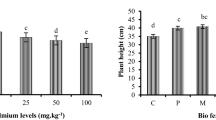
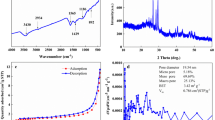
Abstract
Due to the increase of cadmium (Cd)-contaminated land area worldwide, effective measures should be taken to minimize the Cd bioavailability in crops. A study was performed to explore the effectiveness of biochar pyrolyzed from rice straw at 400 °C alone or combined with AM fungi (Funneliformis mosseae) on the corn growth and Cd uptake in corn in Cd-contaminated soil with different levels of phosphorus supplies. The results showed that biochar significantly reduced 66% and 38% of Cd uptake in shoot and root respectively (P < 0.001) attributed to the increase of soil pH and dissolved organic matter. In contrast, AM fungi inoculation of corn plants had little effect on Cd bioavailability due to the AM was suppressed by the highly contaminated acid soil (31.76 mg/kg), and had neither synergistic effect with biochar on decreasing the Cd bioavailability with high or low phosphorus supplies. This study demonstrated that biochar application could be a promising method to immobilize Cd in the contaminated soil to ensure the safety of agro-product while high Cd-contaminated soil would suppress the growth of mycorrhizae, so this remains an open question to be further studied.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd_Allah EF, Hashem A, Alqarawi AA, Alwathnani HA (2015) Alleviation of adverse impact of cadmium stress in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Pak J Bot 47(2):785–795 http://www.pakbs.org/pjbot/papers/1526639131.pdf
Aghababaei F, Raiesi F, Hosseinpur A (2014) The influence of earthworm and mycorrhizal co-inoculation on Cd speciation in a contaminated soil. Soil Bio Biochem 78:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.06.010
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals - concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075
Almaroai YA, Usman ARA, Ahmad M, Moon DH, Cho JS, Joo YK (2014) Effects of biochar, cow, bone, and eggshell on Pb availability to corn in contaminated soil irrigated with saline water. Environ Earth Sci 71(3):1289–1296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2533-6
Bao S (2000) Soil agro-chemical analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Bashir S, Salam A, Rehman M, Khan S, Gulshan AB, Iqbal J, Shaaban M, Mehmood S, Zahra A, Hu H (2019) Effective role of biochar, zeolite and steel slag on leaching behavior of Cd and its fractionations in soil column study. B Environ Contam Tox 102:567–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02573-6
Bian R, Chen D, Liu X, Cui L, Li L, Pan G, Xie D, Zheng J, Zhang X, Zheng J, Chang A (2013) Biochar soil amendment as a solution to prevent Cd-tainted rice from China: results from a cross-site field experiment. Ecol Eng 58:378–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.07.031
Braunberger PG, Peterson RL (1991) Effect of phosphorus nutrition on morphological characteristics of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization of maize. New Phytol 119(1):107–113. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1991.tb01013.x
Chen NC, Zheng YJ, He XF, Li XF, Zhang XX (2017) Investigation on National Soil Pollution Survey Bulletin. Agr Environ Sci 36(9):1689–1692
Ezawa T, Yamamoto K, Yoshida S (2002) Enhancement of the effectiveness of indigenous arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi by inorganic soil amendments. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 48(6):897–900. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2002.10408718
Fellet G, Marchiol L, Delle VG, Peressotti A (2011) Application of biochar on mine tailings: effects and perspectives for land reclamation. Chemosphere 83(9):1262–1267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.03.053
Feng HY, Liu Y, Feng G, Li XL (2005) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on uptake and distribution of cadmium in Lolium L. Agro-Environ Sci 24(3):426–431 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fuertes A, Sevilla M (2009) Chemical and structural properties of carbonaceous products obtained by hydrothermal carbonization of saccharides. Chem-Eur J 15(16):4195–4203. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200802097
Gonzalez-Chavez MC, Carrillo-Gonzalez R, Wright SF, Nichols KA (2004) The role of glomalin, a protein produced by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, in sequestering potentially toxic elements. Environ Pollut 130:317–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.01.004
Han YG, Qi YC, Liu C, Zhou YZ (1993) Effects of temperature and pH on mycorrhizal fungus growth. Chin J Ecology 12(01):15–19 (in Chinese with English abstract)
He L, Zhong H, Liu G, Dai Z, Brookes PC, Xu J (2019) Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by biochar: mechanisms, potential risks and applications in China. Environ Pollut 252:846–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.151
Hou YW, Chi HF, Bi LJ (2014) Effects of biochar application on growth and typical metal accumulation of rape in mining contaminated soil. Ecol Environ Sci 23(6):1057–1063. (In Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2014.06.018
Houben D, Evrard L, Sonnet P (2013) Beneficial effects of biochar application to contaminated soils on the bioavailability of Cd, Pb and Zn and the biomass production of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Biomass Bioenergy 57(11):196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2013.07.019
Hu XM, Yuan XS, Wang LP, Hua PY (2012) Effects of phosphate fertilizer and rice straw on soil heavy metal fraction, microbial activity and phytoavailability. Res Environ Sci 25(1):77–82. (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.13198/j.res.2012.01.80.huxm.014
Huang J, Ling WT, Sun YT, Liu J (2012) Impacts of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation on the uptake of cadmium and zinc by alfalfa in contaminated soil. Agro-Environ Sci 31(1):99–105 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Huang YZ, Hao XW, Lei M, Bo-Qing T (2013) The technology and restoration practice of heavy metal contaminated soil. Agro-Environ Sci 3(3):409–417
Johannes L, Matthias C, Rillig JT, Caroline A, Masiello WC, Hockaday (2011) Biochar effects on soil biota-a review. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1812–1836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.04.022
Koide RT, Mingguang LI (1990) On host regulation of the vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. New Phytol 114(1):59–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1990.tb00373.x
Kuang MJ (2016) Study on the effect of biochar on the transformation and bioavailability of Cd in different paddy soils in Hunan, Hunan Agricultural University, Thesis Dissertation
Lee JW, Kidder M, Evans BR, Paik S, Buchanan AC, Garten CT, Brown RC (2010) Characterization of biochars produced from cornstovers for soil amendment. Environ Sci Technol 44(20):7970–7974. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101337x
Lehmann J, Rillig MC, Thies J, Caroline AM, Hockaday WC, David C (2011) Biochar effects on soil biota -a review. Soil Biol Biochem 43(9):1812–1836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.04.022
Li MY, Du LY, Zhang Y, Gao YD (2013) Influence of pyrolysis temperatures of biochar obtained from the rice straw on Cadmium forms. J Soil Water Conserv 27:261–264. (In Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2013.06.010
Li D, Chen L, Xia Y, Song XN, Liu MH, Zheng H (2014) The effects of biochar on growth and uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus for Chinese cabbage in poor quality soil in Ningxia. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 34(9):2384–2391. (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2014.0550
Li JX, Wu LC, Zhang J, Wang CSS, Yu QQ, Peng Y, Ma YH (2015) Research progresses in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by biochar. Ecol Environ Sci 24(12):2075–2081. (In Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.12.024
Liao N, Li Q, Zhang W, Zhou GW, Ma LJ, Min W, Ye J, Hou ZN (2016) Effects of biochar on soil microbial community composition and activity in drip-irrigated desert soil. Eur J Soil Biol 72:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2015.12.008
Liu Y, Zhu YG, Chen BD, Christie P, Li XL (2005) Influence of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus, Glomus mosseae, on uptake of arsenate by the As hyperaccumulator fern, Pteris vittata, L. Mycorrhiza 15(3):187–192
Liu YX, Liu H, Wu WX (2009) Soil biomass charcoal environmental behavior and environmental effect. Appl Ecol 20(4):977–982. (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.2009.0124
Liu YX, Zhou YQ, Dong Y, Sun GX (2012) Effect of inoculation of arbucular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomus mosseae) on As uptake of upland rice and transformation of As speciation in soil. Ecotoxicology 7(2):195–200 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Liu AM, Xiang YC, Tian DK, Mo HB (2013) Effects of biochar on plant growth and uptake of heavy metal cadmium. Soil Water Conserv 27(5):193–198. (In Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2013.05.002
Liu L, Li J, Yue F, Yan X, Wang F, Bloszies S, Wang Y (2018) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation and biochar amendment on maize growth, cadmium uptake and soil cadmium speciation in Cd-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 194:495–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.025
Liu M, Zhao Z, Chen L, Wang L, Ji L, Xiao Y (2020) Influences of arbuscular mycorrhizae, phosphorus fertiliser and biochar on alfalfa growth, nutrient status and cadmium uptake. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 196:110537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110537
Lu K, Yang X, Shen J, Robinson P, Huang HG, Liu D, Bolan N, Pei JC, Wang LL (2014) Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the bioavailability of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn to Sedum plumbizincicola. Agric Ecosyst Environ 191:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2014.04.010
Lundberg B, Sundqvist B (2011) A review of biochars’ potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 159(12):3269–3282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.07.023
Mao YD, Tie BQ, Ye CC, Zhou Y, Yang SM (2015) The effects of biochar on the cadmium formation of heavy polluted soil and the absorption of cadmium by rape. Ecol Rural Environ 31(04):579–582
Maskina MS, Power JF, Doran JW, Wilhelm WW (1993) Residual effects of no-till crop residues on corn yield and nitrogen uptake. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57:1555–1560. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1993.03615995005700060027x
Matsubara Y, Hasegawa N, Fukui H (2002) Incidence of Fusarium root rot in Asparagus seedlings infected with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus as affected by several soil amendments. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 71:370–374. https://doi.org/10.2503/jjshs.71.370
Nzanza B, Marais D, Soundy P (2012) Response of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) to nursery inoculation with Trichoderma harzianum and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under field conditions. Acta Agr Scand B-S P 62:209–215. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710.2011.598544
Piotrowski JS, Rillig MC (2008) Succession of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: patterns, causes, and considerations for organic agriculture. Adv Agron 97(07):111–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(07)00003-X
Qiao YH, Crowley D, Wang K, Zhang HQ, Li HF (2015) Effects of biochar and Arbuscular mycorrhizae, on bioavailability of potentially toxic elements in an aged contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 206:636–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.08.029
Qin Z, Zhang H, Feng G, Christie P, Zhang J, Li X, Gai J (2020) Soil phosphorus availability modifies the relationship between AM fungal diversity and mycorrhizal benefits to maize in an agricultural soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107790
Renker C, Blanke V, Rstler B, Heinrichs J, Buscot FO (2004) Diversity of cryptococcus and dioszegia yeasts (Basidiomycota) inhabiting arbuscular mycorrhizal roots or spores. FEMS Yeast Res 4:597–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsyr.2004.01.001
Rillig MC, Mummey DL, Ramsey PW, Klironomos JN, Gannon JE (2006) Phylogeny of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi predicts community composition of symbiosis-associated bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 57:389–395. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2006.00129.x
Rillig MC, Wagner M, Salem M, Antunes PM, George C, Ramke HG, Titirici MM, Antonietti M (2010) Material derived from hydrothermal carbonization: effects on plant growth and arbuscular mycorrhiza. Appl Soil Ecol 45(3):238–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2010.04.011
Rodriguez L, Ruiz E, Alonso-Azcarate J, Rincon J (2009) Heavy metal distribution and chemical speciation in tailings and soils around a Pb-Zn mine in Spain. J Environ Manag 90:1106–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.04.007
Smith SR (2009) A critical review of the bioavailability and impacts of heavy metals in municipal solid waste composts compared to sewage sludge. Environ Int 35:142–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2008.06.009
Sołek-Podwika K, Ciarkowska K, Kaleta D (2016) Assessment of the risk of pollution by sulfur compounds and heavy metals in soils located in the proximity of a disused for 20 years sulfur mine (SE Poland). J Environ Manag 180:450–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.05.074
TSO (2006) Welsh Statutory Instrument No.116 (W.14), The feeding stuffs (Wales) Regulations 2006. The Stationary Office, London, UK
Warnock DD, Mummey DL, McBride B, Major J, Lehmann J, Rillig MC (2010) Influences of non-herbaceous biochar on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal abundances in roots and soils: results from growth-chamber and field experiments. Appl Soil Ecol 46(3):450–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2010.09.002
Wei XD, Zou HL, Tie BQ, Chen H, Cai D, Cai L, Fang YY, Yin XH (2015) Effects of different planting patterns on concentrations and migration of soil heavy metals in dryland in southern China. Agro-Environ Sci 34(6):1096–1106 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Xiao Y, Liu M, Chen L, Ji L, Zhao Z, Wang L, Wei L, Zhang Y (2020) Growth and elemental uptake of Trifolium repens in response to biochar addition, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphorus fertilizer applications in low-Cd-polluted soils. Environ Pollut 260:113761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113761
Yuan JH, Xu RK, Zhang H (2011) The forms of alkalis in the biochar produced from crop residues at different temperatures. Bioresour Technol 102(3):3488–3497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.11.018
Zakariam S, Paul B, Lynettek A, Storer P, Krull E (2010) Direct and residual effect of biochar application on mycorrhizal root colonisation, growth and nutrition of wheat. Aust J Soil Res 48(7):546–554. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR10002
Zeng XY, Xiao ZH, Zhang GL, Wang AD, Li ZH, Liu YH, Wang H, Zeng QR, Liang YS, Zou DS (2018) Speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals in pyrolytic biochar of swine and goat manures. J Anal Appl Pyrol 132:82–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2018.03.012
Zhang ZY (2013) Study on the effect of biochar on the bioavailability of cadmium in paddy fields. Doctoral Dissertation
Zhang XH, Lin AJ, Zhang X, Guo LP (2012) The effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) on growth of upland rice in soil contaminated by Cu. Environ Eng 6(5):1677–1681 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Z, Solaiman ZM, Meney K, Murphy DV, Rengel Z (2013a) Biochars immobilize soil cadmium, but do not improve growth of emergent wetland species Juncus subsecundus, in cadmium-contaminated soil. J Soils Sediments 13(1):140–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-012-0571-4
Zhang ZS, Song XL, Lu XG, Xue ZS (2013b) Ecological stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in estuarine wetland soils: influences of vegetation coverage, plant communities, geomorphology, and seawalls, plant communities, geomorphology. J Soils Sediments 13:1043–1051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0693-3
Zhang H, Zhen H, Yue S, Zhang H, Qiao Y (2017) Bioavailability of Cd in contaminated soil after short-term application of rice straw biochar. Ecol Environ Sci 26:1068–1074. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2017.06.021 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng RL, Cai C, Liang JH, Huang Q, Chen Z, Huang YZ, Peter H, Sun GX (2012) The effects of biochars from rice residue on the formation of iron plaque and the accumulation of Cd, Zn, Pb, As in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Chemosphere 89:856–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.008
Zhong XL, Zhou SL, Huang ML (2009) Chemical form distribution characteristic of soil heavy metals and its influencing factors. Ecol Environ Sci 18(4):1266–1273. (In Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2009.04.023
Zhou RX, Hou M, Tang S, Wang YX, Jin HR (2014) Influence of AM fungi on the infection rate and nitrogen and phosphorus content of cotton under different nitrogen and phosphorus levels. Hunan Agri Sci (14):27–29. (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.16498/j.cnki.hnnykx.2014.14.016
Zhu QY (2011) Study on the restoration of Pb and Cd in contaminated soil by biochar. Master Dissertation. Master Thesis. University, pages
Funding
The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41977209 and No. 41471410).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Zhen, H., Huang, C. et al. The effects of biochar and AM fungi (Funneliformis mosseae) on bioavailability Cd in a highly contaminated acid soil with different soil phosphorus supplies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 44440–44451 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10363-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10363-5