Abstract
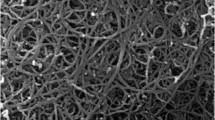
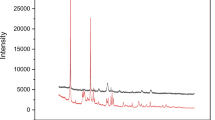
This work aims to synthesize akaganeite nanoparticles (AKNPs) by using microwave and use them to adsorb Congo red dye (CR) from the aqueous solution. The AKNPs with an average particle size of about 50 nm in width and 100 nm in length could be fabricated in 20 min. The effects of pH, CR initial concentration, adsorption time, and adsorbent dosage on the adsorption process were investigated and the artificial neural network (ANN) was used to analyze the adsorption data. The various ANN structures were examined in training the data to find the optimal model. The structure with training function, TRAINLM; adaptation learning function, LARNGDM; transfer function, LOGSIG (in hidden layer) and PURELIN (in output layer); and 10 neutrons in hidden layer having the highest correlation (R2 = 0.996) and the lowest MSE (4.405) is the optimal ANN structure. The consistency between the experimental data and the data predicted by the ANN model showed that the behavior of the adsorption process of CR onto AKNPs under different conditions can be estimated by the ANN model. The adsorption kinetics was studied by fitting the data into pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, Elovich, and intraparticle diffusion models. The results showed that the adsorption kinetics obeyed the pseudo-second-order model and governed by several steps. The adsorption isotherms at the different temperatures were studied by fitting the data to Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin isotherm models. The R2 obtained from the Langmuir model was above 0.9 and the highest value in three of four temperatures, suggesting that the adsorption isotherms were the best fit to the Langmuir model and the maximum adsorption capacity was estimated to be more than 150 mg/g. Thermodynamic studies suggested that the adsorption of CR onto AKNPs was a spontaneous and endothermic process and physicochemical adsorption. The obtained results indicated the potential application of microwave-synthesize AKNPs for removing organic dyes from aqueous solutions.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Afkhami A, Moosavi R (2010) Adsorptive removal of Congo red, a carcinogenic textile dye, from aqueous solutions by maghemite nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 174:398–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.066
Aharoni C, Tompkins FC (1970) Kinetics of adsorption and desorption and the Elovich equation. Adv Catal 21:1–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-0564(08)60563-5
Ali I, AL-Hammadi SA, Saleh TA (2018a) Simultaneous sorption of dyes and toxic metals from waters using synthesized titania-incorporated polyamide. J Mol Liq 269:564–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.08.081
Ali I, Alharbi OML, Alothman ZA et al (2018b) Artificial neural network modelling of amido black dye sorption on iron composite nano material: kinetics and thermodynamics studies. J Mol Liq 250:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.163
Babaei AA, Khataee A, Ahmadpour E et al (2016) Optimization of cationic dye adsorption on activated spent tea: equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamic and artificial neural network modeling. Korean J Chem Eng 33:1352–1361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0334-6
Bashir S, McCabe RW, Boxall C et al (2009) Synthesis of α- and β-FeOOH iron oxide nanoparticles in non-ionic surfactant medium. J Nanopart Res 11:701–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-008-9467-z
Brown MA, De Vito SC (1993) Predicting azo dye toxicity. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 23:249–324
Bulgariu L, Escudero LB, Bello OS et al (2019) The utilization of leaf-based adsorbents for dyes removal: a review. J Mol Liq 276:728–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.12.001
Cai J, Liu J, Gao Z et al (2001) Synthesis and anion exchange of tunnel structure akaganeite. Chem Mater 13:4595–4602. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm010310w
Cornell RM, Schwertmann U (2003) The iron oxides. Structure, properties, reactions, occurrences and uses
Daneshvar N, Khataee AR, Djafarzadeh N (2006) The use of artificial neural networks (ANN) for modeling of decolorization of textile dye solution containing C. I. Basic Yellow 28 by electrocoagulation process. J Hazard Mater 137:1788–1795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.05.042
Deliyanni EA, Bakoyannakis DN, Zouboulis AI, Matis KA (2003) Sorption of As (V) ions by akaganeite-type nanocrystals. Chemosphere 50:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00351-X
Forgacs E, Cserhati T, Oros G (2004) Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environ Int 30:953–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.02.001
Freundlich H (1922) Kapillarchemie, eine Darstellung der Chemie der Kolloide und verwandter Gebiete. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.19230361114
Ghaedi AM, Vafaei A (2017) Applications of artificial neural networks for adsorption removal of dyes from aqueous solution: a review. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 245:20–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2017.04.015
Hassan W, Noureen S, Mustaqeem M et al (2020) Efficient adsorbent derived from Haloxylon recurvum plant for the adsorption of acid brown dye: kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic optimization. Surfaces and Interfaces 20:100510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100510
Huang Z, Han F, Li M et al (2019) Which phase of iron oxyhydroxides ( FeOOH ) is more competent in overall water splitting as a photocatalyst , goethite , akaganeite or lepidocrocite? A DFT-based investigation. Comput Mater Sci 169:109110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2019.109110
Khadhraoui M, Trabelsi H, Ksibi M et al (2009) Discoloration and detoxification of a Congo red dye solution by means of ozone treatment for a possible water reuse. J Hazard Mater 161:974–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.060
Kim J, Li W, Philips BL, Grey CP (2011) Phosphate adsorption on the iron oxyhydroxides goethite (α-FeOOH), akaganeite (β-FeOOH), and lepidocrocite (γ-FeOOH): a 31P NMR Study. Energy Environ Sci 4:4298–4305. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ee02093e
Kolbe F, Weiss H, Morgenstern P et al (2011) Sorption of aqueous antimony and arsenic species onto akaganeite. J Colloid Interface Sci 357:460–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.01.095
Lagergren S, Lagergren S, Lagergren SY, Sven K (1898) Zurtheorie der sogenannten adsorption gelösterstoffe. K Sven Vetenskapsakad Handlingar:1–39
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Lazaridis NK, Bakoyannakis DN, Deliyanni EA (2005) Chromium(VI) sorptive removal from aqueous solutions by nanocrystalline akaganeite. Chemosphere 58:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.09.007
Lima EC, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Moreno-Piraján JC, Anastopoulos I (2019) A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the Van’t Hoof equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J Mol Liq 273:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.048
Limousin G, Gaudet J-P, Charlet L et al (2007) Sorption isotherms: a review on physical bases, modeling and measurement. Appl Geochem 22:249–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.09.010
Milosevic I, Jouni H, David C et al (2011) Jp205334V.Pdf. J Phys Chem C 115:18999–19004. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp205334v
Mohapatra M, Mohapatra L, Anand S, Mishra BK (2010) One-pot synthesis of high surface area nano-akaganeite powder and its cation sorption behavior. J Chem Eng Data 55:1486–1491. https://doi.org/10.1021/je9005932
Munagapati VS, Kim DS (2017) Equilibrium isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics studies for Congo red adsorption using calcium alginate beads impregnated with nano-goethite. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 141:226–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.03.036
Namasivayam C, Kavitha D (2002) Removal of Congo red from water by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from coir pith, an agricultural solid waste. Dyes Pigments 54:47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7208(02)00025-6
Obregón S, Mendoza-Reséndez R, Luna C (2017) Facile synthesis of ultrafine akaganeite nanoparticles for the removal of hexavalent chromium: Adsorption properties, isotherm and kinetics. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 17:4471–4479. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2017.14198
Patel H, Vashi RT (2012) Removal of Congo red dye from its aqueous solution using natural coagulants. J Saudi Chem Soc 16:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2010.12.003
Pathak U, Jhunjhunwala A, Roy A et al (2019) Efficacy of spent tea waste as chemically impregnated adsorbent involving ortho-phosphoric and sulphuric acid for abatement of aqueous phenol—isotherm, kinetics and artificial neural network modelling. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06014-z
Pauletto PS, Gonçalves JO, Pinto LAA et al (2020) Single and competitive dye adsorption onto chitosan–based hybrid hydrogels using artificial neural network modeling. J Colloid Interface Sci 560:722–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.10.106
Pearce CI, Lloyd JR, Guthrie JT (2003) The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: a review. Dyes Pigments 58:179–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7208(03)00064-0
Pigorsch E, Elhaddaoui A, Turrell S (1994) Spectroscopic study of pH and solvent effects on the structure of Congo red and its binding mechanism to amyloid-like proteins. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Spectrosc 50:2145–2152. https://doi.org/10.1016/0584-8539(94)00151-0
Saleh TA (2015) Mercury sorption by silica/carbon nanotubes and silica/activated carbon: a comparison study. J Water Supply Res Technol - AQUA 64:892–903. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2015.050
Saleh TA (2016) Nanocomposite of carbon nanotubes/silica nanoparticles and their use for adsorption of Pb(II): from surface properties to sorption mechanism. Desalin Water Treat 57:10730–10744. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1036784
Saleh TA, Ali I (2018) Synthesis of polyamide grafted carbon microspheres for removal of rhodamine B dye and heavy metals. J Environ Chem Eng 6:5361–5368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.08.033
Saleh TA, Tuzen M, Sarı A (2018) Polyamide magnetic palygorskite for the simultaneous removal of Hg(II) and methyl mercury; with factorial design analysis. J Environ Manag 211:323–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.01.050
Schmidt J, Marques MRG, Botti S, Marques MAL (2019) Recent advances and applications of machine learning in solid-state materials science. npj Comput Mater 5:83. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-019-0221-0
Shahryari Z, Sharifi A, Mohebbi A (2013) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modeling and formulation of phenol adsorption onto activated carbon. J Eng Thermophys 22:322–336. https://doi.org/10.1134/S181023281304005X
Simonin JP (2016) On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem Eng J 300:254–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.079
Sun J, Wang Y, Sun R, Dong S (2009) Photodegradation of azo dye Congo red from aqueous solution by the WO3–TiO2/activated carbon (AC) photocatalyst under the UV irradiation. Mater Chem Phys 115:303–308
Tanzifi M, Hosseini SH, Kiadehi AD et al (2017) Artificial neural network optimization for methyl orange adsorption onto polyaniline nano-adsorbent: kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. J Mol Liq 244:189–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.08.122
Temkin MI (1940) Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalysts. Acta physiochim URSS 12:327–356
Tran HN, You S-J, Chao H-P (2016) Thermodynamic parameters of cadmium adsorption onto orange peel calculated from various methods: a comparison study. J Environ Chem Eng 4:2671–2682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.05.009
Wahi RK, William WY, Liu Y et al (2005) Photodegradation of Congo red catalyzed by nanosized TiO2. J Mol Catal A Chem 242:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2005.07.034
Wan S, Wang S, Li Y, Gao B (2017) Functionalizing biochar with Mg–Al and Mg–Fe layered double hydroxides for removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions. J Ind Eng Chem 47:246–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.11.039
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div 89:31–60
Wu F-C, Tseng R-L, Juang R-S (2009) Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics. Chem Eng J 153:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.04.042
Xu Z, Yu Y, Fang D et al (2015) Microwave-ultrasound assisted synthesis of β-FeOOH and its catalytic property in a photo-Fenton-like process. Ultrason Sonochem 27:287–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2015.05.039
Yang Y, Lin X, Wei B et al (2014) Evaluation of adsorption potential of bamboo biochar for metal-complex dye: equilibrium, kinetics and artificial neural network modeling. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:1093–1100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0306-0
Ys H, Mckay G, Ys H, Mckay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Yusan SD, Akyil S (2008) Sorption of uranium(VI) from aqueous solutions by akaganeite. J Hazard Mater 160:388–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.009
Yusan S, Erenturk SA (2010) Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of U(VI) on beta type of akaganeite. Desalination 263:233–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.06.064
Zhang EL, Sun XJ, Liu XT, Wang QD (2015) Morphology controlled synthesis of α-FeOOH crystals and their shape-dependent adsorption for decontamination of Congo red dye. Mater Res Innov 19:385–391. https://doi.org/10.1179/1433075X15Y.0000000019
Zhao J, Lin W, Chang Q et al (2012) Adsorptive characteristics of akaganeite and its environmental applications: a review. Environ Technol Rev 1:114–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2012.701239
Funding
This research is funded by the Vietnam Ministry of Education and Training under grant code B2019-TNA-17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VDN conceived and designed the experiments, analyzed the data, and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. HTHN performed the experiment of the synthesis of material and wrote the experimental section. VV analyzed data, designed the graphs, and wrote a part of the “Introduction” section. LTNN performed the experiment of the adsorption study. QMB analyzed data of adsorption study and was a contributor in writing the manuscript. TTK analyzed data and wrote the “Synthesis and characterization of AKNPs” and “Optimization of neural network structure.” All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 115 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, V.D., Nguyen, H.T.H., Vranova, V. et al. Artificial neural network modeling for Congo red adsorption on microwave-synthesized akaganeite nanoparticles: optimization, kinetics, mechanism, and thermodynamics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 9133–9145 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10633-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10633-2