposits. Int Geol Rev 54:1093–1112
Li Y, Li W, Xiao Q, Song S, Liu Y, Naidu R (2018) Acid mine drainage remediation strategies: a review on migration and source controls. Miner Metall Process 35:148–158
Lushchak VI (2011) Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 101:13–30
Masindi V, Gitari MW, Tutu H, Debeer M (2015) Efficiency of ball milled South African bentonite clay for remediation of acid mine drainage. J Water Process Eng 8:227–240
Mei D (2013) Effects of landfill leachate on zebrafish acute toxicity and antioxidant enzymes activity. Master dissertation, South China University of Technology
MLRC (Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China) (2001) The general guidelines for inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (DZ/T 0223-2001)
MOEP (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China) (2012) Emission standard of pollutants for mining and mineral processing industry (GB 28661-2012)
MOHC (Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China) (2006) Standards examination methods for drinking water: metal parameters (GB/T 5750.6-2006)
Mohti A, Shuhaimi-Othman M, Gerhardt A (2012) Use of the multispecies freshwater biomonitor to assess behavioral changes of Poecilia reticulata (Cyprinodontiformes: Poeciliidae) and Macrobrachium lanchesteri (Decapoda: Palaemonidae) in response to acid mine drainage: laboratory exposure. J Environ Monit 14:2505–2511
Monserrat JM, Martinez PE, Geracitano LA, Amado LL, Martins CMG, Pinho GLL, Chaves IS, Ferreira-Cravo M, Ventura-Lima J, Bianchini A (2007) Pollution biomarkers in estuarine animals: critical review and new perspectives. Comp Biochem Physiol C 146:221–234
Morth JP, Pedersen BP, Toustrup-Jensen MS, Sorensen TL, Petersen J, Andersen JP, Vilsen B, Nissen P (2007) Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump. Nature 450:1043–1049
Mukherjee A, Bhowmick AR, Mukherjee J, Moniruzzaman M (2019) Physiological response of fish under variable acidic conditions: a molecular approach through the assessment of an eco-physiological marker in the brain. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:23442–23452
Porter CM, Nairn RW (2010) Fluidized bed ash and passive treatment reduce the adverse effects of acid mine drainage on aquatic organisms. Sci Total Environ 408:5445–5451
Ramirez-Paredes FI, Manzano-Munoz T, Garcia-Prieto JC, Zhadan GG, Shnyrov VL, Kennedy JF, Roig MG (2011) Biosorption of heavy metals from acid mine drainage onto biopolymers (chitin and alpha (1,3) beta-D-glucan) from industrial biowaste exhausted brewer’s yeasts (Saccharomyces cerevisiae L.). Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 16:1262–1272
Ratn A, Prasad R, Awasthi Y, Kumar M, Misra A, Trivedi SP (2018) Zn2+ induced molecular responses associated with oxidative stress, DNA damage and histopathological lesions in liver and kidney of the fish, Channa punctatus (Bloch, 1793). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 151:10–20
Rodríguez-Galán M, Baena-Moreno FM, Vázquez S, Arroyo-Torralvo F, Vilches LF, Zhang ZE (2019) Remediation of acid mine drainage. Environ Chem Lett 17:1529–1538
Sabullah MK, Ahmad SA, Shukor MY, Gansau AJ, Syed MA, Sulaiman MR, Shamaan NA (2015) Heavy metal biomarker: fish behavior, cellular alteration, enzymatic reaction and proteomics approaches. Int Food Res J 22:435–454
SEPA (State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China) (1987) Water quality-determination of the sum of calcium and magnesium-EDTA titrimetric method (GB 7477-87)
Souid G, Souayed N, Yaktiti F, Maaroufi K (2013) Effect of acute cadmium exposure on metal accumulation and oxidative stress biomarkers of Sparus aurata. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 89:1–7
Talukdar B, Kalita HK, Basumatary S, Saikia DJ, Sarma D (2017) Cytotoxic and genotoxic affects of acid mine drainage on fish Channa punctata (Bloch). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 144:72–78
Taylor LN, Van der Vliet LA, Scroggins RP (2010) Sublethal toxicity testing of Canadian metal mining effluents: national trends and site-specific uses. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 16:264–281
US-EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2000) Understanding and accounting for method variability in whole effluent toxicity application under the national pollutant discharge elimination system (EPA 833-R-00-003)
van Dam R, Hogan A, Harford A, Markich S (2008) Toxicity and metal speciation characterisation of waste water from an abandoned gold mine in tropical northern Australia. Chemosphere 73:305–313
Vasile D, Gaina G, Petcu CL, Copreanm D, Tofan L, Dinischiotu A (2019) Bioaccumulation of copper and zinc and the effects on antioxidant enzyme activities in the liver of Acipenser stellatus (Pallas, 1771). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102:39–45
Vidal T, Pereira JL, Abrantes N, Soares AMVM, Gonçalves F (2012) Ecotoxicological assessment of contaminated river sites as a proxy for the Water Framework Directive: an acid mine drainage case study. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:6009–6023
Vieira LR, Gravato C, Soares AMVM, Morgado F, Guilhermino L (2009) Acute effects of copper and mercury on the estuarine fish Pomatoschistus microps: linking biomarkers to behavior. Chemosphere 76:1416–1427
Vieira MC, Torronteras R, Córdoba F, Canalejo A (2012) Acute toxicity of manganese in goldfish Carassius auratus is associated with oxidative stress and organ specific antioxidant responses. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 78:212–217
Wang PA, Ishihara S (2001) Metallogeny, minerogenic series, and gold mineralization of the Qinling orogen, China. Int Geol Rev 43:523–538
Westholm LJ, Repo E, Sillanpää M (2014) Filter materials for metal removal from mine drainage—a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9109–9128
Wu L, Yu QG, Zhang G, Wu FL, Zhang YY, Yuan C, Zhang T, Wang ZZ (2019) Single and combined exposures of waterborne Cu and Cd induced oxidative stress responses and tissue injury in female rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Comp Biochem Physiol C 22:90–99
Xue XC, Chen F (2013) Field-study on the surface water pollution in-situ caused by the heavy-metal sediments in Xiaoyu Gully gold-mining site. J Saf Environ 13:112–117 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yuan GD, Theng BKG, Churchman GJ, Gates WP (2013) Chapter 5.1-Clays and clay minerals for pollution control. In: Faïza B, Gerhard L (eds) Developments in clay science. Elsevier, pp 587–644
Zeng QD, Liu JM, Qin KZ, Fan HR, Chu SX, Wang YB, Zhou LL (2013) Types, characteristics, and time-space distribution of molybdenum deposits in China. Int Geol Rev 55:1311–1358
Zhang JH, Wang KY, Xu YN, Wu YG, Chen HQ (2018) Ecological hazard assessment of heavy metal pollution in sediments of Taiyu water system in Xiaoqinling. Geol Bull China 37:2224–2232 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng JL, Yuan SS, Wu CW, Li WY (2016) Chronic waterborne zinc and cadmium exposures induced different responses towards oxidative stress in the liver of zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 177:261–268
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Aaron Ellison for the valuable suggestions and language editing on the manuscript. We also appreciate the editor and reviewers for their valuable comments that greatly improved the manuscript.
Funding
The study was financed by the Science and Technology Service Network Initiative (STS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KFJ-EW-STS-124). Dong Chen received financial support from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (UCAS) Joint PhD Training Program (2017-71).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yi-ping Chen designed the experiments. Dong Chen, Jing Zhang, and Yi-ping Chen all executed the work, analyzed the data, wrote the manuscript, and approved the final version for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics declarations
All the animal experiments were performed in accordance with the local regulation of Guidelines on Laboratory Animals in Shaanxi, China (Decree No.150 of the People’s Government of Shaanxi Province, 2011).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Zhang, J. & Chen, Yp. Ecotoxicity assessment of a molybdenum mining effluent using acute lethal, oxidative stress, and osmoregulatory endpoints in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 5137–5148 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10841-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10841-w