Abstract
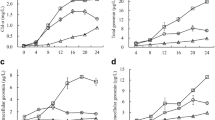
Geosmin is one of the most common earthy-musty odor compounds, which is mainly produced by cyanobacteria in surface water. Nitrogen (N) is an important factor affecting the growth of cyanobacteria and its secondary metabolites production due to the eutrophication. In this study, we compared the effects of elevated N on the growth and geosmin productivity of Dolichospermum smithii NIES-824 (synonym Anabaena smithii NIES-824), aiming to better understand the mechanisms involved and give an important and fundamental knowledge to solve off-flavor problem. Results show that elevated N concentration promoted more chlorophyll a (Chl-a) production, whereas the geosmin synthesis decreased, revealing a possible competitive correlation between the Chl-a concentration and geosmin production of D. smithii NIES-824. The majority of geosmin (> 90%) was retained intracellularly during the 28 days of cultivation. The qRT-PCR analysis demonstrates that the expression level of the geosmin synthase gene (geoA) was constitutive and decreased at the higher N concentration during the exponential growth phase of cyanobacterial cells. Furthermore, the decrease of geoA expression during the decline phase suggested that geoA transcription was closely related to cell activity and isoprenoid productivity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajikumar PK, Tyo K, Carlsen S, Mucha O, Phon TH, Stephanopoulos G (2008) Terpenoids: opportunities for biosynthesis of natural product drugs using engineered microorganisms. Mol Pharm 5(2):167–190
Alghanmi HA, Fo’ad MA, Al-Taee MM (2018) Effect of light and temperature on new cyanobacteria producers for geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol. J Appl Phycol 30(1):319–328
APHA (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Blevins WT, Schrader KK, Saadoun I (1995) Comparative physiology of geosmin production by Streptomyces halstedii and Anabaena sp. Water Sci Technol 31(11):127–133
Cai F, Yu G, Zhang K, Chen Y, Li Q, Yang Y, Xie J, Wang Y, Li R (2017) Geosmin production and polyphasic characterization of Oscillatoria limosa Agardh ex Gomont isolated from the open canal of a large drinking water system in Tianjin City, China. Harmful Algae 69:28–37
Cook D, Newcombe G, Sztajnbok P (2001) The application of powdered activated carbon for MIB and geosmin removal: predicting PAC doses in four raw waters. Water Res 35(5):1325–1333
Dolman AM, Rücker J, Pick FR, Fastner J, Rohrlack T, Mischke U, Wiedner C (2012) Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins: the influence of nitrogen versus phosphorus. PLoS One 7(6):e38757
Dzialowski AR, Smith VH, Huggins DG, deNoyelles F, Lim NC, Baker DS, Beury JH (2009) Development of predictive models for geosmin-related taste and odor in Kansas, USA, drinking water reservoirs. Water Res 43(11):2829–2840
Elser JJ, Bracken ME, Cleland EE, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Ngai JT, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2007) Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 10(12):1135–1142
Frank D, Poole S, Kirchhoff S, Forde C (2009) Investigation of sensory and volatile characteristics of farmed and wild barramundi (Lates calcarifer) using gas chromatography−olfactometry mass spectrometry and descriptive sensory analysis. J Agric Food Chem 57(21):10302–10312
Giglio S, Jiang J, Saint CP, Cane DE, Monis PT (2008) Isolation and characterization of the gene associated with geosmin production in cyanobacteria. Environ Sci Technol 42(21):8027–8032
Giglio S, Saint CP, Monis PT (2011) Expression of the geosmin synthase gene in the cyanobacterium Anabaena circinalis AWQC3181. J Phycol 47(6):1338–1343
Ho L, Hoefel D, Bock F, Saint CP, Newcombe G (2007) Biodegradation rates of 2-methylisoborneol (MIB) and geosmin through sand filters and in bioreactors. Chemosphere 66(11):2210–2218
Hsieh ST, Lin TF, Wang GS (2010) Biodegradation of MIB and geosmin with slow sand filters. J Environ Sci Heal A 45(8):951–957
Japan Water Works Association (2011) Standard methods for the examination of water. Japan Water Works Association, Tokyo, Japan (in Japanese)
Jiang J, Cane DE (2008) Geosmin biosynthesis. Mechanism of the fragmentation−rearrangement in the conversion of germacradienol to geosmin. J Am Chem Soc 130(2):428–429
Jiang J, He X, Cane DE (2006) Geosmin biosynthesis. Streptomyces coelicolor germacradienol/germacrene D synthase converts farnesyl diphosphate to geosmin. J Am Chem Soc 128(25):8128–8129
Jüttner F, Watson SB (2007) Biochemical and ecological control of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in source waters. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(14):4395–4406
Kakimoto M, Ishikawa T, Miyagi A, Saito K, Miyazaki M, Asaeda T, Yamaguchi M, Uchiyama H, Kawai-Yamada M (2014) Culture temperature affects gene expression and metabolic pathways in the 2-methylisoborneol-producing cyanobacterium Pseudanabaena galeata. J Plant Physiol 171(3-4):292–300
Kutovaya OA, Watson SB (2014) Development and application of a molecular assay to detect and monitor geosmin-producing cyanobacteria and actinomycetes in the Great Lakes. J Great Lakes Res 40(2):404–414
Lange BM, Rujan T, Martin W, Croteau R (2000) Isoprenoid biosynthesis: the evolution of two ancient and distinct pathways across genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(24):13172–13177
Lee J, Rai PK, Jeon YJ, Kim KH, Kwon EE (2017) The role of algae and cyanobacteria in the production and release of odorants in water. Environ Pollut 227:252–262
Li Z, Yu J, Yang M, Zhang J, Burch MD, Han W (2010) Cyanobacterial population and harmful metabolites dynamics during a bloom in Yanghe Reservoir, North China. Harmful Algae 9(5):481–488
Naes H, Post AF (1988) Transient states of geosmin, pigments, carbohydrates and proteins in continuous cultures of Oscillatoria brevis induced by changes in nitrogen supply. Arch Microbiol 150(4):333–337
Olsen BK, Chislock MF, Wilson AE (2016) Eutrophication mediates a common off-flavor compound, 2-methylisoborneol, in a drinking water reservoir. Water Res 92:228–234
Pattanaik B, Lindberg P (2015) Terpenoids and their biosynthesis in cyanobacteria. Life 5(1):269–293
Perkins RG, Slavin EI, Andrade TMC, Blenkinsopp C, Pearson P, Froggatt T, Godwin G, Parslow J, Hurley S, Luckwell R, Wain DJ (2019) Managing taste and odour metabolite production in drinking water reservoirs: the importance of ammonium as a key nutrient trigger. J Environ Manag 244:276–284
Proteau PJ (1998) Biosynthesis of phytol in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. UTEX 2470: utilization of the non-mevalonate pathway. J Nat Prod 61(6):841–843
Rasch D, Kubinger KD, Moder K (2011) The two-sample t test: pre-testing its assumptions does not play off. Stat Pap 52:219–231
Robin J, Cravedi JP, Hillenweck A, Deshayes C, Vallod D (2006) Off flavor characterization and origin in French trout farming. Aquaculture 260(1-4):128–138
Saadoun IM, Schrader KK, Blevins WT (2001) Environmental and nutritional factors affecting geosmin synthesis by Anabaena sp. Water Res 35(5):1209–1218
Smith JL, Boyer GL, Zimba PV (2008) A review of cyanobacterial odorous and bioactive metabolites: impacts and management alternatives in aquaculture. Aquaculture 280(1-4):5–20
Smith VH (2003) Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems a global problem. Environ Sci Pollut Res 10(2):126–139
Smith VH, Schindler DW (2009) Eutrophication science: where do we go from here? Trends Ecol Evol 24(4):201–207
Srinivasan R, Sorial GA (2011) Treatment of taste and odor causing compounds 2-methyl isoborneol and geosmin in drinking water: a critical review. J Environ Sci 23(1):1–13
Suwanpakdee S, Gutierrez R, Pithakpol S, Jampeetong A, Pathom-aree W, Nomura N, Itayama N, Whangchai N (2016) Earthy-musty odor and off-flavour taints in Phayao Lake, Thailand. Chiang Mai J Sci 43(1):22–31
Tsao HW, Michinaka A, Yen HK, Giglio S, Hobson P, Monis P, Lin TF (2014) Monitoring of geosmin producing Anabaena circinalis using quantitative PCR. Water Res 49:416–425
Wang Z, Li R (2015) Effects of light and temperature on the odor production of 2-methylisoborneol-producing Pseudanabaena sp. and geosmin-producing Anabaena ucrainica (cyanobacteria). Biochem Syst Ecol 58:219–226
Wang Z, Xu Y, Shao J, Wang J, Li R (2011) Genes associated with 2-methylisoborneol biosynthesis in cyanobacteria: isolation, characterization, and expression in response to light. PLoS One 6(4):e18665
Watanabe MM, Hiroki M (1997) NIES-Collection. List of strains, algae and protozoa. National Institute for Environmental Studies, Environment Agency, Japan, 140.
Watson SB, Monis P, Baker P, Giglio S (2016) Biochemistry and genetics of taste-and odor-producing cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 54:112–127
Westerhoff P, Rodriguez-Hernandez M, Baker L, Sommerfeld M (2005) Seasonal occurrence and degradation of 2-methylisoborneol in water supply reservoirs. Water Res 39(20):4899–4912
Zhang T, Li L, Song L, Chen W (2009) Effects of temperature and light on the growth and geosmin production of Lyngbya kuetzingii (Cyanophyta). J Appl Phycol 21(3):279–285
Zhang T, Li L, Zheng L, Song L (2017) Effects of nutritional factors on the geosmin production of Lyngbya kuetzingii UTEX 1547 (Oscillatoriales, Cyanobacteria). Phycologia 56(2):221–229
Zimba PV, Dionigi CP, Millie DF (1999) Evaluating the relationship between photopigment synthesis and 2-methylisoborneol accumulation in cyanobacteria. J Phycol 35(6):1422–1429
Funding
This study was supported by a Health Labor Sciences Research Grant (H30-Kenki-Ippan-004) from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Q., Shimizu, K., Miao, H. et al. Effects of elevated nitrogen on the growth and geosmin productivity of Dolichospermum smithii. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 177–184 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10429-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10429-4